ZHCSEJ3B June 2015 – April 2020 ADS131E08S
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Programming
- 9.5.1 SPI Interface
- 9.5.2 Data Retrieval
- 9.5.3
SPI Command Definitions
- 9.5.3.1 WAKEUP: Exit STANDBY Mode
- 9.5.3.2 STANDBY: Enter STANDBY Mode
- 9.5.3.3 RESET: Reset Registers to Default Values
- 9.5.3.4 START: Start Conversions
- 9.5.3.5 STOP: Stop Conversions
- 9.5.3.6 OFFSETCAL: Channel Offset Calibration
- 9.5.3.7 RDATAC: Start Read Data Continuous Mode
- 9.5.3.8 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous Mode
- 9.5.3.9 RDATA: Read Data
- 9.5.3.10 RREG: Read from Register
- 9.5.3.11 WREG: Write to Register
- 9.5.3.12 Sending Multibyte Commands
- 9.6
Register Map
- 9.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9.6.1.1 ID: ID Control Register (Factory-Programmed, Read-Only) (address = 00h) [reset = D2h]
- 9.6.1.2 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 01h) [reset = 94h]
- 9.6.1.3 CONFIG2: Configuration Register 2 (address = 02h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.4 CONFIG3: Configuration Register 3 (address = 03h) [reset = E0h]
- 9.6.1.5 FAULT: Fault Detect Control Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.6 CHnSET: Individual Channel Settings (address = 05h to 0Ch) [reset = 10h]
- 9.6.1.7 FAULT_STATP: Fault Detect Positive Input Status (address = 12h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.8 FAULT_STATN: Fault Detect Negative Input Status (address = 13h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.9 GPIO: General-Purpose IO Register (address = 14h) [reset = 0Fh]
- 9.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
10.1.4 Voltage Sensing
Figure 59 illustrates a simplified diagram of commonly-used differential and single-ended methods of voltage sensing. A resistor divider network is used to step down the line voltage to within the acceptable ADS131E08S input range and then connect to the inputs (INxP and INxN) through an antialiasing RC filter formed by resistor R3 and capacitor C. The common-mode bias voltage [(AVDD + AVSS) / 2] can be obtained from the ADS131E08S by either configuring the internal op amp in a unity-gain configuration using the RF resistor and setting the OPAMP_REF bit of the CONFIG3 register, or generated externally by using a resistor divider network between the positive and negative supplies.
In either of the cases illustrated in Figure 59 (Figure 59a for a differential input and Figure 59b for a single-ended input), the line voltage is divided down by a factor of [R2 / (R1 + R2)]. Values of R1 and R2 must be carefully chosen so that the voltage across the ADS131E08S inputs (INxP and INxN) does not exceed the range of the ADS131E08S over the full operating dynamic range. Use separate external op amps to source and sink current because the internal op amp has very limited current sink and source capability. Additionally, separate op amps for each channel help isolate individual phases from one another to limit crosstalk.
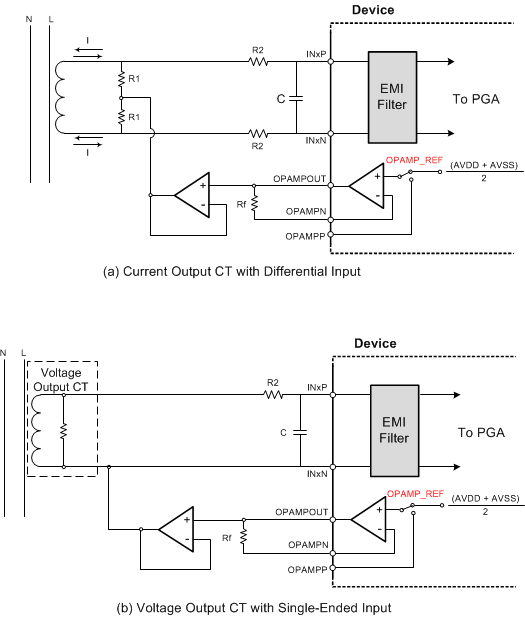 Figure 58. Simplified Current-Sensing Connections
Figure 58. Simplified Current-Sensing Connections 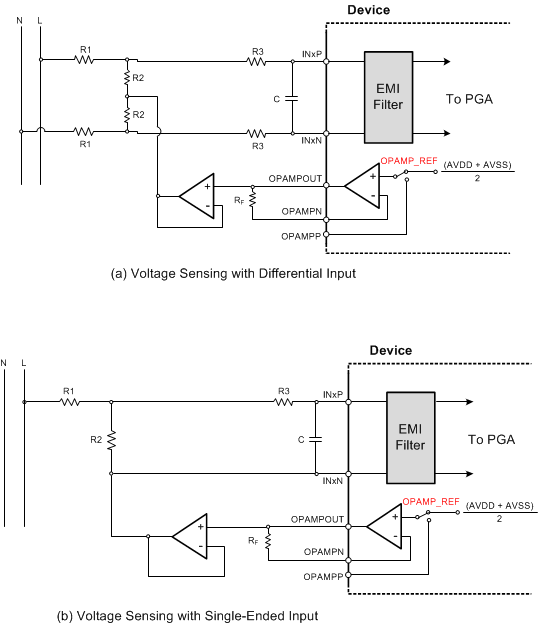 Figure 59. Simplified Voltage-Sensing Connections
Figure 59. Simplified Voltage-Sensing Connections