ZHCSAM3B December 2012 – April 2022 ADS54T01
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Test Pattern Output
- 8.3.2 Clock Inputs
- 8.3.3 SNR and Clock Jitter
- 8.3.4 Analog Inputs
- 8.3.5 Over-Range Indication
- 8.3.6 Interleaving Correction
- 8.3.7 High-Resolution Output Data
- 8.3.8 Low-Resolution Output Data
- 8.3.9 Full Speed – 7 Bit
- 8.3.10 Decimated Low-Resolution Output Data
- 8.3.11 Multi Device Synchronization
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.3 SNR and Clock Jitter
The signal-to-noise ratio of the ADC is limited by three different factors: the quantization noise is typically not noticeable in pipeline converters and is 72 dB for a 12-bit ADC. The thermal noise limits the SNR at low input frequencies while the clock jitter sets the SNR for higher input frequencies.

Use Equation 2 to calculate the SNR limitation due to sample clock jitter.
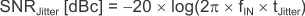
The total clock jitter (tJitter) has three components: the internal aperture jitter (100 fs for ADS54T01) which is set by the noise of the clock input buffer, the external clock jitter, and the jitter from the analog input signal. Use Equation 3 to calculate the total clock jitter.

External clock jitter can be minimized by using high-quality clock sources and jitter cleaners as well as bandpass filters at the clock input while a faster clock slew rate improves the ADC aperture jitter.
The ADS54T01 has a thermal noise of 61.2 dBFS and internal aperture jitter of 100 fs. Figure 8-4 shows the SNR depending on amount of external jitter for different input frequencies.