ZHCSIJ5C August 2018 – June 2019 ADS9224R , ADS9234R
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: ADS92x4R
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: ADS9224R
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: ADS9234R
- 6.8 Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics: ADS9224R
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics: ADS9234R
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 READY/STROBE Output
- 7.6
Programming
- 7.6.1 Output Data Word
- 7.6.2
Data Transfer Protocols
- 7.6.2.1
Protocols for Reading From the Device
- 7.6.2.1.1 Legacy, SPI-Compatible Protocols (SPI-xy-S-SDR)
- 7.6.2.1.2 SPI-Compatible Protocols With Bus Width Options and Single Data Rate (SPI-xy-D-SDR and SPI-xy-Q-SDR)
- 7.6.2.1.3 SPI-Compatible Protocols With Bus Width Options and Double Data Rate (SPI-x1-S-DDR, SPI-x1-D-DDR, SPI-x1-Q-DDR)
- 7.6.2.1.4 Clock Re-Timer (CRT) Protocols (CRT-S-SDR, CRT-D-SDR, CRT-Q-SDR, CRT-S-DDR, CRT-D-DDR, CRT-Q-DDR)
- 7.6.2.1.5 Parallel Byte Protocols (PB-xy-AB-SDR, PB-xy-AA-SDR)
- 7.6.2.2 Device Setup
- 7.6.2.3 Protocols for Configuring the Device
- 7.6.2.1
Protocols for Reading From the Device
- 7.6.3 Reading and Writing Registers
- 7.7
Register Maps
- 7.7.1
ADS92x4R Registers
- 7.7.1.1 DEVICE_STATUS Register (Offset = 0h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.7.1.2 POWER_DOWN_CFG Register (Offset = 1h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.7.1.3 PROTOCOL_CFG Register (Offset = 2h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.7.1.4 BUS_WIDTH Register (Offset = 3h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.7.1.5 CRT_CFG Register (Offset = 4h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.7.1.6 OUTPUT_DATA_WORD_CFG Register (Offset = 5h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.7.1.7 DATA_AVG_CFG Register (Offset = 6h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.7.1.8 REFBY2_OFFSET Register (Offset = 7h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.7.1
ADS92x4R Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
7.6.2.1.4 Clock Re-Timer (CRT) Protocols (CRT-S-SDR, CRT-D-SDR, CRT-Q-SDR, CRT-S-DDR, CRT-D-DDR, CRT-Q-DDR)
In clock re-timer (CRT) protocols, the device sends out data on the SDO lines with a synchronized clock on the STROBE line. The data are synchronized to the rising edges of the STROBE pulses. For CRT protocols with a single data rate, the host can capture data on the falling edges of the STROBE pulses. For double data rate, the host must capture data on both edges of STROBE. The clock source for the STROBE output can be selected as an external clock (SCLK) or an internal clock by configuring the CRT_CLK_SELECT bits in the CRT_CFG register. For reading data from the device, SCLK is only required when the STROBE output is selected as an external clock. The SDOs that are not enabled by the BUS_WIDTH register are set to tri-state. Table 6 provides the details of different CRT protocols to read data from the device.
Table 6. CRT-S-SDR, CRT-D-SDR, CRT-Q-SDR, CRT-S-DDR, CRT-D-DDR, and CRT-Q-DDR Protocols for Reading From Device
| PROTOCOL(1) | SCLK POLARITY(2) | CAPTURE EDGE | MSB LAUNCH EDGE | BUS WIDTH(4) | tREAD(3) | TIMING DIAGRAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRT-S-SDR | Low (CPOL = 0) | STROBE falling | 1st STROBE rising | 1 | [15.5 × tSTROBE + m] | Figure 56 |
| CRT-D-SDR | Low (CPOL = 0) | STROBE falling | 1st STROBE rising | 2 | [7.5 × tSTROBE + m] | Figure 58 |
| CRT-Q-SDR | Low (CPOL = 0) | STROBE falling | 1st STROBE rising | 4 | [3.5 × tSTROBE + m] | Figure 60 |
| CRT-S-DDR | Low (CPOL = 0) | STROBE rising and falling | 1st STROBE rising | 1 | [7.5 × tSTROBE + m] | Figure 57 |
| CRT-D-DDR | Low (CPOL = 0) | STROBE rising and falling | 1st STROBE rising | 2 | [3.5× tSTROBE + m] | Figure 59 |
| CRT-Q-DDR | Low (CPOL = 0) | STROBE rising and falling | 1st STROBE rising | 4 | [1.5 × tSTROBE + m] | Figure 61 |
Figure 56 through Figure 61 illustrate timing diagrams for the CRT-S-SDR, CRT-S-DDR, CRT-D-SDR, CRT-D-DDR, CRT-Q-SDR, and CRT-Q-DDR protocols, respectively.
