SNAS519H July 2011 – August 2015 ADC12D1000RF , ADC12D1600RF
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Device Overview
- 2 Revision History
- 3 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
4 Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Thermal Information
- 4.5 Electrical Characteristics: Static Converter
- 4.6 Electrical Characteristics: Dynamic Converter
- 4.7 Electrical Characteristics: Analog Input/Output and Reference
- 4.8 Electrical Characteristics: I-Channel to Q-Channel
- 4.9 Electrical Characteristics: Sampling Clock
- 4.10 Electrical Characteristics: AutoSync Feature
- 4.11 Electrical Characteristics: Digital Control and Output Pin
- 4.12 Electrical Characteristics: Power Supply
- 4.13 Electrical Characteristics: AC
- 4.14 Timing Requirements: Serial Port Interface
- 4.15 Timing Requirements: Calibration
- 4.16 Typical Characteristics
-
5 Detailed Description
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 5.3 Feature Description
- 5.4 Device Functional Modes
- 5.5
Programming
- 5.5.1
Control Modes
- 5.5.1.1
Non-Extended Control Mode
- 5.5.1.1.1 Dual Edge Sampling Pin (DES)
- 5.5.1.1.2 Non-Demultiplexed Mode Pin (NDM)
- 5.5.1.1.3 Dual Data Rate Phase Pin (DDRPh)
- 5.5.1.1.4 Calibration Pin (CAL)
- 5.5.1.1.5 Calibration Delay Pin (CalDly)
- 5.5.1.1.6 Power-Down I-channel Pin (PDI)
- 5.5.1.1.7 Power-Down Q-channel Pin (PDQ)
- 5.5.1.1.8 Test Pattern Mode Pin (TPM)
- 5.5.1.1.9 Full-Scale Input Range Pin (FSR)
- 5.5.1.1.10 AC- and DC-Coupled Mode Pin (VCMO)
- 5.5.1.1.11 LVDS Output Common-mode Pin (VBG)
- 5.5.1.2 Extended Control Mode
- 5.5.1.1
Non-Extended Control Mode
- 5.5.1
Control Modes
- 5.6 Register Maps
- 6 Application and Implementation
- 7 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
4 Specifications
4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)(2)
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (VA, VTC, VDR, VE) | 2.2 | V | ||
| Supply Difference - max(VA/TC/DR/E) - min(VA/TC/DR/E) | 0 | 100 | mV | |
| Voltage on Any Input Pin (except VIN±) | –0.15 | (VA + 0.15) | V | |
| VIN± Voltage | –0.5 | 2.5 | V | |
| Ground Difference - max(GNDTC/DR/E) – min(GNDTC/DR/E) | 0 | 100 | mV | |
| Input Current at Any Pin(3) | ±50 | mA | ||
| ADC12D1x00RF Package Power Dissipation at TA ≤ 85°C(3) | 3.45 | W | ||
| Storage Temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages are measured with respect to GND = GNDTC = GNDDR = GNDE = 0 V, unless otherwise specified.
(3) When the input voltage at any pin exceeds the power supply limits, that is, less than GND or greater than VA, the current at that pin should be limited to 50 mA. In addition, overvoltage at a pin must adhere to the maximum voltage limits. Simultaneous overvoltage at multiple pins requires adherence to the maximum package power dissipation limits. These dissipation limits are calculated using JEDEC JESD51-7 thermal model. Higher dissipation may be possible based on specific customer thermal situation and specified package thermal resistances from junction to case.
4.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge(1) | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(2) | ±2500 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(3) | ±1000 | |||
| Machine model (MM) | ±250 | |||
(1) Human body model is 100-pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5-kΩ resistor. Machine model is 220 pF discharged through 0 Ω. Charged device model simulates a pin slowly acquiring charge (such as from a device sliding down the feeder in an automated assembler) then rapidly being discharged.
(2) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(3) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions(1)(2)
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ambient Temperature, TA | ADC12D1x00RF (Standard JEDEC thermal model) | –40 | 85 | °C | ||
| Junction Temperature, TJ | 140 | °C | ||||
| Supply Voltage (VA, VTC, VE) | 1.8 | 2 | V | |||
| Driver Supply Voltage (VDR) | 1.8 | VA | V | |||
| VIN± Voltage(3) | DC-coupled | –0.4 | 2.4 | V | ||
| VIN± Differential Voltage(4) | DC-coupled at 100% duty cycle | 1 | V | |||
| DC-coupled at 20% duty cycle | 2 | |||||
| DC-coupled at 10% duty cycle | 2.8 | |||||
| VIN± Current(3) | AC-coupled | –50 | 50 | mA | ||
| VIN± Power | Maintaining common-mode voltage, AC-coupled | 15.3 | dBm | |||
| Not maintaining common-mode voltage, AC-coupled | 17.1 | |||||
| Ground Difference – max(GNDTC/DR/E) -min(GNDTC/DR/E) | 0 | V | ||||
| CLK± Voltage | 0 | VA | V | |||
| Differential CLK Amplitude | 0.4 | 2 | VP-P | |||
| VCMI Common-Mode Input Voltage | VCMO – 150 | VCMO +150 | mV | |||
(1) Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. There is no specification of operation at the Absolute Maximum Ratings. Recommended Operating Conditions indicate conditions for which the device is functional, but do not ensure specific performance limits. For ensured specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The ensured specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics may degrade when the device is not operated under the listed test conditions.
(2) All voltages are measured with respect to GND = GNDTC = GNDDR = GNDE = 0 V, unless otherwise specified.
(3) Proper common-mode voltage must be maintained to ensure proper output codes, especially during input overdrive.
(4) This rating is intended for DC-coupled applications; the voltages and duty cycles listed may be safely applied to VIN+/- for the lifetime of the part.
