ZHCS161D April 2011 – July 2015 AMC1200
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DUB|8
订购信息
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over the operating ambient temperature range, unless otherwise noted.(1)
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM) JEDEC standard 22, test method A114-C.01(1) | ±2500 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | Operating ambient temperature range | –40 | 105 | °C | |
| VDD1 | High-side power supply | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | V |
| VDD2 | Low-side power supply | 2.7 | 5 | 5.5 | V |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | AMC1200, AMC1200B | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DUB (SOP) | DWV (SOIC) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 75.1 | 102.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 61.6 | 49.8 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 39.8 | 56.6 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 27.2 | 16 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 39.4 | 55.2 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
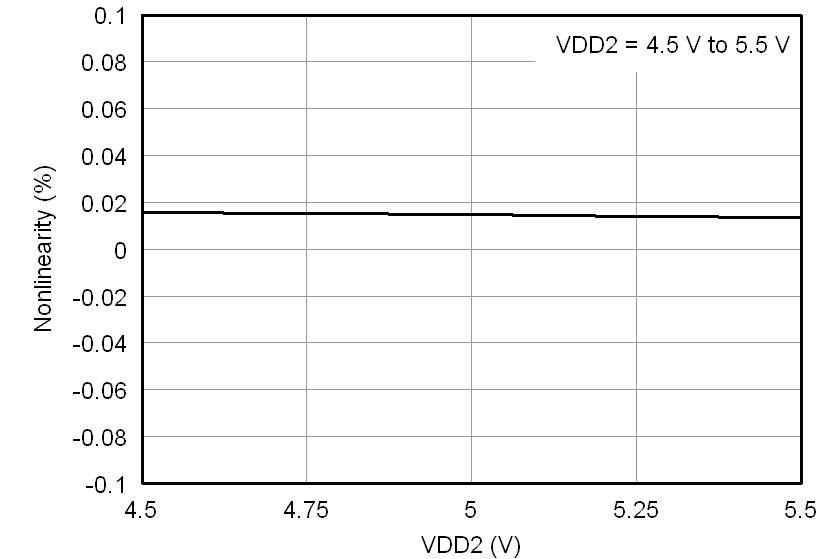
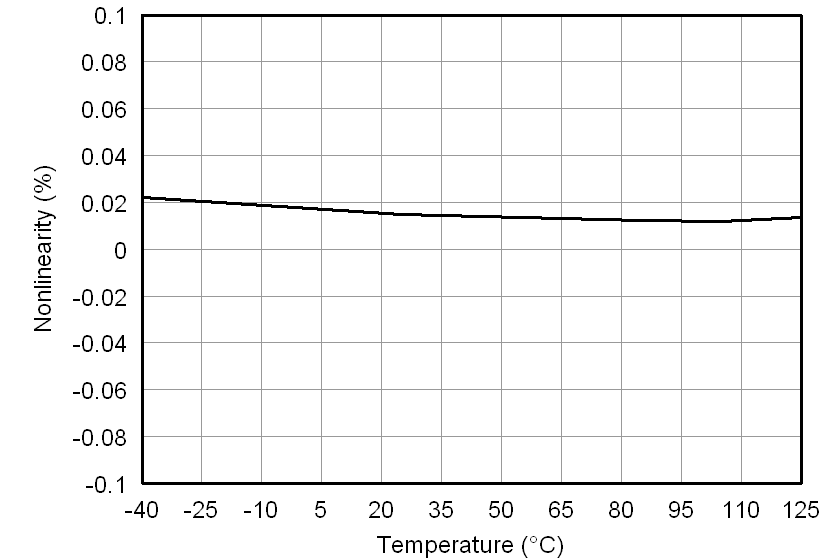
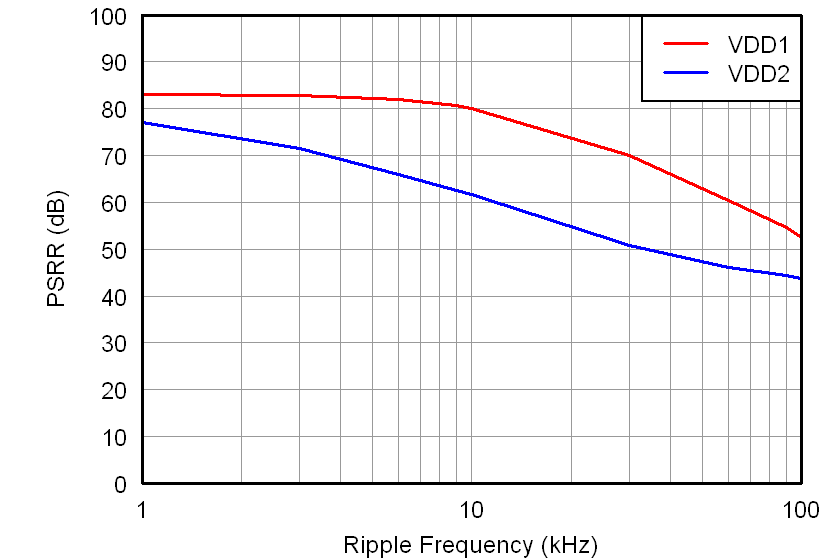
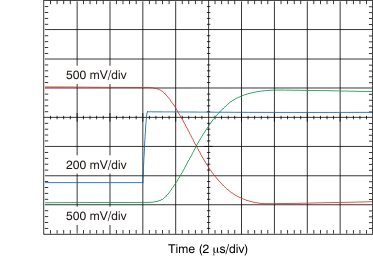
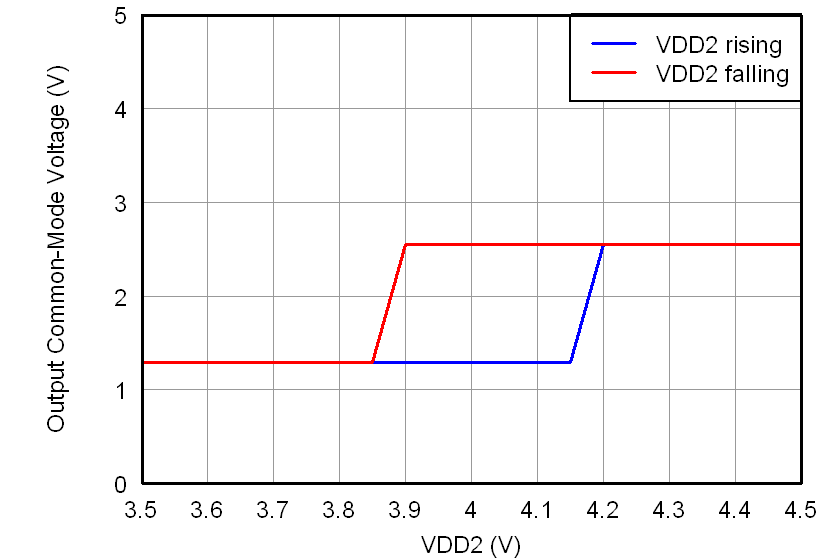
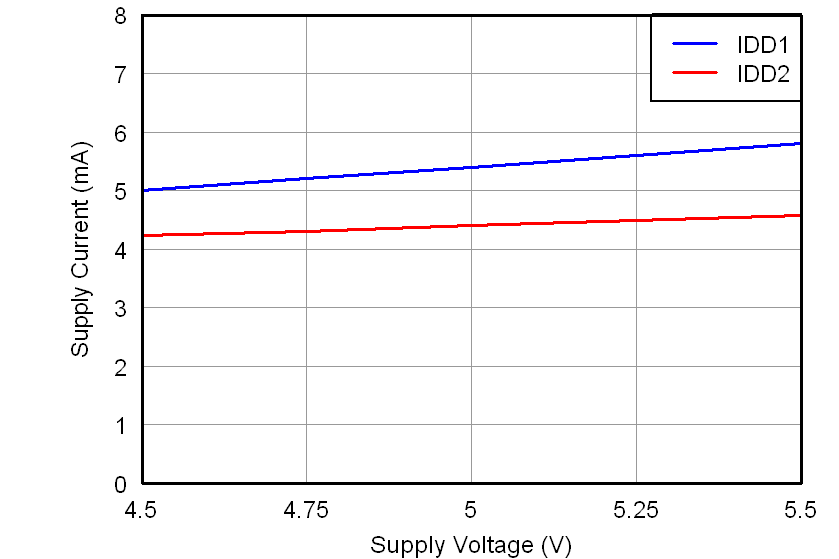
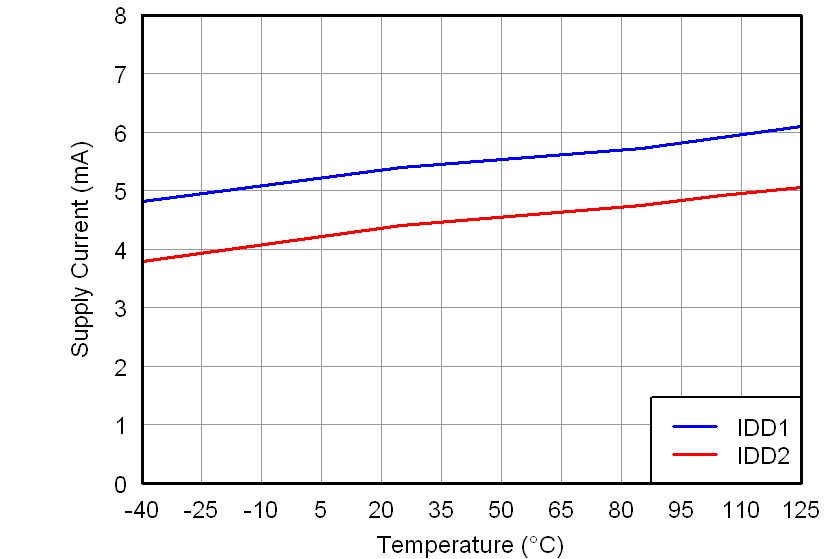
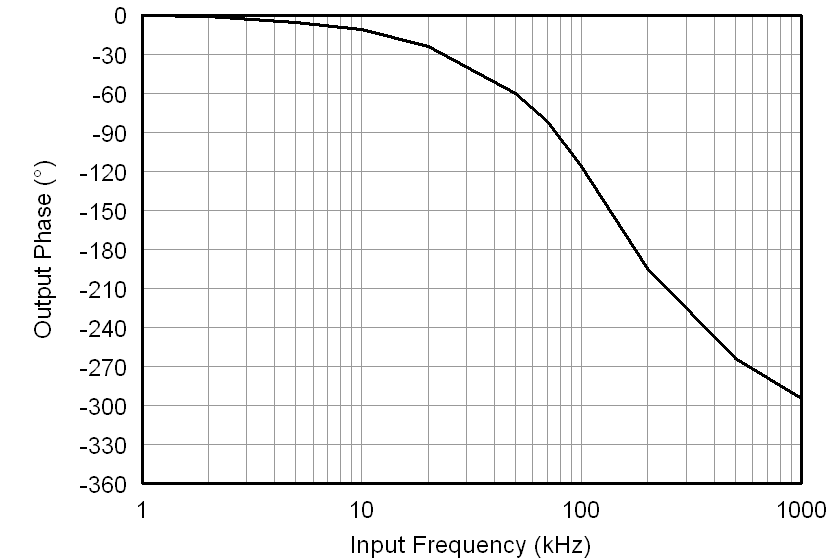
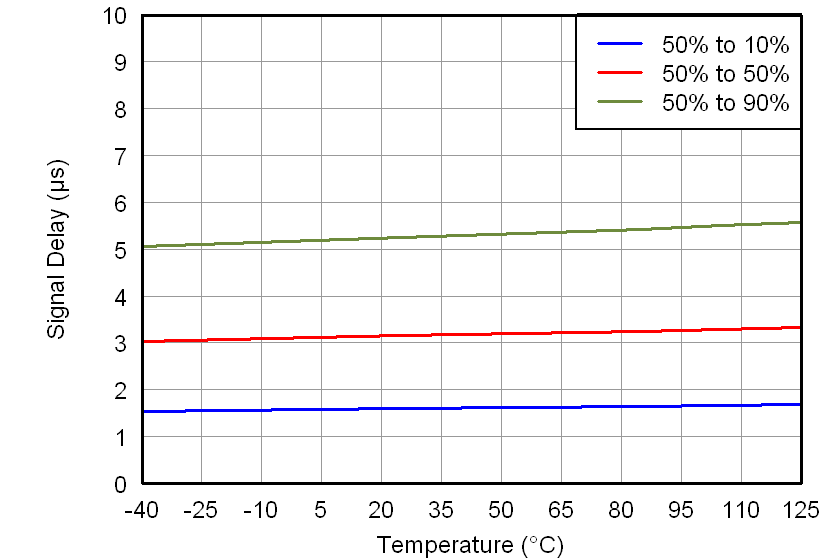