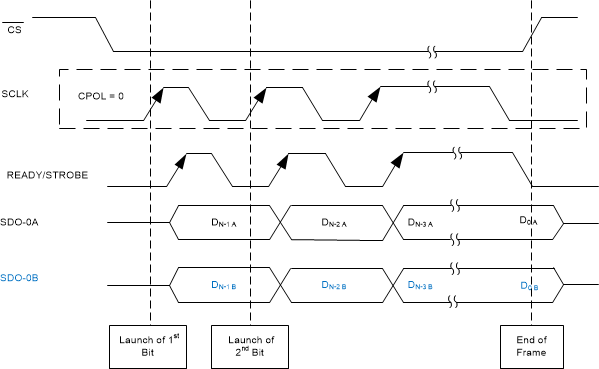 Figure 56. CRT-S-SDR Protocol
Figure 56. CRT-S-SDR Protocol 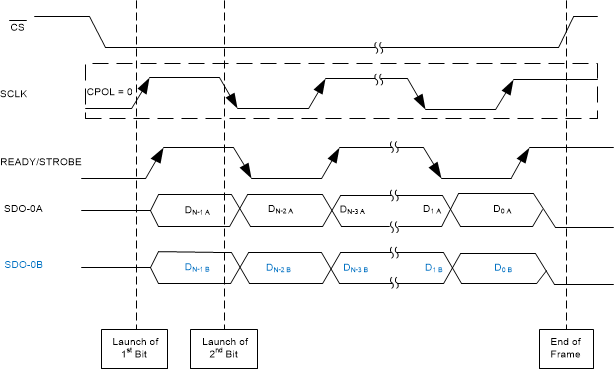 Figure 57. CRT-S-DDR Protocol
Figure 57. CRT-S-DDR Protocol 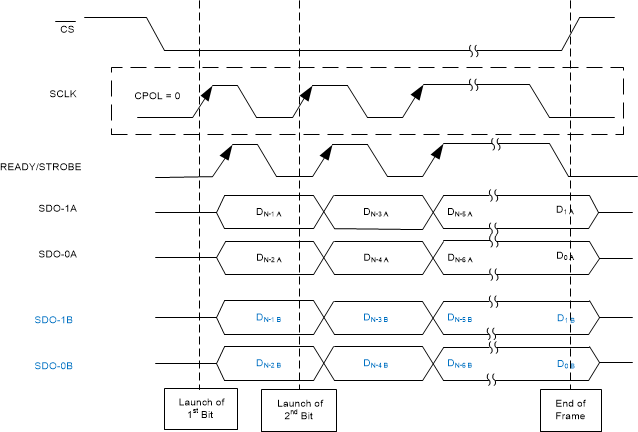 Figure 58. CRT-D-SDR Protocol
Figure 58. CRT-D-SDR Protocol 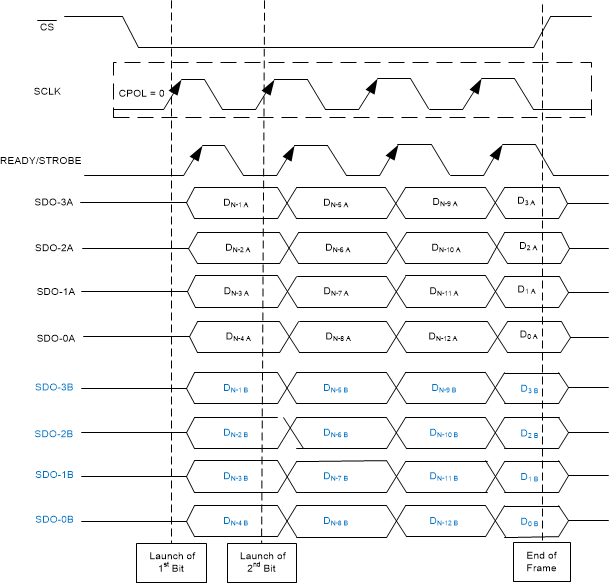 Figure 60. CRT-Q-SDR Protocol
Figure 60. CRT-Q-SDR Protocol 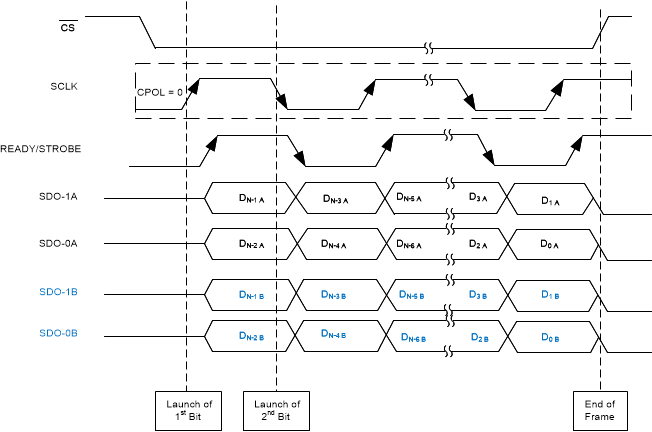 Figure 59. CRT-D-DDR Protocol
Figure 59. CRT-D-DDR Protocol 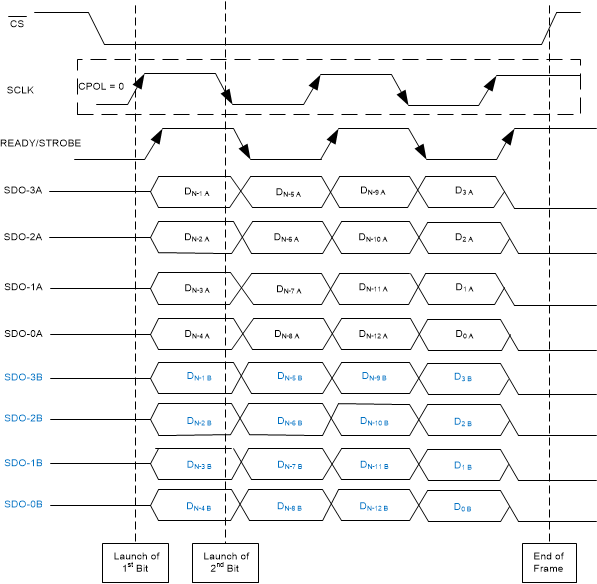 Figure 61. CRT-Q-DDR Protocol
Figure 61. CRT-Q-DDR Protocol For reading data, SCLK is only required when the STROBE output is selected as SCLK (external clock) in the CRT_CFG register. However, for configuring registers, SCLK is always required.