4.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | ADC12D1x00RF | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NXA [BGA] | |||
| 40 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 16 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 2.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 2.5 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
4.5 Electrical Characteristics: Static Converter
Unless otherwise specified, the following apply after calibration for VA = VDR = VTC = VE = 1.9 V; I- and Q-channels, AC-coupled, unused channel terminated to AC ground, FSR Pin = High; CL = 10 pF; Differential, AC-coupled Sine Wave Sampling Clock, fCLK = 1600/1000 MHz at 0.5 VP-P with 50% duty cycle (as specified); VBG = Floating; Non-Extended Control Mode; Rext = Rtrim = 3300 Ω ± 0.1%; Analog Signal Source Impedance = 100-Ω Differential; Non-Demux Non-DES Mode; Duty Cycle Stabilizer on. All other limits TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution with No Missing Codes | TA = TMIN to TMAX | 12 | bits | |||
| INL | Integral Non-Linearity (Best fit) | 1 MHz DC-coupled over-ranged sine wave, TA = 25°C |
±2.5 | ±7.25 | LSB | |
| DNL | Differential Non-Linearity | 1 MHz DC-coupled over-ranged sine wave, TA = TMIN to TMAX |
±0.4 | ±0.96 | LSB | |
| VOFF | Offset Error | 5 | LSB | |||
| VOFF_ADJ | Input Offset Adjustment Range | Extended Control Mode | ±45 | mV | ||
| PFSE | Positive Full-Scale Error | See (4) | ±25 | mV | ||
| NFSE | Negative Full-Scale Error | See (4) | ±25 | mV | ||
| Out-of-Range Output Code(5) | (VIN+) − (VIN−) > + Full Scale, TA = TMIN to TMAX |
4095 | ||||
| (VIN+) − (VIN−) < − Full Scale, TA = TMIN to TMAX |
0 | |||||
(1) The analog inputs, labeled "I/O", are protected as shown below. Input voltage magnitudes beyond the Absolute Maximum Ratings may damage this device.
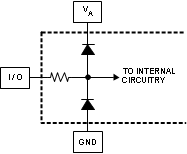

(2) To ensure accuracy, it is required that VA, VTC, VE and VDR be well-bypassed. Each supply pin must be decoupled with separate bypass capacitors.
(3) Typical figures are at TA = 25°C, and represent most likely parametric norms. Test limits are specified to TI's AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
(4) Calculation of Full-Scale Error for this device assumes that the actual reference voltage is exactly its nominal value. Full-Scale Error for this device, therefore, is a combination of Full-Scale Error and Reference Voltage Error. See Figure 4-8. For relationship between Gain Error and Full-Scale Error, see Specification Definitions for Gain Error.
(5) This parameter is specified by design and is not tested in production.
4.6 Electrical Characteristics: Dynamic Converter(2)
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | DESIQ MODE | ||||||
| –3 dB(6) | 1.75 | GHz | |||||
| –6 dB | 2.7 | GHz | |||||
| DESI, DESQ MODE | |||||||
| –3 dB(6) | 1.2 | GHz | |||||
| –6 dB | 2.3 | GHz | |||||
| –9 dB | 2.7 | GHz | |||||
| –12 dB | 3 | GHz | |||||
| NON-DES MODE, DESCLKIQ MODE | |||||||
| –3 dB(6) | 2.7 | GHz | |||||
| –6 dB | 3.1 | GHz | |||||
| –9 dB | 3.5 | GHz | |||||
| –12 dB | 4 | GHz | |||||
| Gain Flatness | NON-DES MODE | ||||||
| D.C. to Fs/2 | ±0.3 | dB | |||||
| D.C. to Fs | ADC12D1600RF | ±0.8 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | ±0.4 | ||||||
| D.C. to 3Fs/2 | ADC12D1600RF | ±1 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | ±0.8 | ||||||
| D.C. to 2Fs | ADC12D1600RF | ±3.6 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | ±0.9 | ||||||
| DESI, DESQ MODE | |||||||
| D.C. to Fs/2 | ADC12D1600RF | ±2.2 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | ±1 | ||||||
| D.C. to Fs | ADC12D1600RF | ±7.4 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | ±2.7 | ||||||
| DESIQ MODE | |||||||
| D.C. to Fs/2 | ADC12D1600RF | ±0.9 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | ±0.7 | ||||||
| D.C. to Fs | ADC12D1600RF | ±5.4 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | ±1.3 | ||||||
| DESCLKIQ MODE | |||||||
| D.C. to Fs/2 | ADC12D1600RF | ±0.7 | |||||
| ADC12D1000RF | ±0.6 | ||||||
| D.C. to Fs | ADC12D1600RF | ±4.2 | |||||
| ADC12D1000RF | ±0.9 | ||||||
| CER | Code Error Rate | 10–18 | Error/ Sample |
||||
| IMD3 | 3rd order Intermodulation Distortion | DES MODE | |||||
| FIN = 2670 MHz ± 2.5 MHz at –13 dBFS |
ADC12D1600RF | –76.7 | dBFS | ||||
| –63.7 | dBc | ||||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –73 | dBFS | |||||
| –60 | dBc | ||||||
| FIN = 2070 MHz ± 2.5 MHz at –13 dBFS |
ADC12D1600RF | –78.6 | dBFS | ||||
| –65.6 | dBc | ||||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –77 | dBFS | |||||
| –64 | dBc | ||||||
| FIN = 2670 MHz ± 2.5 MHz at –16 dBFS |
ADC12D1600RF | –82.7 | dBFS | ||||
| –66.7 | dBc | ||||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –85 | dBFS | |||||
| –69 | dBc | ||||||
| FIN = 2070 MHz ± 2.5 MHz at –16 dBFS |
ADC12D1600RF | –80.1 | dBFS | ||||
| –64.1 | dBc | ||||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –83 | dBFS | |||||
| –67 | dBc | ||||||
| Noise Floor Density | 50-Ω single-ended termination, DES Mode |
ADC12D1600RF | –154.6 | dBm/Hz | |||
| –153.6 | dBFS/Hz | ||||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –154 | dBm/Hz | |||||
| –153 | dBFS/Hz | ||||||
| NON-DES MODE(3)(5)(7) | |||||||
| ENOB | Effective Number of Bits | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 9.4 | bits | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 9.6 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 9.3 | bits | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 9.6 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 8.6(1) | 9.2 | bits | |||
| ADC12D1000RF | 8.7(1) | 9.4 | |||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 9 | bits | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 9.3 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 8.8 | bits | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 9 | ||||||
| SINAD | Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion Ratio | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 58 | dB | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 59.7 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 57.5 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 59.7 | dB | |||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 53.5(1) | 57.4 | dB | |||
| ADC12D1000RF | 54.1(1) | 58.6 | |||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 55.9 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 57.6 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 54.9 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 55.9 | ||||||
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 59 | dB | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 60.1 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 58.6 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 60 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 54.6(1) | 58.2 | dB | |||
| ADC12D1000RF | 55.1(1) | 58.8 | |||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 57 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 58.2 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 55.4 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 56.1 | ||||||
| THD | Total Harmonic Distortion | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –65 | dB | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | –69.7 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –64 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –71.9 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –64.9 | –60(1) | dB | |||
| ADC12D1000RF | –72 | –61(1) | |||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –62.4 | 8 | dB | |||
