ZHCSSS9A march 2023 – august 2023 AM62A3 , AM62A3-Q1 , AM62A7 , AM62A7-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
-
6 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 6.1 Pin Diagrams
- 6.2 Pin Attributes
- 6.3
Signal Descriptions
- 15
- 6.3.1 CPSW3G
- 6.3.2 CPTS
- 6.3.3 CSI-2
- 6.3.4 DDRSS
- 6.3.5 DSS
- 6.3.6 ECAP
- 6.3.7 Emulation and Debug
- 6.3.8 EPWM
- 6.3.9 EQEP
- 6.3.10 GPIO
- 6.3.11 GPMC
- 6.3.12 I2C
- 6.3.13 MCAN
- 6.3.14 MCASP
- 6.3.15 MCSPI
- 6.3.16 MDIO
- 6.3.17 MMC
- 6.3.18 OSPI
- 6.3.19 Power Supply
- 6.3.20 Reserved
- 6.3.21 System and Miscellaneous
- 6.3.22 TIMER
- 6.3.23 UART
- 6.3.24 USB
- 6.4 Pin Connectivity Requirements
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Operating Performance Points
- 7.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 7.7
Electrical
Characteristics
- 7.7.1 I2C Open-Drain, and Fail-Safe (I2C OD FS) Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7.2 Fail-Safe Reset (FS RESET) Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7.3 High-Frequency Oscillator (HFOSC) Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7.4 Low-Frequency Oscillator (LFXOSC) Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7.5 SDIO Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7.6 LVCMOS Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7.7 CSI-2 (D-PHY) Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7.8 USB2PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7.9 DDR Electrical Characteristics
- 7.8 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 7.9 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 7.10
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 7.10.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 7.10.2 Power Supply Requirements
- 7.10.3 System Timing
- 7.10.4
Clock Specifications
- 7.10.4.1 Input Clocks / Oscillators
- 7.10.4.2 Output Clocks
- 7.10.4.3 PLLs
- 7.10.4.4 Recommended System Precautions for Clock and Control Signal Transitions
- 7.10.5
Peripherals
- 7.10.5.1 CPSW3G
- 7.10.5.2 CPTS
- 7.10.5.3 CSI-2
- 7.10.5.4 DDRSS
- 7.10.5.5 DSS
- 7.10.5.6 ECAP
- 7.10.5.7 Emulation and Debug
- 7.10.5.8 EPWM
- 7.10.5.9 EQEP
- 7.10.5.10 GPIO
- 7.10.5.11 GPMC
- 7.10.5.12 I2C
- 7.10.5.13 MCAN
- 7.10.5.14 MCASP
- 7.10.5.15 MCSPI
- 7.10.5.16
MMCSD
- 7.10.5.16.1
MMC0 - eMMC/SD/SDIO Interface
- 7.10.5.16.1.1 Legacy SDR Mode
- 7.10.5.16.1.2 High Speed SDR Mode
- 7.10.5.16.1.3 HS200 Mode
- 7.10.5.16.1.4 Default Speed Mode
- 7.10.5.16.1.5 High Speed Mode
- 7.10.5.16.1.6 UHS–I SDR12 Mode
- 7.10.5.16.1.7 UHS–I SDR25 Mode
- 7.10.5.16.1.8 UHS–I SDR50 Mode
- 7.10.5.16.1.9 UHS–I DDR50 Mode
- 7.10.5.16.1.10 UHS–I SDR104 Mode
- 7.10.5.16.2 MMC1/MMC2 - SD/SDIO Interface
- 7.10.5.16.1
MMC0 - eMMC/SD/SDIO Interface
- 7.10.5.17 OSPI
- 7.10.5.18 Timers
- 7.10.5.19 UART
- 7.10.5.20 USB
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Processor Subsystems
- 8.3 Accelerators and Coprocessors
- 8.4 Other Subsystems
- 8.5
Peripherals
- 8.5.1 Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW3G)
- 8.5.2 Camera Serial Interface Receiver (CSI_RX_IF)
- 8.5.3 Display Subsystem (DSS)
- 8.5.4 Enhanced Capture (ECAP)
- 8.5.5 Error Location Module (ELM)
- 8.5.6 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulation (EPWM)
- 8.5.7 Error Signaling Module (ESM)
- 8.5.8 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (EQEP)
- 8.5.9 General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 8.5.10 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 8.5.11 Global Timebase Counter (GTC)
- 8.5.12 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 8.5.13 Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 8.5.14 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (MCASP)
- 8.5.15 Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (MCSPI)
- 8.5.16 Multi-Media Card Secure Digital (MMCSD)
- 8.5.17 Octal Serial Peripheral Interface (OSPI)
- 8.5.18 Timers
- 8.5.19 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 8.5.20 Universal Serial Bus Subsystem (USBSS)
-
9 Applications,
Implementation, and Layout
- 9.1 Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 9.2 Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 9.3 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.10.5.19 UART
For more details about features and additional description information on the device Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter, see the corresponding subsections within Signal Descriptions and Detailed Description sections.
