SLOS738E September 2012 – August 2015 AFE5809
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Digital Demodulator Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Digital Characteristics
- 7.8 Switching Characteristics
- 7.9 SPI Switching Characteristics
- 7.10 Output Interface Timing Requirements (14-bit)
- 7.11 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
ADC and VCA Register Description
- 8.6.1.1 ADC Register Map
- 8.6.1.2
AFE5809 ADC Register/Digital Processing Description
- 8.6.1.2.1 AVERAGING_ENABLE: Address: 2[11]
- 8.6.1.2.2 ADC_OUTPUT_FORMAT: Address: 4[3]
- 8.6.1.2.3 ADC Reference Mode: Address 1[13] and 3[15]
- 8.6.1.2.4 DIGITAL_GAIN_ENABLE: Address: 3[12]
- 8.6.1.2.5 DIGITAL_HPF_ENABLE
- 8.6.1.2.6 DIGITAL_HPF_FILTER_K_CHX
- 8.6.1.2.7 LOW_FREQUENCY_NOISE_SUPPRESSION: Address: 1[11]
- 8.6.1.2.8 LVDS_OUTPUT_RATE_2X: Address: 1[14]
- 8.6.1.2.9 CHANNEL_OFFSET_SUBSTRACTION_ENABLE: Address: 3[8]
- 8.6.1.2.10 SERIALIZED_DATA_RATE: Address: 3[14:13]
- 8.6.1.2.11 TEST_PATTERN_MODES: Address: 2[15:13]
- 8.6.1.2.12 SYNC_PATTERN: Address: 10[8]
- 8.6.1.3 VCA Register Map
- 8.6.1.4 VCA Register Description
- 8.6.2 Digital Demodulator Register Description
- 8.6.1
ADC and VCA Register Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Application
- 9.3 System Example
- 9.4
Do's and Don'ts
- 9.4.1 Driving the Inputs (Analog or Digital) Beyond the Power-Supply Rails
- 9.4.2 Driving the Device Signal Input With an Excessively High Level Signal
- 9.4.3 Driving the VCNTL Signal With an Excessive Noise Source
- 9.4.4 Using a Clock Source With Excessive Jitter, an Excessively Long Input Clock Signal Trace, or Having Other Signals Coupled to the ADC or CW Clock Signal Trace
- 9.4.5 LVDS Routing Length Mismatch
- 9.4.6 Failure to Provide Adequate Heat Removal
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Proper grounding and bypassing, short lead length, and the use of ground and power-supply planes are particularly important for high-frequency designs. Achieving optimum performance with a high-performance device such as the AFE5809 requires careful attention to the PCB layout to minimize the effects of board parasitics and optimize component placement. A multilayer PCB usually ensures best results and allows convenient component placement. To maintain proper LVDS timing, all LVDS traces should follow a controlled impedance design. In addition, all LVDS trace lengths should be equal and symmetrical; TI recommends to keep trace length variations less than 150 mil (0.150 inch or 3.81 mm).
NOTE
To avoid noise coupling through supply pins, TI recommends keeping sensitive input net classes, such as INM, INP, ACT pins, away from AVDD 3.3 V, AVDD_5V, DVDD, AVDD_ADC, DVDD_LDO1/2 nets or planes. For example, vias connected to these pins should NOT be routed across any supply plane. That is to avoid power planes under INM, INP, and ACT pins.
In addition, appropriate delay matching should be considered for the CW clock path, especially in systems with high channel count. For example, if clock delay is half of the 16× clock period, a phase error of 22.5°C could exist. Thus, the timing delay difference among channels contributes to the beamformer accuracy.
Additional details on BGA PCB layout techniques can be found in the TI application report MicroStar BGA Packaging Reference Guide (SSYZ015), which can be downloaded from www.ti.com.