| ADC12D1000RF | –66. | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –64.1 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –69 | ||||||
| 2nd Harm | Second Harmonic Distortion | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –78.6 | dBc | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | –79.3 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –83 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –91.6 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –74 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –86.3 | ||||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –70.6 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –73 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –71 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –73.7 | ||||||
| 3rd Harm | Third Harmonic Distortion | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –67.5 | dBc | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | –71.9 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –64.4 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –75.4 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –71 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –74.8 | ||||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –63.2 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –68.9 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –75.7 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –73.5 | ||||||
| SFDR | Spurious-Free Dynamic Range | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 67.9 | dBc | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 71.4 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 64.5 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 75 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 58(1) | 66.7 | dBc | |||
| ADC12D1000RF | 61(1) | 71.9 | |||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 63.8 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 68.4 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 67.3 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 66.5 | ||||||
| DES MODE(3)(4)(7) | |||||||
| ENOB | Effective Number of Bits | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 9.3 | bits | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 9.5 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 9.3 | bits | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 9.4 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | 9.3 | bits | |||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 8.9 | bits | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 8.8 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | 8.7 | bits | |||||
| SINAD | Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion Ratio | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 57.9 | dB | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 58.7 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 57.5 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 58.2 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 57.5 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 57.7 | ||||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 55.1 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 54.8 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | 54.1 | dB | |||||
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 58.8 | dB | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 59.2 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | 58.5 | dB | |||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 58.1 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 58 | ||||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 55.9 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 55 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | 54.3 | dB | |||||
| THD | Total Harmonic Distortion | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –65.2 | dB | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | –68.1 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –64.2 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –68.4 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –66.2 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –68.3 | ||||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –62.9 | dB | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –66.4 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | –67 | dB | |||||
| 2nd Harm | Second Harmonic Distortion | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –81.5 | dBc | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | –87.4 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –84.2 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –77.1 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –69.7 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –73.4 | ||||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –70.5 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –76.4 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | –73.6 | dBc | |||||
| 3rd Harm | Third Harmonic Distortion | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –66 | dBc | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | –69.3 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –63.8 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –73.3 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –69.7 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –72.6 | ||||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | –63.5 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | –69.9 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | –67.1 | dBc | |||||
| SFDR | Spurious-Free Dynamic Range | AIN = 125 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 66.9 | dBc | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 69 | ||||||
| AIN = 248 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 65 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 67.1 | ||||||
| AIN = 498 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 70.4 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 65 | ||||||
| AIN = 998 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | ADC12D1600RF | 64.1 | dBc | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 61.7 | ||||||
| AIN = 1448 MHz at –0.5 dBFS | 61.3 | dBc | |||||
(1) TA = TMIN to TMAX
(2) This parameter is specified by design and/or characterization and is not tested in production.
(3) The Dynamic Specifications are ensured for room to hot ambient temperature only (25°C to 85°C). Refer to the plots of the dynamic performance vs. temperature in Typical Characteristics to see typical performance from cold to room temperature (–40°C to 25°C).
(4) These measurements were taken in Extended Control Mode (ECM) with the DES Timing Adjust feature enabled (Addr: 7h). This feature is used to reduce the interleaving timing spur amplitude, which occurs at fs/2-fin, and thereby increase the SFDR, SINAD and ENOB.
(5) The Fs/2 spur was removed from all the dynamic performance specifications.
(6) The –3 dB point is the traditional Full-Power Bandwidth (FPBW) specification. Although the insertion loss is approximately half at this frequency, the dynamic performance of the ADC does not necessarily begin to degrade to a level below which it may be effectively used in an application. The ADC may be used at input frequencies above the –3 dB FPBW point, for example for the ADC12D1000RF, into the 5th Nyquist zone. Depending on system requirements, it is only necessary to compensate for the insertion loss.
(7) Typical dynamic performance is only tested at Fin = 498 MHz; other input frequencies are specified by design and / or characterization and are not tested in production.
