ZHCSDC3D June 2014 – September 2016 AM4372 , AM4376 , AM4377 , AM4378 , AM4379
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Device Comparison
-
4Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1
Pin Diagrams
- ZDN Ball Map [Section Top Left - Top View]
- Table 4-1 ZDN Ball Map [Section Top Middle - Top View]
- Table 4-2 ZDN Ball Map [Section Top Right - Top View]
- Table 4-3 ZDN Ball Map [Section Middle Left - Top View]
- ZDN Ball Map [Section Middle Middle - Top View]
- ZDN Ball Map [Section Middle Right - Top View]
- Table 4-4 ZDN Ball Map [Section Bottom Left - Top View]
- Table 4-5 ZDN Ball Map [Section Bottom Middle - Top View]
- Table 4-6 ZDN Ball Map [Section Bottom Right - Top View]
- 4.2 Pin Attributes
- 4.3
Signal Descriptions
- 4.3.1 ADC Interfaces
- 4.3.2 CAN Interfaces
- 4.3.3 Camera (VPFE) Interfaces
- 4.3.4 Debug Subsystem Interface
- 4.3.5 Display Subsystem (DSS) Interface
- 4.3.6 Ethernet (GEMAC_CPSW) Interfaces
- 4.3.7 External Memory Interfaces
- 4.3.8 General Purpose IOs
- 4.3.9 HDQ Interface
- 4.3.10 I2C Interfaces
- 4.3.11 McASP Interfaces
- 4.3.12 Miscellaneous
- 4.3.13 PRU-ICSS0 Interface
- 4.3.14 PRU-ICSS1 Interface
- 4.3.15 QSPI Interface
- 4.3.16 RTC Subsystem Interface
- 4.3.17 Removable Media Interfaces
- 4.3.18 SPI Interfaces
- 4.3.19 Timer Interfaces
- 4.3.20 UART Interfaces
- 4.3.21 USB Interfaces
- 4.3.22 eCAP Interfaces
- 4.3.23 eHRPWM Interfaces
- 4.3.24 eQEP Interfaces
- 4.1
Pin Diagrams
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 5.4 Operating Performance Points
- 5.5 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.7 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.8 ADC0: Touch Screen Controller and Analog-to-Digital Subsystem Electrical Parameters
- 5.9 ADC1: Analog-to-Digital Subsystem Electrical Parameters
- 5.10 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 5.11 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 5.12 External Capacitors
- 5.13
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.13.1 Power Supply Sequencing
- 5.13.2
Clock
- 5.13.2.1 PLLs
- 5.13.2.2 Input Clock Specifications
- 5.13.2.3 Input Clock Requirements
- 5.13.2.4 Output Clock Specifications
- 5.13.2.5 Output Clock Characteristics
- 5.13.3 Timing Parameters and Board Routing Analysis
- 5.13.4 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 5.13.5 Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 5.13.6 DMTimer
- 5.13.7
Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) and Switch
- 5.13.7.1
Ethernet MAC and Switch Electrical Data and Timing
- Table 5-23 Ethernet MAC and Switch Timing Conditions
- 5.13.7.1.1 Ethernet MAC/Switch MDIO Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.13.7.1.2
Ethernet MAC and Switch MII Electrical Data and Timing
- Table 5-27 Timing Requirements for GMII[x]_RXCLK - MII Mode
- Table 5-28 Timing Requirements for GMII[x]_TXCLK - MII Mode
- Table 5-29 Timing Requirements for GMII[x]_RXD[3:0], GMII[x]_RXDV, and GMII[x]_RXER - MII Mode
- Table 5-30 Switching Characteristics for GMII[x]_TXD[3:0], and GMII[x]_TXEN - MII Mode
- 5.13.7.1.3 Ethernet MAC and Switch RMII Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.13.7.1.4
Ethernet MAC and Switch RGMII Electrical Data and Timing
- Table 5-34 Timing Requirements for RGMII[x]_RCLK - RGMII Mode
- Table 5-35 Timing Requirements for RGMII[x]_RD[3:0], and RGMII[x]_RCTL - RGMII Mode
- Table 5-36 Switching Characteristics for RGMII[x]_TCLK - RGMII Mode
- Table 5-37 Switching Characteristics for RGMII[x]_TD[3:0], and RGMII[x]_TCTL - RGMII Mode
- 5.13.7.1
Ethernet MAC and Switch Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.13.8
External Memory Interfaces
- 5.13.8.1 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 5.13.8.2
Memory Interface
- 5.13.8.2.1
DDR3 and DDR3L Routing Guidelines
- 5.13.8.2.1.1 Board Designs
- 5.13.8.2.1.2 DDR3 Device Combinations
- 5.13.8.2.1.3
DDR3 Interface
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.1 DDR3 Interface Schematic
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.2 Compatible JEDEC DDR3 Devices