11.2 Layout Example
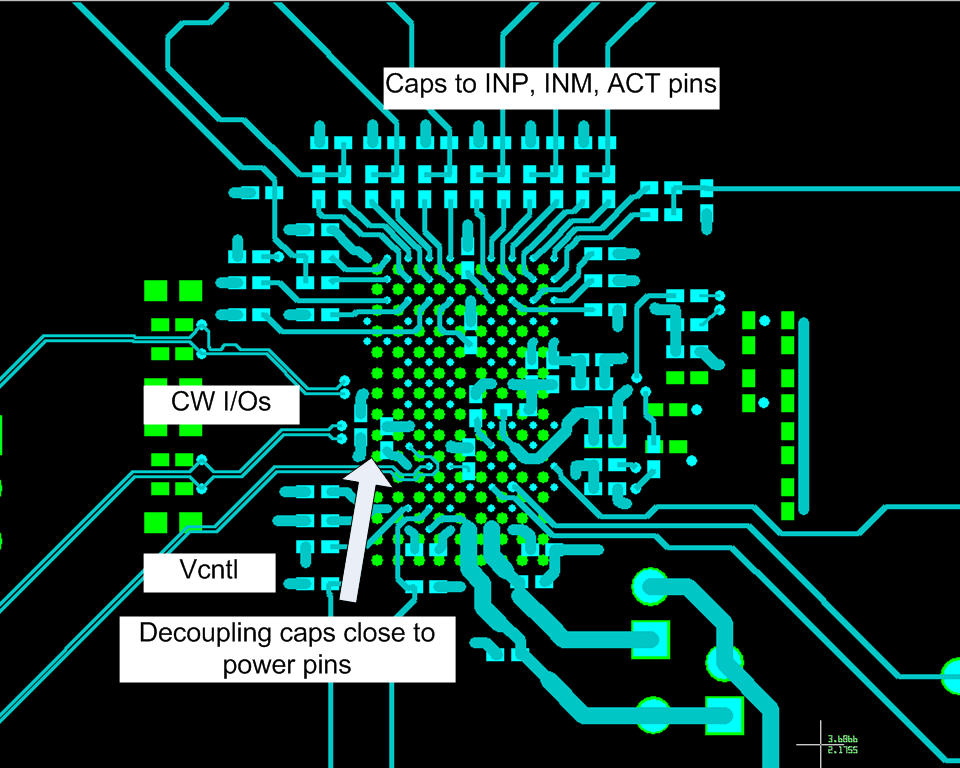 Figure 114. Layout Example
Figure 114. Layout Example
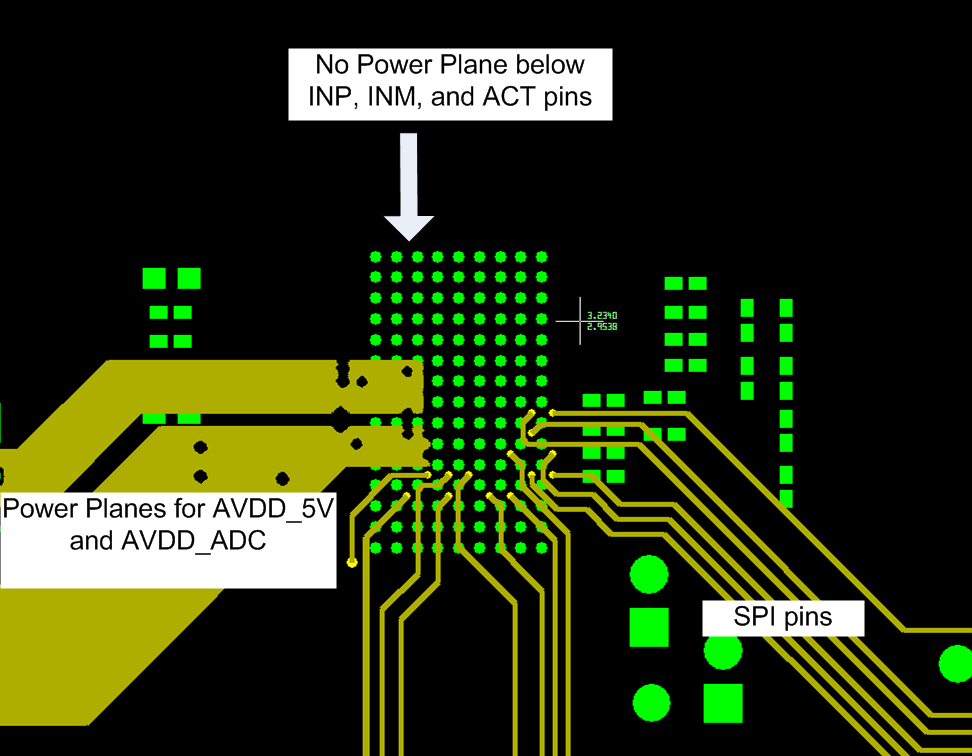 Figure 115. Layout Example
Figure 115. Layout Example
