ZHCSBT2G November 2012 – October 2017 66AK2H06 , 66AK2H12 , 66AK2H14
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 器件概述
- 2 修订历史记录
- 3 Device Comparison
- 4 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 C66x CorePac
- 7 ARM CorePac
-
8 Memory, Interrupts, and EDMA for 66AK2Hxx
- 8.1 Memory Map Summary for 66AK2Hxx
- 8.2 Memory Protection Unit (MPU) for 66AK2Hxx
- 8.3 Interrupts for 66AK2Hxx
- 8.4 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA3) Controller for 66AK2Hxx
- 9 System Interconnect
-
10Device Boot and Configuration
- 10.1
Device Boot
- 10.1.1 Boot Sequence
- 10.1.2
Boot Modes Supported
- 10.1.2.1 Boot Device Field
- 10.1.2.2 Device Configuration Field
- 10.1.2.3 Serial Rapid I/O Boot Device Configuration
- 10.1.2.4 Ethernet (SGMII) Boot Device Configuration
- 10.1.2.5
Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.1 EMIF16 Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.2 SRIO Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.3 Ethernet Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.4 PCIe Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.5 I2C Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.6 SPI Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.7 HyperLink Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.8 UART Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.9 NAND Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.10 DDR3 Configuration Table
- 10.1.2.6 Second-Level Bootloaders
- 10.1.3 SoC Security
- 10.1.4 System PLL Settings
- 10.2
Device Configuration
- 10.2.1 Device Configuration at Device Reset
- 10.2.2 Peripheral Selection After Device Reset
- 10.2.3
Device State Control Registers
- 10.2.3.1 Device Status (DEVSTAT) Register
- 10.2.3.2 Device Configuration Register
- 10.2.3.3 JTAG ID (JTAGID) Register Description
- 10.2.3.4 Kicker Mechanism (KICK0 and KICK1) Register
- 10.2.3.5 DSP Boot Address Register (DSP_BOOT_ADDRn)
- 10.2.3.6 LRESETNMI PIN Status (LRSTNMIPINSTAT) Register
- 10.2.3.7 LRESETNMI PIN Status Clear (LRSTNMIPINSTAT_CLR) Register
- 10.2.3.8 Reset Status (RESET_STAT) Register
- 10.2.3.9 Reset Status Clear (RESET_STAT_CLR) Register
- 10.2.3.10 Boot Complete (BOOTCOMPLETE) Register
- 10.2.3.11 Power State Control (PWRSTATECTL) Register
- 10.2.3.12 NMI Event Generation to C66x CorePac (NMIGRx) Register
- 10.2.3.13 IPC Generation (IPCGRx) Registers
- 10.2.3.14 IPC Acknowledgment (IPCARx) Registers
- 10.2.3.15 IPC Generation Host (IPCGRH) Register
- 10.2.3.16 IPC Acknowledgment Host (IPCARH) Register
- 10.2.3.17 Timer Input Selection Register (TINPSEL)
- 10.2.3.18 Timer Output Selection Register (TOUTPSEL)
- 10.2.3.19 Reset Mux (RSTMUXx) Register
- 10.2.3.20 Device Speed (DEVSPEED) Register
- 10.2.3.21 ARM Endian Configuration Register 0 (ARMENDIAN_CFGr_0), r=0..7
- 10.2.3.22 ARM Endian Configuration Register 1 (ARMENDIAN_CFGr_1), r=0..7
- 10.2.3.23 ARM Endian Configuration Register 2 (ARMENDIAN_CFGr_2), r=0..7
- 10.2.3.24 Chip Miscellaneous Control (CHIP_MISC_CTL0) Register
- 10.2.3.25 Chip Miscellaneous Control (CHIP_MISC_CTL1) Register
- 10.2.3.26 System Endian Status Register (SYSENDSTAT)
- 10.2.3.27 SYNECLK_PINCTL Register
- 10.2.3.28
USB PHY Control (USB_PHY_CTLx) Registers
- Table 10-57 USB_PHY_CTL0 Register Field Descriptions
