ZHCSE48B September 2015 – January 2019 ADC31JB68
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Analog Inputs and Input Buffer
- 8.3.2 Amplitude and Phase Imbalance Correction
- 8.3.3 Over-Range Detection
- 8.3.4 Input Clock Divider
- 8.3.5 SYSREF Detection Gate
- 8.3.6 Serial Differential Output Drivers
- 8.3.7 ADC Core Calibration
- 8.3.8 Data Format
- 8.3.9 JESD204B Supported Features
- 8.3.10 JESD204B Interface
- 8.3.11 Transport Layer Configuration
- 8.3.12 Test Pattern Sequences
- 8.3.13 JESD204B Link Initialization
- 8.3.14 SPI
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Register Map
- 8.5.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.5.1.1 CONFIG_A (address = 0x0000) [reset = 0x3C]
- 8.5.1.2 DEVICE CONFIG (address = 0x0002) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.1.3 CHIP_TYPE (address = 0x0003 ) [reset = 0x03]
- 8.5.1.4 CHIP_ID (address = 0x0005, 0x0004) [reset = 0x00, 0x1B]
- 8.5.1.5 CHIP_VERSION (address =0x0006) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.1.6 VENDOR_ID (address = 0x000D, 0x000C) [reset = 0x04, 0x51]
- 8.5.1.7 SPI_CFG (address = 0x0010 ) [reset = 0x01]
- 8.5.1.8 OM1 (Operational Mode 1) (address = 0x0012) [reset = 0xC1]
- 8.5.1.9 OM2 (Operational Mode 2) (address = 0x0013) [reset = 0x20]
- 8.5.1.10 IMB_ADJ (Imbalance Adjust) (address = 0x0014) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.1.11 OVR_EN (Over-Range Enable) (address = 0x003A) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.1.12 OVR_HOLD (Over-Range Hold) (address = 0x003B) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.1.13 OVR_TH (Over-Range Threshold) (address = 0x003C) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.1.14 DC_MODE (DC Offset Correction Mode) (address = 0x003D) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.1.15 SER_CFG (Serial Lane Transmitter Configuration) (address = 0x0047) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.1.16 JESD_CTRL1 (JESD Configuration Control 1) (address = 0x0060) [reset = 0x7F]
- 8.5.1.17 JESD_CTRL2 (JESD Configuration Control 2) (address = 0x0061) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.1.18 JESD_RSTEP (JESD Ramp Pattern Step) (address = 0x0063, 0x0062) [reset = 0x00, 0x01]
- 8.5.1.19 SER_INV (Serial Lane Inversion Control) (address = 0x0064) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.1.20 JESD_STATUS (JESD Link Status) (address = 0x006C) [reset = N/A]
- 8.5.1
Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
9.1.1.2 External Noise Sources
Noise sources external to the ADC device that impact the overall system performance through the ADC include: 1) Analog Input Signal Path noise, 2) Sampling Clock Signal Path Noise, 3) Supply Noise
Analog input signal path noise comes from devices in the signal path prior to the ADC and enters through the analog input (VIN+/-). An anti-aliasing filter must be included in front of the ADC to limit the noise bandwidth and prevent the aliasing of noise into any band of interest. Sampling clock signal path noise enters through the sampling clock input (CLKIN+/-) and adds noise similar to the Aperture Jitter. External clock jitter can be minimized by using high quality clock sources and jitter cleaners (PLLs) as well as bandpass filters at the clock input.
The total clock jitter (TJitter), including the aperture jitter of the ADC and external clock noise can be calculated with Equation 3 and applied to Equation 1 and Equation 2 to determine the system impact. Figure 59 shows the simulated impact on the SNR of the ADC31JB68 output spectrum for a given total jitter and input signal frequency.

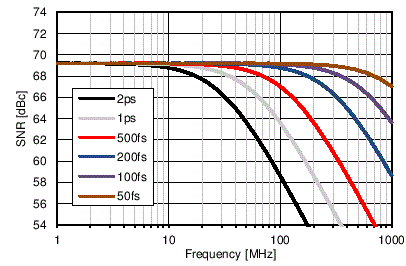 Figure 59. SNR Limit Due to Total Jitter of Sampling Clock With a -1 dBFS Input Signal
Figure 59. SNR Limit Due to Total Jitter of Sampling Clock With a -1 dBFS Input Signal Additional noise may couple to the clock path through power supplies. Take care to provide a very-low noise power supply and isolated supply return path to minimize noise added to the supply. Spurious noise added to the clock path results in symmetrical, modulated spurs around large input signals. These spurs have a constant magnitude in units of dB relative to the input signal amplitude or carrier, [dBc].