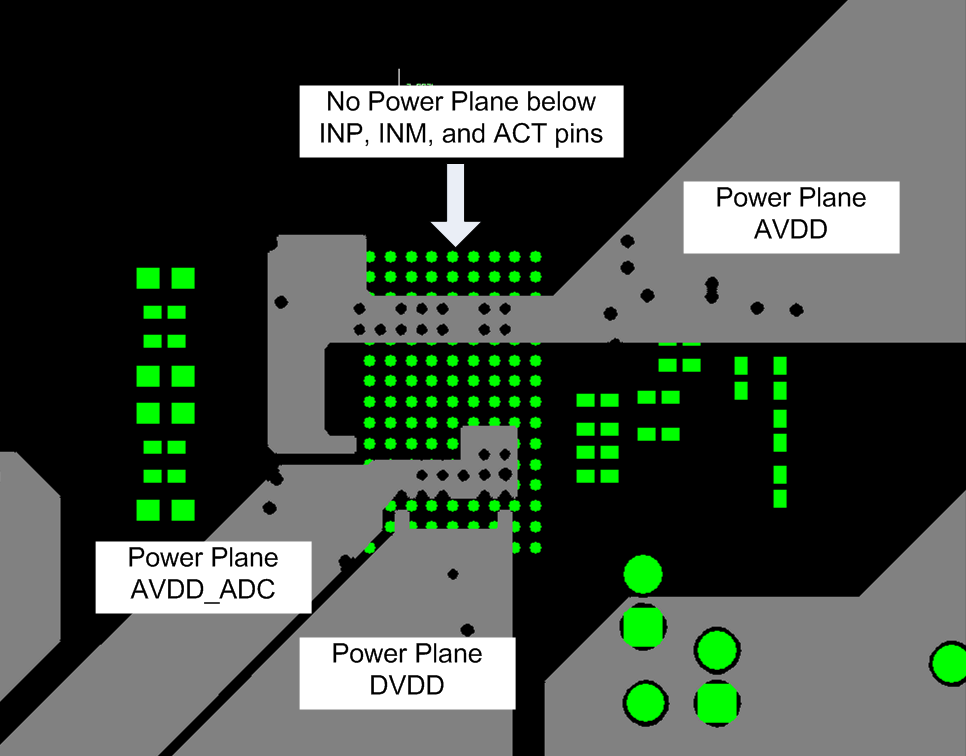 Figure 116. Layout Example
Figure 116. Layout Example
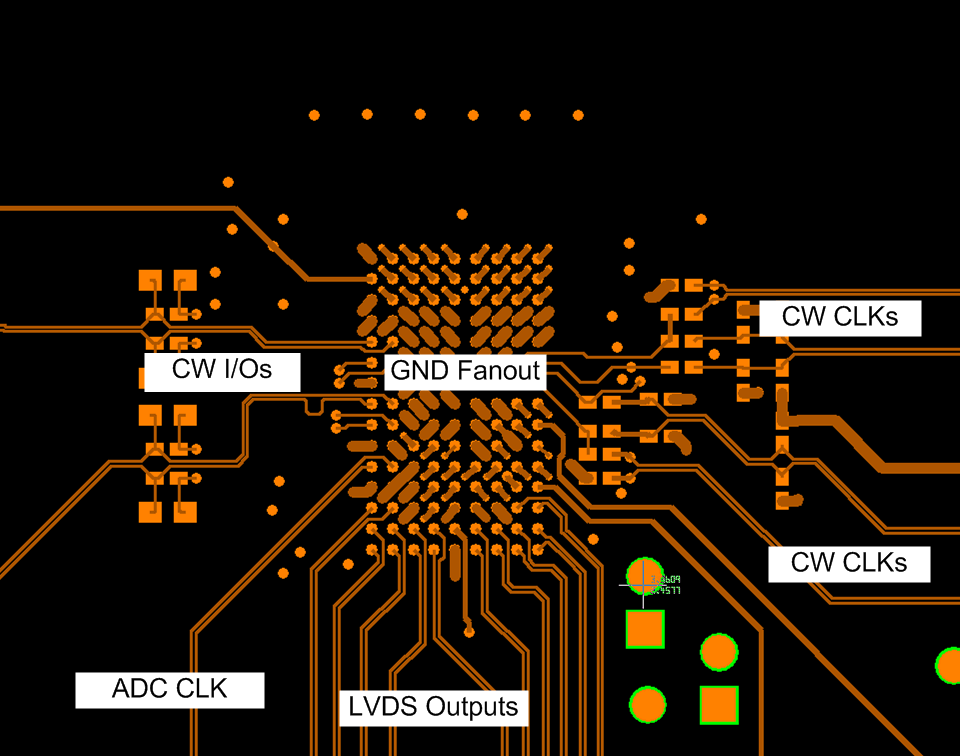 Figure 117. Layout Example
Figure 117. Layout Example