Table 7-127 UART Timing Conditions
| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT CONDITIONS | ||||
| SRI | Input slew rate | 0.5 | 5 | V/ns |
| OUTPUT CONDITIONS | ||||
| CL | Output load capacitance | 1 | 30(1) | pF |
(1) This value represents an absolute
maximum load capacitance. As the UART baud rate increases, it may be necessary
to reduce the load capacitance to a value less than this maximum limit to
provide enough timing margin for the attached device. The output rise/fall times
increase as capacitive load increases, which decreases the time data is valid
for the receiver of the attached devices. Therefore, it is important to
understand the minimum data valid time required by the attached device at the
operating baud rate. Then use the device IBIS models to verify the actual load
capacitance on the UART signals does not increase the rise/fall times beyond the
point where the minimum data valid time of the attached device is violated.
Table 7-128 UART Timing Requirements see Figure 7-108
| NO. | PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tw(RXD) | Pulse width, receive data bit high or low | 0.95U(1)(2) | 1.05U(1)(2) | ns |
| 2 | tw(RXDS) | Pulse width, receive start bit low | 0.95U(1)(2) | ns |
(1) U = UART baud time in ns =
1/programmed baud rate.
(2) This value defines the data valid time, where the input voltage is required to
be above VIH or below VIL.
Table 7-129 UART Switching
Characteristics see Figure 7-108
| NO. | PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f(baud) | Programmable baud rate for Main Domain UARTs | 12 | Mbps | ||
| Programmable baud rate for MCU and WKUP Domain UARTs | 3.7 | Mbps | |||
| 3 | tw(TXD) | Pulse width, transmit data bit high or low | U(1) - 2 | U(1) + 2 | ns |
| 4 | tw(TXDS) | Pulse width, transmit start bit low | U(1) - 2 | ns |
(1) U = UART baud time in ns = 1/actual baud rate, where the actual baud rate is
defined in the UART Baud Rate Settings table of the device TRM.
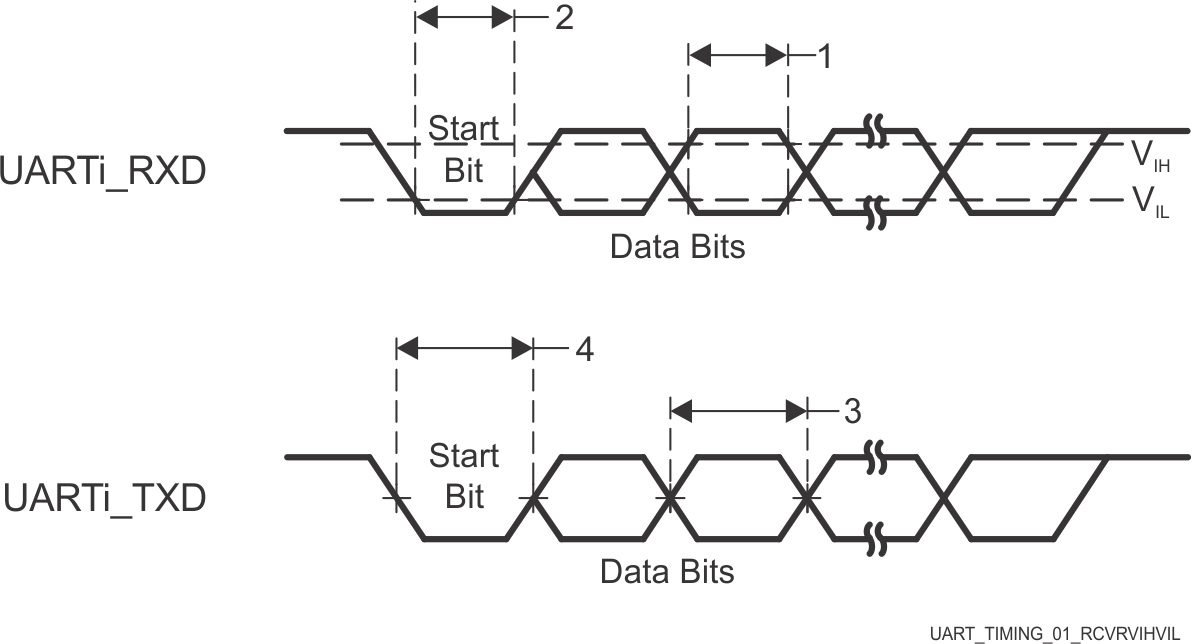 Figure 7-108 UART Timing Requirements and
Switching Characteristics
Figure 7-108 UART Timing Requirements and
Switching CharacteristicsFor more information, see Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) section in Peripherals chapter in the device TRM.