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.3 DDR3 PCB Stackup
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.4 DDR3 Placement
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.5 DDR3 Keepout Region
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.6 DDR3 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.7 DDR3 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.8 DDR3 Net Classes
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.9 DDR3 Signal Termination
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.10 DDR3 DDR_VREF Routing
- 5.13.8.2.1.3.11 DDR3 VTT
- 5.13.8.2.1.4 DDR3 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies and Routing Definition
- 5.13.8.2.1.5 Data Topologies and Routing Definition
- 5.13.8.2.1.6 Routing Specification
- 5.13.8.2.2
LPDDR2 Routing Guidelines
- 5.13.8.2.2.1 LPDDR2 Board Designs
- 5.13.8.2.2.2 LPDDR2 Device Configurations
- 5.13.8.2.2.3
LPDDR2 Interface
- 5.13.8.2.2.3.1 LPDDR2 Interface Schematic
- 5.13.8.2.2.3.2 Compatible JEDEC LPDDR2 Devices
- 5.13.8.2.2.3.3 LPDDR2 PCB Stackup
- 5.13.8.2.2.3.4 LPDDR2 Placement
- 5.13.8.2.2.3.5 LPDDR2 Keepout Region
- 5.13.8.2.2.3.6 LPDDR2 Net Classes
- 5.13.8.2.2.3.7 LPDDR2 Signal Termination
- 5.13.8.2.2.3.8 LPDDR2 DDR_VREF Routing
- 5.13.8.2.2.4 Routing Specification
- 5.13.8.2.1
DDR3 and DDR3L Routing Guidelines
- 5.13.9 Display Subsystem (DSS)
- 5.13.10 Camera (VPFE)
- 5.13.11 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 5.13.12 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 5.13.13 Multichannel Serial Port Interface (McSPI)
- 5.13.14 Quad Serial Port Interface (QSPI)
- 5.13.15 HDQ/1-Wire Interface (HDQ/1-Wire)
- 5.13.16
Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem and Industrial Communication Subsystem (PRU-ICSS)
- 5.13.16.1
Programmable Real-Time Unit (PRU-ICSS PRU)
- Table 5-100 PRU-ICSS PRU Timing Conditions
- 5.13.16.1.1 PRU-ICSS PRU Direct Input/Output Mode Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.13.16.1.2 PRU-ICSS PRU Parallel Capture Mode Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.13.16.1.3 PRU-ICSS PRU Shift Mode Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.13.16.1.4 PRU-ICSS Sigma Delta Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.13.16.1.5 PRU-ICSS ENDAT Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.13.16.2
PRU-ICSS EtherCAT (PRU-ICSS ECAT)
- Table 5-109 PRU-ICSS ECAT Timing Conditions
- 5.13.16.2.1
PRU-ICSS ECAT Electrical Data and Timing
- Table 5-110 PRU-ICSS ECAT Timing Requirements - Input Validated With LATCH_IN
- Table 5-111 PRU-ICSS ECAT Timing Requirements - Input Validated With SYNCx
- Table 5-112 PRU-ICSS ECAT Timing Requirements - Input Validated With Start of Frame (SOF)
- Table 5-113 PRU-ICSS ECAT Timing Requirements - LATCHx_IN
- Table 5-114 PRU-ICSS ECAT Switching Requirements - Digital IOs
- 5.13.16.3 PRU-ICSS MII_RT and Switch
- 5.13.16.4 PRU-ICSS Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (PRU-ICSS UART)
- 5.13.16.1
Programmable Real-Time Unit (PRU-ICSS PRU)
- 5.13.17
Multimedia Card (MMC) Interface
- 5.13.17.1
MMC Electrical Data and Timing
- Table 5-125 MMC Timing Conditions
- Table 5-126 Timing Requirements for MMC[0]_CMD and MMC[0]_DAT[7:0]
- Table 5-127 Timing Requirements for MMC[1/2]_CMD and MMC[1/2]_DAT[7:0]
- Table 5-128 Switching Characteristics for MMC[x]_CLK
- Table 5-129 Switching Characteristics for MMC[x]_CMD and MMC[x]_DAT[7:0]—HSPE=0
- Table 5-130 Switching Characteristics for MMC[x]_CMD and MMC[x]_DAT[7:0]—HSPE=1
- 5.13.17.1
MMC Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.13.18 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 5.14 Emulation and Debug
- 6Device and Documentation Support
- 7Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
5.13.9.1.2.2 DSS—Parallel Interface—RFBI Mode—Pico DLP
The Remote Frame Buffer Interface (RFBI) module can provide also the necessary control signals and data to interface to the Pico DLP driver of the Pico DLP panel. Table 5-78 assumes testing over the recommended operating conditions and electrical characteristic conditions below (see Figure 5-98).