4.7 Electrical Characteristics: Analog Input/Output and Reference
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG INPUTS | ||||||
| VIN_FSR | Analog Differential Input Full Scale Range | NON-EXTENDED CONTROL MODE | ||||
| FSR Pin Low | 540(1) | 600 | 660(1) | mVP-P | ||
| FSR Pin High | 740(1) | 800 | 860(1) | mVP-P | ||
| EXTENDED CONTROL MODE | ||||||
| FM(14:0) = 0000h | 600 | mVP-P | ||||
| FM(14:0) = 4000h (default) | 800 | mVP-P | ||||
| FM(14:0) = 7FFFh | 1000 | mVP-P | ||||
| CIN | Analog Input Capacitance, Non-DES Mode(3)(4) | Differential | 0.02 | pF | ||
| Each input pin to ground | 1.6 | pF | ||||
| Analog Input Capacitance, DES Mode(3)(4) | Differential | 0.08 | pF | |||
| Each input pin to ground | 2.2 | pF | ||||
| RIN | Differential Input Resistance | 91(1) | 100 | 109(1) | Ω | |
| COMMON-MODE OUTPUT | ||||||
| VCMO | Common-Mode Output Voltage | ICMO = ±100 µA | 1.15(1) | 1.25 | 1.35(1) | V |
| TC_VCMO | Common-Mode Output Voltage Temperature Coefficient | ICMO = ±100 µA(2) | 38 | ppm/°C | ||
| VCMO_LVL | VCMO input threshold to set DC-coupling Mode | See (2) | 0.63 | V | ||
| CL_VCMO | Maximum VCMO Load Capacitance | See (3) | 80(1) | pF | ||
| BANDGAP REFERENCE | ||||||
| VBG | Bandgap Reference Output Voltage | IBG = ±100 µA | 1.15(1) | 1.25 | 1.35(1) | V |
| TC_VBG | Bandgap Reference Voltage Temperature Coefficient | IBG = ±100 µA(2) | 32 | ppm/°C | ||
| CL_VBG | Maximum Bandgap Reference load Capacitance | See (3) | 80(1) | pF | ||
(1) TA = TMIN to TMAX
(2) This parameter is specified by design and/or characterization and is not tested in production.
(3) This parameter is specified by design and is not tested in production.
(4) The differential and pin-to-ground input capacitances are lumped capacitance values from design.
4.8 Electrical Characteristics: I-Channel to Q-Channel
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Offset Match | See (1) | 2 | LSB | |||
| Positive Full-Scale Match | Zero offset selected in Control Register | 2 | LSB | |||
| Negative Full-Scale Match | Zero offset selected in Control Register | 2 | LSB | |||
| Phase Matching (I, Q) | fIN = 1.0 GHz(1) | < 1 | Degree | |||
| X-TALK | Crosstalk from I-channel (Aggressor) to Q-channel (Victim) |
Aggressor = 867 MHz F.S., Victim = 100 MHz F.S. |
–70 | dB | ||
| Crosstalk from Q-channel (Aggressor) to I-channel (Victim) |
Aggressor = 867 MHz F.S., Victim = 100 MHz F.S. |
–70 | dB | |||
(1) This parameter is specified by design and/or characterization and is not tested in production.
4.9 Electrical Characteristics: Sampling Clock
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN_CLK | Differential Sampling Clock Input Level(2) | Sine Wave Clock Differential Peak-to-Peak | 0.4(1) | 0.6 | 2(1) | VP-P |
| Square Wave Clock Differential Peak-to-Peak | 0.4(1) | 0.6 | 2(1) | |||
| CIN_CLK | Sampling Clock Input Capacitance(3) | Differential | 0.1 | pF | ||
| Each input to ground | 1 | pF | ||||
| RIN_CLK | Sampling Clock Differential Input Resistance | See (2) | 100 | Ω | ||
(1) TA = TMIN to TMAX
(2) This parameter is specified by design and/or characterization and is not tested in production.
(3) This parameter is specified by design and is not tested in production.
4.10 Electrical Characteristics: AutoSync Feature
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN_RCLK | Differential RCLK Input Level(1) | Differential Peak-to-Peak | 360 | mVP-P | ||
| CIN_RCLK | RCLK Input Capacitance(1) | Differential | 0.12 | pF | ||
| Each input to ground | 1 | pF | ||||
| RIN_RCLK | RCLK Differential Input Resistance | See (1) | 100 | Ω | ||
| IIH_RCLK | Input Leakage Current; VIN = VA | 22 | µA | |||
| IIL_RCLK | Input Leakage Current; VIN = GND | 33 | µA | |||
| VO_RCOUT | Differential RCOut Output Voltage | –360 | mVP-P | |||
(1) This parameter is specified by design and/or characterization and is not tested in production.
4.11 Electrical Characteristics: Digital Control and Output Pin
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIGITAL CONTROL PINS (DES, CalDly, CAL, PDI, PDQ, TPM, NDM, FSR, DDRPh, ECE, SCLK, SDI, SCS) | ||||||
| VIH | Logic High Input Voltage | 0.7×VA(1) | V | |||
| VIL | Logic Low Input Voltage | 0.3×VA(1) | V | |||
| IIH | Input Leakage Current; VIN = VA | 0.02 | μA | |||
| IIL | Input Leakage Current; VIN = GND | FSR, CalDly, CAL, NDM, TPM, DDRPh, DES | –0.02 | μA | ||
| SCS, SCLK, SDI | –17 | μA | ||||
| PDI, PDQ, ECE | –38 | μA | ||||
| CIN_DIG | Digital Control Pin Input Capacitance(3) | Measured from each control pin to GND | 1.5 | pF | ||
| DIGITAL OUTPUT PINS (Data, DCLKI, DCLKQ, ORI, ORQ) | ||||||
| VOD | LVDS Differential Output Voltage | VBG = Floating, OVS = High | 400(1) | 630 | 800(1) | mVP-P |
| VBG = Floating, OVS = Low | 230(1) | 460 | 630(1) | mVP-P | ||
| VBG = VA, OVS = High | 670 | mVP-P | ||||
| VBG = VA, OVS = Low | 500 | mVP-P | ||||
| ΔVO DIFF | Change in LVDS Output Swing Between Logic Levels | ±1 | mV | |||
| VOS | Output Offset Voltage(2) | VBG = Floating | 0.8 | V | ||
| VBG = VA | 1.2 | V | ||||
| ΔVOS | Output Offset Voltage Change Between Logic Levels | See (2) | ±1 | mV | ||
| IOS | Output Short-Circuit Current(2) | VBG = Floating; D+ and D− connected to 0.8 V |
±4 | mA | ||
| ZO | Differential Output Impedance | See (2) | 100 | Ω | ||
| VOH | Logic High-Output Level | CalRun, IOH = −100 µA,(2)
SDO, IOH = −400 µA(2) |
1.65 | V | ||
| VOL | Logic Low-Output Level | CalRun, IOL = 100 µA,(2)
SDO, IOL = 400 µA(2) |
0.15 | V | ||
| VCMI_DRST | DCLK_RST Common-Mode Input Voltage | See (2) | 1.25 | V | ||
| VID_DRST | Differential DCLK_RST Input Voltage | See (2) | VIN_CLK | VP-P | ||
| RIN_DRST | Differential DCLK_RST Input Resistance | See (2) | 100 | Ω | ||
(1) TA = TMIN to TMAX
(2) This parameter is specified by design and/or characterization and is not tested in production.