- Table 10-58 USB_PHY_CTL1 Register Field Descriptions
- Table 10-59 USB_PHY_CTL2 Register Field Descriptions
- Table 10-60 USB_PHY_CTL3 Register Field Descriptions
- Table 10-61 USB_PHY_CTL4 Register Field Descriptions
- Table 10-62 USB_PHY_CTL5 Register Field Descriptions
- 10.1
Device Boot
-
1166AK2Hxx Peripheral Information
- 11.1 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 11.2 Power Supplies
- 11.3 Power Sleep Controller (PSC)
- 11.4 Reset Controller
- 11.5
Main PLL, ARM PLL, DDR3A PLL, DDR3B PLL, PASS PLL and the PLL Controllers
- 11.5.1 Main PLL Controller Device-Specific Information
- 11.5.2
PLL Controller Memory Map
- 11.5.2.1 PLL Secondary Control Register (SECCTL)
- 11.5.2.2 PLL Controller Divider Register (PLLDIV3 and PLLDIV4)
- 11.5.2.3 PLL Controller Clock Align Control Register (ALNCTL)
- 11.5.2.4 PLLDIV Divider Ratio Change Status Register (DCHANGE)
- 11.5.2.5 SYSCLK Status Register (SYSTAT)
- 11.5.2.6 Reset Type Status Register (RSTYPE)
- 11.5.2.7 Reset Control Register (RSTCTRL)
- 11.5.2.8 Reset Configuration Register (RSTCFG)
- 11.5.2.9 Reset Isolation Register (RSISO)
- 11.5.3 Main PLL Control Registers
- 11.5.4 ARM PLL Control Registers
- 11.5.5 Main PLL Controller, ARM, SRIO, HyperLink, PCIe, USB Clock Input Electrical Data and Timing
- 11.6 DDR3A PLL and DDR3B PLL
- 11.7 PASS PLL
- 11.8 External Interrupts
- 11.9 DDR3A and DDR3B Memory Controllers
- 11.10 I2C Peripheral
- 11.11 SPI Peripheral
- 11.12 HyperLink Peripheral
- 11.13 UART Peripheral
- 11.14 PCIe Peripheral
- 11.15 Packet Accelerator
- 11.16 Security Accelerator
- 11.17 Network Coprocessor Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) Switch Subsystem
- 11.18 SGMII and XFI Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 11.19 Ten-Gigabit Ethernet (10GbE) Switch Subsystem
- 11.20 Timers
- 11.21 Serial RapidIO (SRIO) Port
- 11.22 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 11.23 Semaphore2
- 11.24 Universal Serial Bus 3.0 (USB 3.0)
- 11.25 EMIF16 Peripheral
- 11.26 Emulation Features and Capability
- 11.27 Debug Port (EMUx)
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11.5 Main PLL, ARM PLL, DDR3A PLL, DDR3B PLL, PASS PLL and the PLL Controllers
This section provides a description of the Main PLL, ARM PLL, DDR3A PLL, DDR3B PLL, PASS PLL, and the PLL Controller. For details on the operation of the PLL Controller module, see the KeyStone Architecture Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Controller User's Guide.
The Main PLL is controlled by the standard PLL Controller. The PLL Controller manages the clock ratios, alignment, and gating for the system clocks to the device. By default, the device powers up with the main PLL bypassed. Figure 11-7 shows a block diagram of the Main PLL and the PLL Controller.
The ARM PLL, DDR3A PLL, DDR3B PLL, and PASS PLL are used to provide dedicated clock to the ARM CorePac, DDR3A, DDR3B, and PASS respectively. These chip level PLLs support a wide range of multiplier and divider values, which can be programmed through the chip level registers in the Device Control register block. The Boot ROM will program the multiplier values for main PLL, ARM PLL and PASS PLL based on boot mode. (See Section 10 for more details.)