Table 5-78 DSS Timing Conditions—RFBI Mode—Pico DLP
| TIMING CONDITION PARAMETER | VALUE | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | |||
| Output Condition | ||||
| CLOAD | Output load capacitance | 5 | pF | |
To use Pico DLP application, RFBI register must be configured as shown in Table 5-79:
Table 5-79 DSS Register Configuration—RFBI Mode—Pico DLP
| DESCRIPTION | REGISTER AND BIT FIELD(1) | BIT | VALUES |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selection parallel mode | RFBI_CONFIGi and ParallelMode | [1:0] | 0b11: 16-bit parallel output interface selected |
| Time Granularity (multiplies signal timing latencies by 2). | RFBI_CONFIGi andTimeGranularity | [4] | 0b0: x2 latency disable |
| CS signal assertion time from Start Access Time | RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi and CSOnTime | [3:0] | 0b0000 |
| CS signal deassertion time from Start Access Time | RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi and CSOffTime | [9:4] | 0b000100: 4 cycles |
| WE signal assertion time from Start Access Time | RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi and WEOnTime | [13:10] | 0b0000 |
| WE signal deassertion time from Start Access Time | RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi and WEOffTime | [19:14] | 0b000010: 2 cycles |
| RE signal assertion time from Start Access Time | RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi and REOnTime | [23:20] | 0b0000 |
| RE signal deassertion time from Start Access Time | RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi and REOffTime | [29:24] | 0b0000 |
| Write cycle time | RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi and WECycleTime | [5:0] | 0b000100: 4 cycles |
| Read cycle time | RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi and ReCycleTime | [11:6] | 0b000000 |
| CS pulse width | RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi and CSPulseWidth | [17:12] | 0b000000 |
| Read to Write CS pulse width enable | RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi and RWEnable | [18] | 0b0 |
| Read to Read CS pulse width enable | RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi and RREnable | [19] | 0b0 |
| Write to Write CS pulse width enable | RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi and WWEnable | [20] | 0b0 |
| Write to Read CS pulse width enable | RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi and WREnable | [21] | 0b0 |
| From Start Access Time to CLK rising edge used for the first data capture | RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi and AccessTime | [27:22] | 0b000000 |
- i is equal to 0 or 1. For more information, see the DSS chapter in the AM437x Sitara Processors Technical Reference Manual.
Table 5-80 DSS Switching Characteristics—RFBI Mode—Pico DLP(1)(2)(3)
| PARAMETER | OPP100 | OPP50 | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||
| tw(wrH) | Pulse duration, output write enable rfbi_wr high | A(4) | A(4) | ns | ||
| tw(wrL) | Pulse duration, output write enable rfbi_wr low | B(5) | B(5) | ns | ||
| td(a0-wrL) | Delay time, output command/data control rfbi_a0 transition to output write enable rfbi_wr low | C(6) | C(6) | ns | ||
| td(wrH-a0) | Delay time, output write enable rfbi_wr high to output command/data control rfbi_a0 transition | D(7) | D(7) | ns | ||
| td(csx-wrL) | Delay time, output chip select rfbi_csx(8) low to output write enable rfbi_wr low | E(9) | E(9) | ns | ||
| td(wrH-csxH) | Delay time, output write enable rfbi_wr high to output chip select rfbi_csx(8) high | F(10) | F(10) | ns | ||
| td(dataV) | Output data rfbi_da[15:0](11) valid | G(12) | G(12) | ns | ||
| td(Skew) | Skew between output write enable falling rfbi_wr and output data rfbi_da[15:0](11) high or low | 15.5 | 15.5 | ns | ||
| td(a0H-rdL) | Delay time, output command/data control rfbi_a0 high to output read enable rfbi_rd low | H(13) | H(13) | ns | ||