(3) This parameter is specified by design and is not tested in production.
4.12 Electrical Characteristics: Power Supply
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IA | Analog Supply Current | PDI = PDQ = Low | ADC12D1600RF | 1225 | mA | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 1140 | ||||||
| PDI = Low; PDQ = High | ADC12D1600RF | 670 | mA | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 625 | ||||||
| PDI = High; PDQ = Low | ADC12D1600RF | 670 | mA | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 625 | ||||||
| PDI = PDQ = High | 2.7 | mA | |||||
| ITC | Track-and-Hold and Clock Supply Current | PDI = PDQ = Low | ADC12D1600RF | 490 | mA | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 410 | ||||||
| PDI = Low; PDQ = High | ADC12D1600RF | 290 | mA | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 250 | ||||||
| PDI = High; PDQ = Low | ADC12D1600RF | 290 | mA | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 250 | ||||||
| PDI = PDQ = High | 0.65 | µA | |||||
| IDR | Output Driver Supply Current | PDI = PDQ = Low | 270 | mA | |||
| PDI = Low; PDQ = High | 140 | mA | |||||
| PDI = High; PDQ = Low | 140 | mA | |||||
| PDI = PDQ = High | 6 | µA | |||||
| IE | Digital Encoder Supply Current | PDI = PDQ = Low | ADC12D1600RF | 105 | mA | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 55 | ||||||
| PDI = Low; PDQ = High | ADC12D1600RF | 50 | mA | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 30 | ||||||
| PDI = High; PDQ = Low | ADC12D1600RF | 50 | mA | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 30 | ||||||
| PDI = PDQ = High | 34 | µA | |||||
| ITOTAL | Total Supply Current | 1:2 DEMUX MODE
PDI = PDQ = Low |
ADC12D1600RF | 2090 | 2310(1) | mA | |
| ADC12D1000RF | 1875 | 2105(1) | |||||
| NON-DEMUX MODE
PDI = PDQ = Low |
ADC12D1600RF | 2075 | mA | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 1800 | ||||||
| PC | Power Consumption | 1:2 DEMUX MODE | |||||
| PDI = PDQ = Low | ADC12D1600RF | 4 | 4.4(1) | W | |||
| ADC12D1000RF | 3.6 | 4(1) | |||||
| PDI = Low; PDQ = High | ADC12D1600RF | 2.2 | W | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 2 | ||||||
| PDI = High; PDQ = Low | ADC12D1600RF | 2.2 | W | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 2 | ||||||
| PDI = PDQ = High | 6.4 | mW | |||||
| NON-DEMUX MODE | |||||||
| PDI = PDQ = Low | ADC12D1600RF | 3.94 | W | ||||
| ADC12D1000RF | 3.42 | ||||||
(1) TA = TMIN to TMAX
4.13 Electrical Characteristics: AC
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAMPLING CLOCK (CLK) | |||||||
| fCLK (max) | Maximum Sampling Clock Frequency | ADC12D1600RF | 1.6(1) | GHz | |||
| ADC12D1000RF | 1(1) | ||||||
| fCLK (min) | Minimum Sampling Clock Frequency | Non-DES Mode; LFS = 0b | 300(1) | MHz | |||
| Non-DES Mode; LFS = 1b | 150(1) | MHz | |||||
| DES Mode | 500(1) | MHz | |||||
| Sampling Clock Duty Cycle | fCLK(min) ≤ fCLK ≤ fCLK(max)(3) | 20%(1) | 50% | 80%(1) | |||
| tCL | Sampling Clock Low Time | See (2) | ADC12D1600RF | 200(1) | 500 | ps | |
| ADC12D1000RF | 125(1) | 312.5 | |||||
| tCH | Sampling Clock High Time | See (2) | ADC12D1600RF | 200(1) | 500 | ps | |
| ADC12D1000RF | 125(1) | 312.5 | |||||
| DATA CLOCK (DCLKI, DCLKQ) | |||||||
| DCLK Duty Cycle | See (2) | 45%(1) | 50% | 55%(1) | |||
| tSR | Setup Time DCLK_RST± | See (3) | 45 | ps | |||
| tHR | Hold Time DCLK_RST± | See (3) | 45 | ps | |||
| tPWR | Pulse Width DCLK_RST± | See (2) | 5(1) | Sampling Clock Cycles | |||
| tSYNC_DLY | DCLK Synchronization Delay | 90° Mode(2) | 4(1) | Sampling Clock Cycles | |||
| 0° Mode(2) | 5(1) | ||||||
| tLHT | Differential Low-to-High Transition Time | 10%-to-90%, CL = 2.5 pF(3) | 200 | ps | |||
| tHLT | Differential High-to-Low Transition Time | 10%-to-90%, CL = 2.5 pF(3) | 200 | ps | |||
| tSU | Data-to-DCLK Setup Time | DDR 90° Mode(2) | ADC12D1600RF | 500 | ps | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 870 | ||||||
| tH | DCLK-to-Data Hold Time | DDR 90° Mode(2) | ADC12D1600RF | 500 | ps | ||
| ADC12D1000RF | 870 | ||||||
| tOSK | DCLK-to-Data Output Skew | 50% of DCLK transition to 50% of Data transition DDR 0° Mode, SDR Mode (2) |
±50 | ps | |||
| DATA INPUT-TO-OUTPUT | |||||||
| tAD | Aperture Delay(3) | Sampling CLK+ Rise to Acquisition of Data | 1.29 | ns | |||
| tAJ | Aperture Jitter | See (3) | 0.2 | ps (rms) | |||
| tOD | Sampling Clock-to Data Output Delay (in addition to Latency) | 50% of Sampling Clock transition to 50% of Data transition(3) | 3.2 | ns | |||
| tLAT | Latency in 1:2 Demux Non-DES Mode(2) | DI, DQ Outputs | 34(1) | Sampling Clock Cycles | |||
| DId, DQd Outputs | 35(1) | ||||||
| Latency in 1:4 Demux DES Mode(2) | DI Outputs | 34(1) | |||||
| DQ Outputs | 34.5(1) | ||||||
| DId Outputs | 35(1) | ||||||
| DQd Outputs | 35.5(1) | ||||||
| Latency in Non-Demux Non-DES Mode(2) | DI Outputs | 34(1) | |||||
| DQ Outputs | 34(1) | ||||||
| Latency in Non-Demux DES Mode(2) | DI Outputs | 34(1) | |||||
| DQ Outputs | 34.5(1) | ||||||
| tORR | Over Range Recovery Time (3) | Differential VIN step from ±1.2 V to 0 V to accurate conversion | 1 | Sampling Clock Cycles | |||
| tWU | Wake-Up Time (PDI/PDQ low to Rated Accuracy Conversion) | Non-DES Mode(2) | 500 | ns | |||
| DES Mode(2) | 1 | µs | |||||
(1) TA = TMIN to TMAX
(2) This parameter is specified by design and is not tested in production.
