ZHCSCV9A August 2014 – October 2014 ADS1120-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Multiplexer
- 8.3.2 Low-Noise PGA
- 8.3.3 Modulator
- 8.3.4 Digital Filter
- 8.3.5 Output Data Rate
- 8.3.6 Voltage Reference
- 8.3.7 Clock Source
- 8.3.8 Excitation Current Sources
- 8.3.9 Low-Side Power Switch
- 8.3.10 Sensor Detection
- 8.3.11 System Monitor
- 8.3.12 Offset Calibration
- 8.3.13 Power Supplies
- 8.3.14 Temperature Sensor
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power-Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械封装和可订购信息
10 Power-Supply Recommendations
The device requires two power supplies: analog (AVDD, AVSS) and digital (DVDD, DGND). The analog power supply can be bipolar (for example, AVDD = 2.5 V, AVSS = –2.5 V) or unipolar (for example, AVDD = 3.3 V, AVSS = 0 V) and is independent of the digital power supply. The digital supply sets the digital I/O levels.
10.1 Power-Supply Sequencing
The power supplies can be sequenced in any order but in no case must any analog or digital inputs exceed the respective analog or digital power-supply voltage limits. Wait approximately 50 µs after all power supplies are stabilized before communicating with the device to allow the power-up reset process to complete.
10.2 Power-Supply Decoupling
Good power-supply decoupling is important to achieve optimum performance. AVDD, AVSS (when using a bipolar supply) and DVDD must be decoupled with at least a 0.1-µF capacitor, as shown in Figure 83 and Figure 84. Place the bypass capacitors as close to the power-supply pins of the device as possible using low-impedance connections. TI recommends using multi-layer ceramic chip capacitors (MLCCs) that offer low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and inductance (ESL) characteristics for power-supply decoupling purposes. For very sensitive systems, or for systems in harsh noise environments, avoiding the use of vias for connecting the capacitors to the device pins may offer superior noise immunity. The use of multiple vias in parallel lowers the overall inductance and is beneficial for connections to ground planes. TI recommends connecting analog and digital ground together as close to the device as possible.
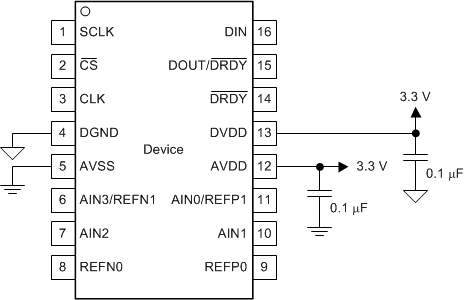 Figure 83. Unipolar Analog Power Supply
Figure 83. Unipolar Analog Power Supply
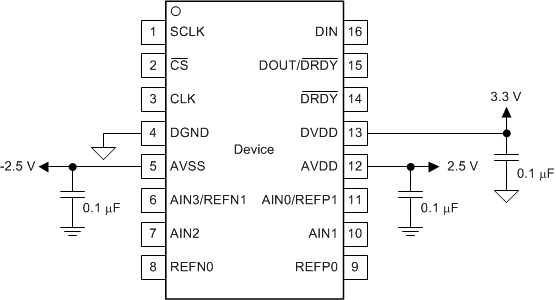 Figure 84. Bipolar Analog Power Supply
Figure 84. Bipolar Analog Power Supply