| td(rdlH-a0) | Delay time, output read enable rfbi_rd high to output command/data control rfbi_a0 transition | I(14) | I(14) | ns | ||
| tw(rdH) | Pulse duration, output read enable rfbi_rd high | J(15) | J(15) | ns | ||
| tw(rdL) | Pulse duration, output read enable rfbi_rd low | K(16) | K(16) | ns | ||
| td(rdL-csxL) | Delay time, output read enable rfbi_rd low to output chip select rfbi_csx(8) low | L(17) | L(17) | ns | ||
| td(rdL-csxH) | Delay time, output read enable rfbi_rd low to output chip select rfbi_csx(8) high | M(18) | M(18) | ns | ||
| tR(wr) | Rise time, output write enable rfbi_wr | 7 | 7 | ns | ||
| tF(wr) | Fall time, output write enable rfbi_wr | 7 | 7 | ns | ||
| tR(a0) | Rise time, output command/data control rfbi_a0 | 7 | 7 | ns | ||
| tF(a0) | Fall time, output command/data control rfbi_a0 | 7 | 7 | ns | ||
| tR(csx) | Rise time, output chip select rfbi_csx(8) | 7 | 7 | ns | ||
| tF(csx) | Fall time, output chip select rfbi_csx(8) | 7 | 7 | ns | ||
| tR(d) | Rise time, output data rfbi_da[15:0](11) | 7 | 7 | ns | ||
| tF(d) | Fall time, output data rfbi_da[15:0](11) | 7 | 7 | ns | ||
| tR(rd) | Rise time, output read enable rfbi_rd | 7 | 7 | ns | ||
| tF(rd) | Fall time, output read enable rfbi_rd | 7 | 7 | ns | ||
| CsOnTime | CS signal assertion time from Start Access Time – RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi Register | 0(19) | ns | |||
| CsOffTime | CS signal deassertion time from Start Access Time – RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi Register | 40(19) | ns | |||
| WeOnTime | WE signal assertion time from Start Access Time – RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi Register | 0(19) | ns | |||
| WeOffTime | WE signal deassertion time from Start Access Time – RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi Register | 20(19) | ns | |||
| ReOnTime | RE signal assertion time from Start Access Time – RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi Register | - | ns | |||
| ReOffTime | RE signal deassertion time from Start Access Time – RFBI_ONOFF_TIMEi Register | - | ns | |||
| WeCycleTime | Write cycle time – RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi Register | 40(19) | ns | |||
| ReCycleTime | Read cycle time – RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi Register | - | ns | |||
| CsPulseWidth | CS pulse width – RFBI_CYCLE_TIMEi Register | 0(19) | ns | |||
- See DM Operating Condition Addendum for OPP voltages.
- At OPP100, L4 clock is 100 MHz and at OPP50, L4 clock is 50 MHz.
- rfbi_wr must be at 25 MHz.
- A = (WECycleTime – WEOffTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- B = (WEOffTime – WEOntime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- C = WEOnTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- D = (WECycleTime + CSPulseWidth – WEOffTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK if mode Write to Read or Read to Write is enabled.
- In rfbi_csx, x is equal to 0 or 1.
- E = (WEOnTime – CSOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- F = (CSOffTime – WEOffTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- 16-bit parallel output interface is selected in DSS register.
- G = WECycleTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- H = REOnTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- I = (RECycleTime + CSPulseWidth – REOffTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK if mode Write to Read or Read to Write is enabled.
- J = (RECycleTime – REOffTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- K = (REOffTime – REOntime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- L = (REOnTime – CSOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- M = (CSOffTime – REOffTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × L4CLK
- These values are calculated by the following formula: RFBI Register (Value) × L4 Clock (ns).
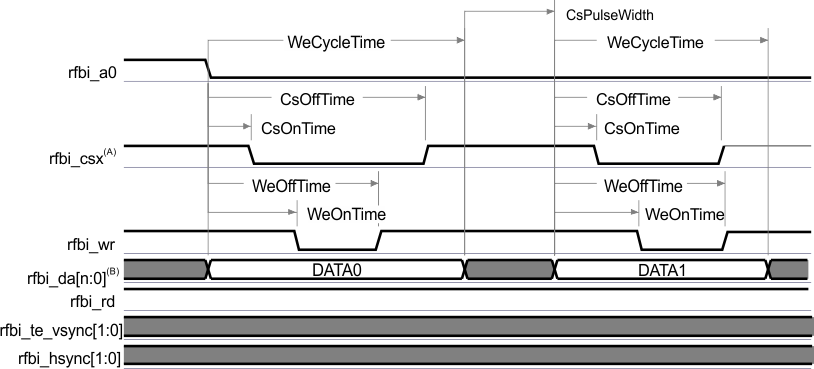
A. In rfbi_csx, x is equal to 0 or 1.
B. rfbi_da[n:0], n up to 15
Figure 5-98 DSS—RFBI Mode—Pico DLP—Command / Data Write