(3) This parameter is specified by design and/or characterization and is not tested in production.
4.14 Timing Requirements: Serial Port Interface
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fSCLK | Serial Clock Frequency | See (2) | 15 | MHz | ||
| Serial Clock Low Time | 30(1) | ns | ||||
| Serial Clock High Time | 30(1) | ns | ||||
| tSSU | Serial Data-to-Serial Clock Rising Setup Time | See (2) | 2.5 | ns | ||
| tSH | Serial Data-to-Serial Clock Rising Hold Time | See (2) | 1 | ns | ||
| tSCS | SCS-to-Serial Clock Rising Setup Time | See (3) | 2.5 | ns | ||
| tHCS | SCS-to-Serial Clock Falling Hold Time | See (3) | 1.5 | ns | ||
| tBSU | Bus turnaround time | See (3) | 10 | ns | ||
(1) TA = TMIN to TMAX
(2) This parameter is specified by design and is not tested in production.
(3) This parameter is specified by design and/or characterization and is not tested in production.
4.15 Timing Requirements: Calibration
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tCAL | Calibration Cycle Time | Non-ECM | 4.1×107 | Sampling Clock Cycles | ||
| ECM CSS = 0b | ||||||
| ECM CSS = 1b | ||||||
| tCAL_L | CAL Pin Low Time | See (2) | 1280(1) | Sampling Clock Cycles | ||
| tCAL_H | CAL Pin High Time | See (2) | 1280(1) | |||
| tCalDly | Calibration delay determined by CalDly Pin(2) | CalDly = Low | 224(1) | Sampling Clock Cycles | ||
| CalDly = High | 230(1) | |||||
(1) TA = TMIN to TMAX
(2) This parameter is specified by design and is not tested in production.
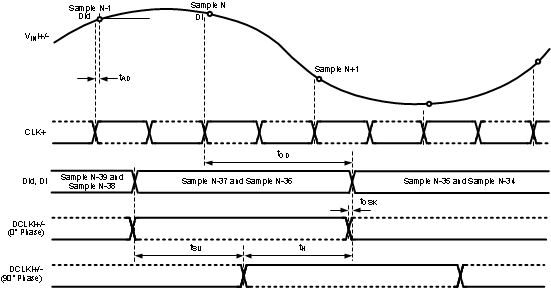
The timing for these figures is shown for the one input only (I or Q). However, both I- and Q-inputs may be used. For this case, the I-channel functions precisely the same as the Q-channel, with VinI, DCLKI, DId and DI instead of VinQ, DCLKQ, DQd and DQ. Both I- and Q-channel use the same CLK.
Figure 4-1 Clocking in 1:2 Demux Non-DES Mode
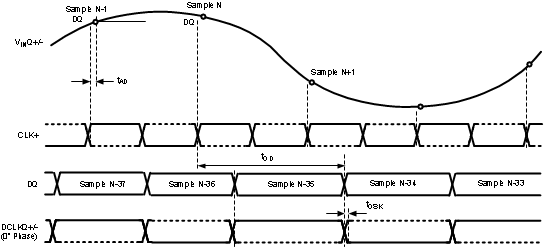
The timing for these figures is shown for the one input only (I or Q). However, both I- and Q-inputs may be used. For this case, the I-channel functions precisely the same as the Q-channel, with VinI, DCLKI, DId and DI instead of VinQ, DCLKQ, DQd and DQ. Both I- and Q-channel use the same CLK.
Figure 4-2 Clocking in Non-Demux Non-DES Mode
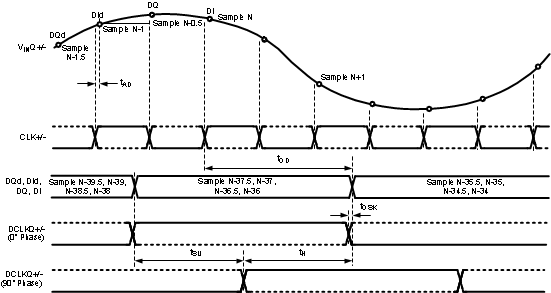
The timing for these figures is shown for the one input only (I or Q). However, both I- and Q-inputs may be used. For this case, the I-channel functions precisely the same as the Q-channel, with VinI, DCLKI, DId and DI instead of VinQ, DCLKQ, DQd and DQ. Both I- and Q-channel use the same CLK.
