SLAS611C October 2009 – January 2016 ADS5400
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- PZP|100
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- PZP|100
订购信息
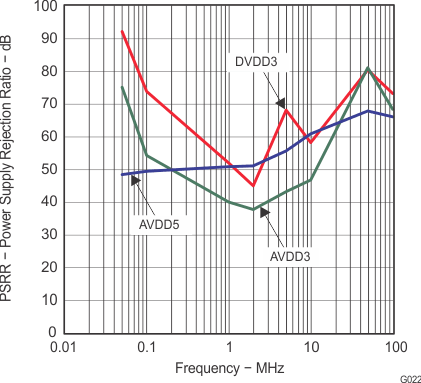
9 Power Supply Recommendations
The ADS5400 uses three power supplies. For the analog portion of the design, a 5-V and 3.3-V supply (AVDD5 and AVDD3) are used, while the digital portion uses a 3.3-V supply (DVDD3). The use of low-noise power supplies with adequate decoupling is recommended. Linear supplies are preferred to switched supplies; switched supplies generate more noise components that can be coupled to the ADS5400. The PSRR value and the plot shown in Figure 40 were obtained without bulk supply decoupling capacitors. When bulk (0.1 μF) decoupling capacitors are used, the board-level PSRR is much higher than the stated value for the ADC. The power consumption of the ADS5400 does not change substantially over clock rate or input frequency as a result of the architecture and process.