The DDR3A PLL and DDR3B PLL are used to supply clocks to DDR3A and DDR3B EMIF logic. These PLLs can also be used without programming the PLL Controller. Instead, they can be controlled using the chip-level registers (DDR3APLLCTL0, DDR3APLLCTL1, DDR3BPLLCTL0, DDR3BPLLCTL1) in the Device Control register block. To write to these registers, software must go through an unlocking sequence using the KICK0/KICK1 registers.
The multiplier values for all chip-level PLLs can be reprogrammed later based on the input parameter table. This feature provides flexibility in that these PLLs may be able to reuse other clock sources instead of having its own clock source.
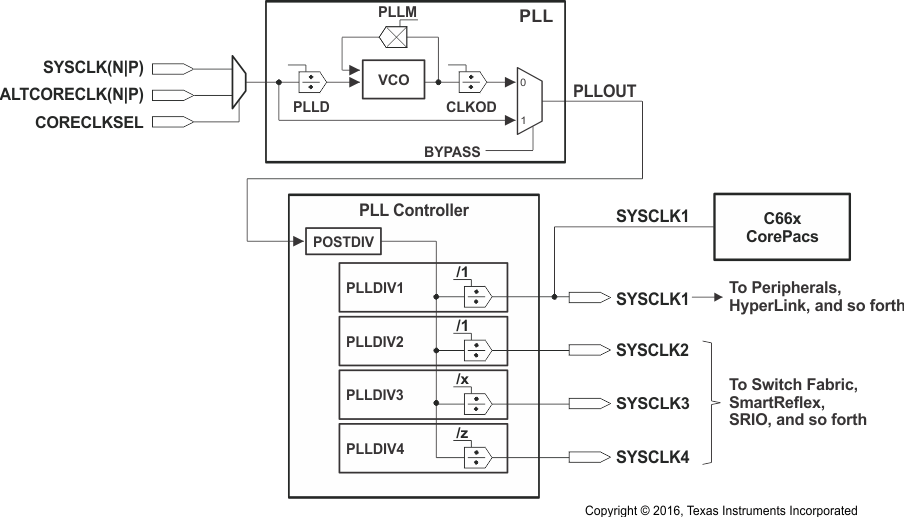 Figure 11-7 Main PLL and PLL Controller
Figure 11-7 Main PLL and PLL Controller
The Main PLL Controller registers can be accessed by any master in the device. The PLLM[5:0] bits of the multiplier are controlled by the PLLM Register inside the PLL Controller and the PLLM[12:6] bits are controlled by the chip-level MAINPLLCTL0 Register. The output divide and bypass logic of the PLL are controlled by fields in the SECCTL Register in the PLL Controller. Only PLLDIV3, and PLLDIV4 are programmable on the device. See the KeyStone Architecture Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Controller User's Guide for more details on how to program the PLL controller.
The multiplication and division ratios within the PLL and the post-division for each of the chip-level clocks are determined by a combination of this PLL and the Main PLL Controller. The Main PLL Controller also controls reset propagation through the chip, clock alignment, and test points. The Main PLL Controller monitors the PLL status and provides an output signal indicating when the PLL is locked.
Main PLL power is supplied externally via the Main PLL power-supply pin (AVDDA1). An external EMI filter circuit must be added to all PLL supplies. See Hardware Design Guide for KeyStone II Devices for detailed recommendations. For the best performance, TI recommends that all the PLL external components be on a single side of the board without jumpers, switches, or components other than those shown. For reduced PLL jitter, maximize the spacing between switching signal traces and the PLL external components (C1, C2, and the EMI Filter).
The minimum SYSCLK rise and fall times should also be observed. For the input clock timing requirements, see Section 11.5.5.
It should be assumed that any registers not included in these sections are not supported by the device. Furthermore, only the bits within the registers described here are supported. Avoid writing to any reserved memory location or changing the value of reserved bits.
The PLL Controller module as described in the KeyStone Architecture Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Controller User's Guide includes a superset of features, some of which are not supported on the 66AK2Hxx device. The following sections describe the registers that are supported.