Figure 4-3 Clocking in 1:4 Demux DES Mode
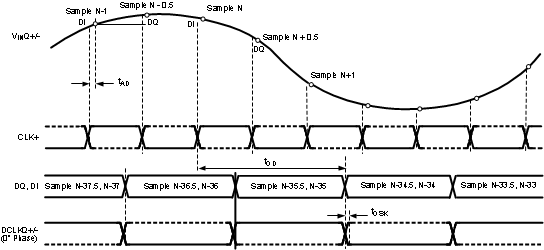
The timing for these figures is shown for the one input only (I or Q). However, both I- and Q-inputs may be used. For this case, the I-channel functions precisely the same as the Q-channel, with VinI, DCLKI, DId and DI instead of VinQ, DCLKQ, DQd and DQ. Both I- and Q-channel use the same CLK.
Figure 4-4 Clocking in Non-Demux Mode DES Mode
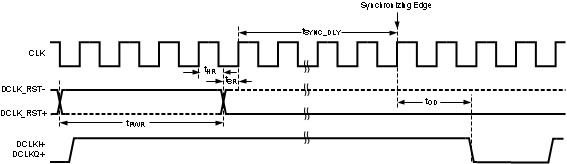 Figure 4-5 Data Clock Reset Timing (Demux Mode)
Figure 4-5 Data Clock Reset Timing (Demux Mode)
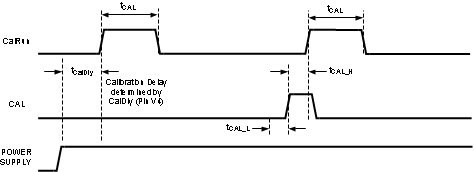 Figure 4-6 Power-on and On-Command Calibration Timing
Figure 4-6 Power-on and On-Command Calibration Timing
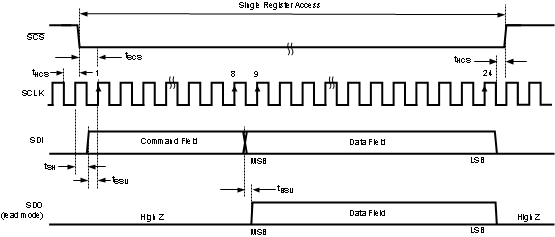 Figure 4-7 Serial Interface Timing
Figure 4-7 Serial Interface Timing
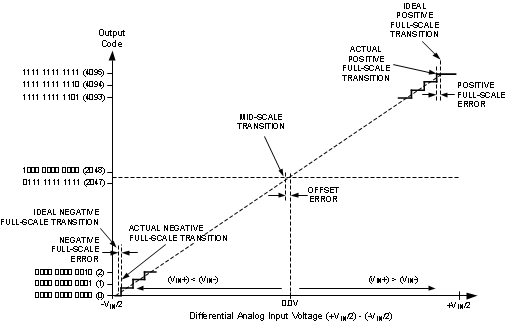 Figure 4-8 Input / Output Transfer Characteristic
Figure 4-8 Input / Output Transfer Characteristic
4.16 Typical Characteristics
VA = VDR = VTC = VE = 1.9 V, fCLK = 1600 MHz / 1000 MHz for the ADC12D1600RF / ADC12D1000RF, respectively, fIN = 498 MHz, TA= 25°C, I-channel, Demux Non-DES Mode, unless otherwise stated.
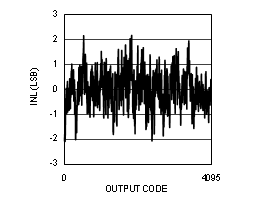 Figure 4-9 INL vs Code (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-9 INL vs Code (ADC12D1600RF)
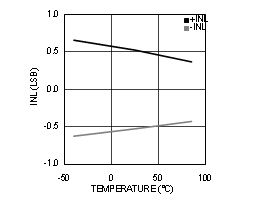 Figure 4-11 INL vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-11 INL vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
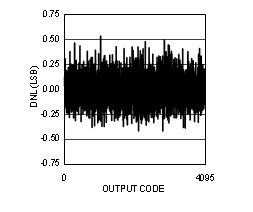 Figure 4-13 DNL vs Code (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-13 DNL vs Code (ADC12D1600RF)
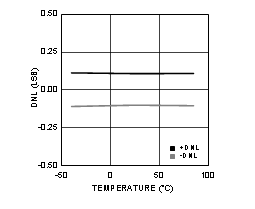 Figure 4-15 DNL vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-15 DNL vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
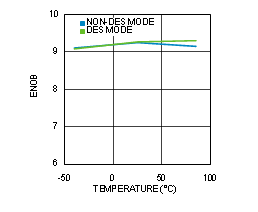 Figure 4-17 ENOB vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-17 ENOB vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
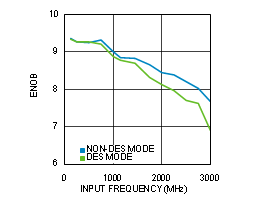 Figure 4-19 ENOB vs Input Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-19 ENOB vs Input Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
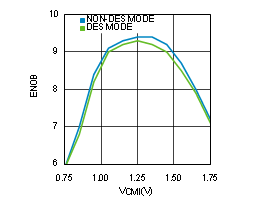 Figure 4-21 ENOB vs VCMI (ADC12D1000RF)
Figure 4-21 ENOB vs VCMI (ADC12D1000RF)
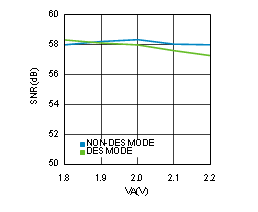 Figure 4-23 SNR vs Supply Voltage (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-23 SNR vs Supply Voltage (ADC12D1600RF)
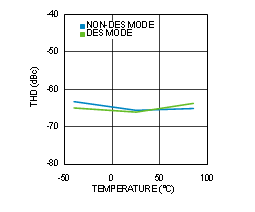 Figure 4-25 THD vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-25 THD vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
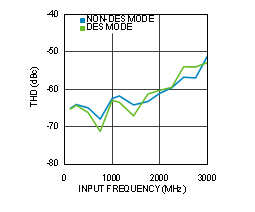 Figure 4-27 THD vs Input Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-27 THD vs Input Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
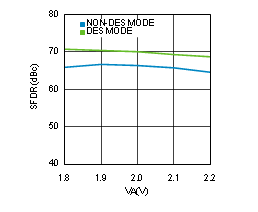 Figure 4-29 SFDR vs Supply Voltage (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-29 SFDR vs Supply Voltage (ADC12D1600RF)
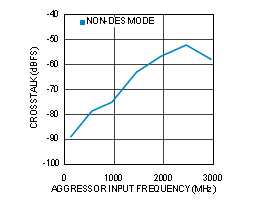 Figure 4-31 CROSSTALK vs Source Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-31 CROSSTALK vs Source Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
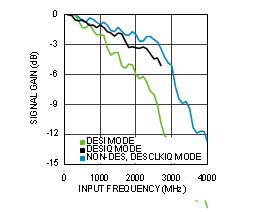 Figure 4-33 Insertion Loss (ADC12D1x00RF)
Figure 4-33 Insertion Loss (ADC12D1x00RF)
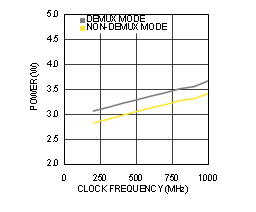 Figure 4-35 Power Consumption vs Clock Frequency (ADC12D1000RF)
Figure 4-35 Power Consumption vs Clock Frequency (ADC12D1000RF)
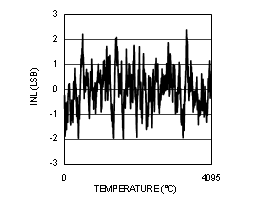 Figure 4-10 INL vs Code (ADC12D1000RF)
Figure 4-10 INL vs Code (ADC12D1000RF)
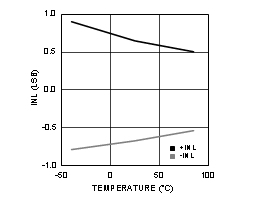 Figure 4-12 INL vs Temperature (ADC12D1000RF)
Figure 4-12 INL vs Temperature (ADC12D1000RF)
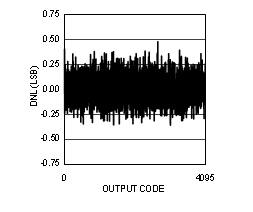 Figure 4-14 DNL vs Code (ADC12D1000RF)
Figure 4-14 DNL vs Code (ADC12D1000RF)
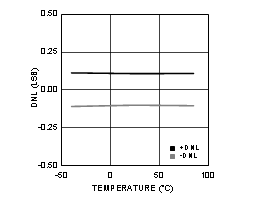 Figure 4-16 DNL vs Temperature (ADC12D1000RF)
Figure 4-16 DNL vs Temperature (ADC12D1000RF)
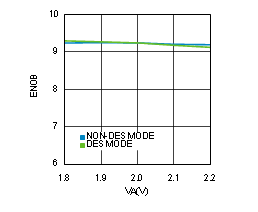 Figure 4-18 ENOB vs Supply Voltage (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-18 ENOB vs Supply Voltage (ADC12D1600RF)
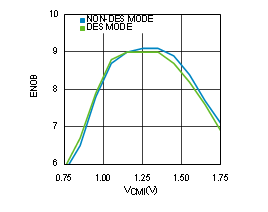 Figure 4-20 ENOB vs VCMI (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-20 ENOB vs VCMI (ADC12D1600RF)
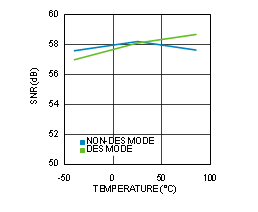 Figure 4-22 SNR vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-22 SNR vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
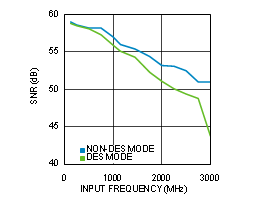 Figure 4-24 SNR vs Input Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-24 SNR vs Input Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
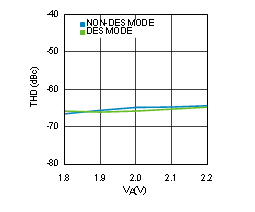 Figure 4-26 THD vs Supply Voltage (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-26 THD vs Supply Voltage (ADC12D1600RF)
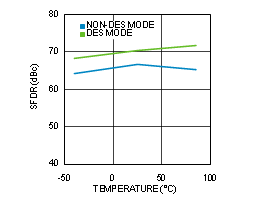 Figure 4-28 SFDR vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-28 SFDR vs Temperature (ADC12D1600RF)
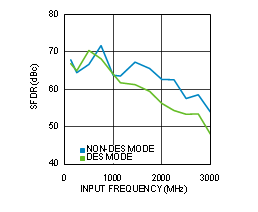 Figure 4-30 SFDR vs Input Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-30 SFDR vs Input Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
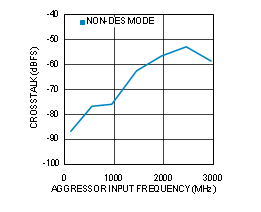 Figure 4-32 CROSSTALK vs Source Frequency (ADC12D1000RF)
Figure 4-32 CROSSTALK vs Source Frequency (ADC12D1000RF)
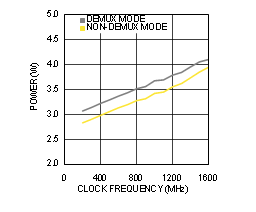 Figure 4-34 Power Consumption vs Clock Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)
Figure 4-34 Power Consumption vs Clock Frequency (ADC12D1600RF)