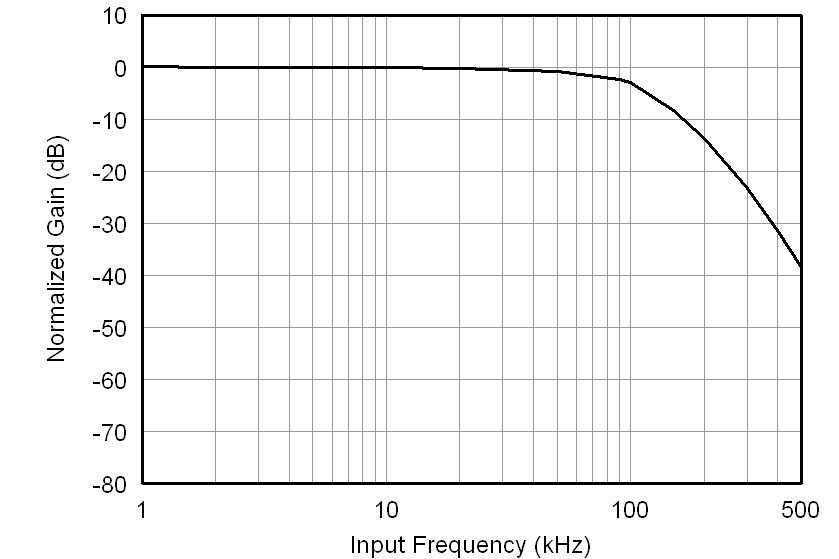
All minimum/maximum specifications at TA = –40°C to 105°C and within the specified voltage range, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = 25°C, VDD1 = 5 V, and VDD2 = 3.3 V.6.6 Typical Characteristics
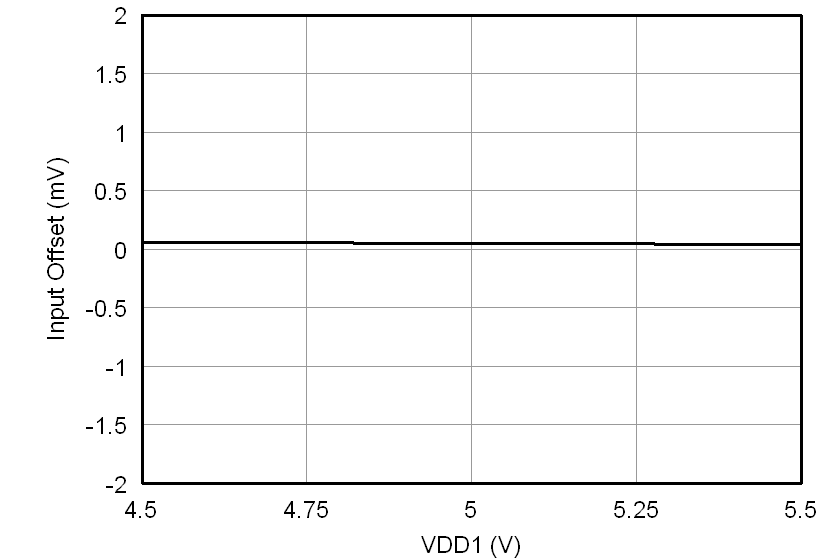
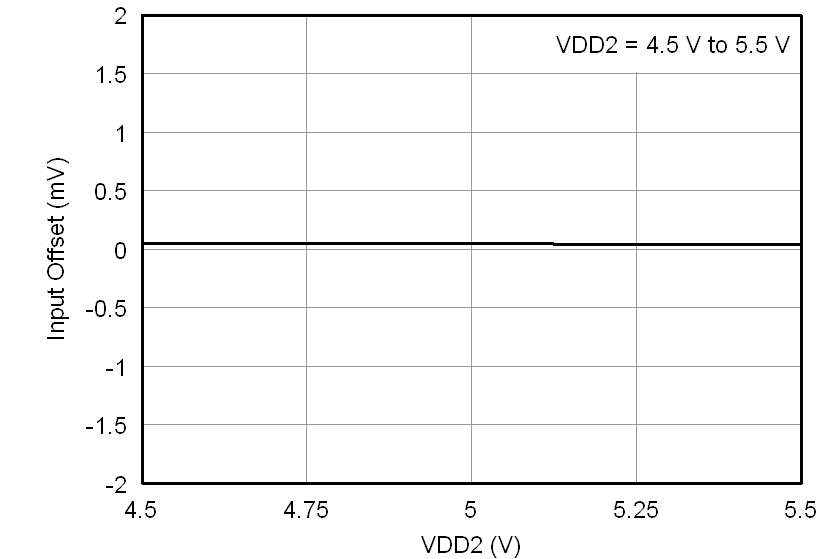
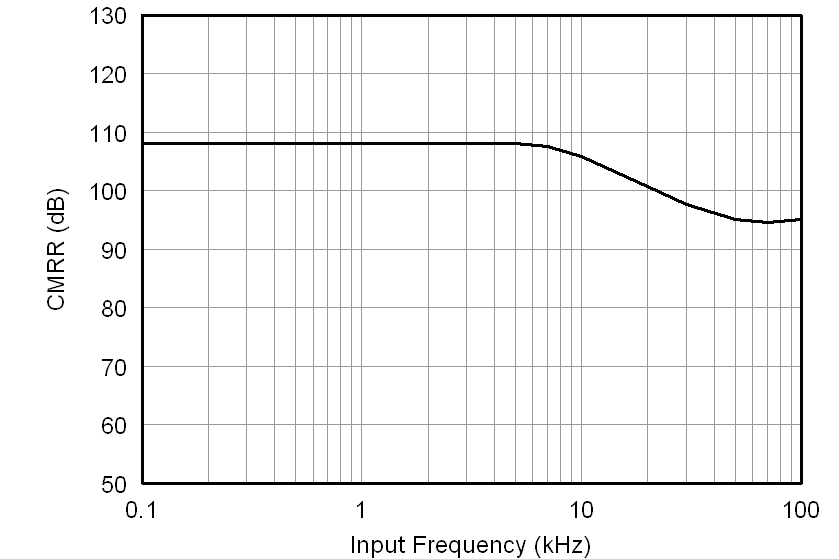
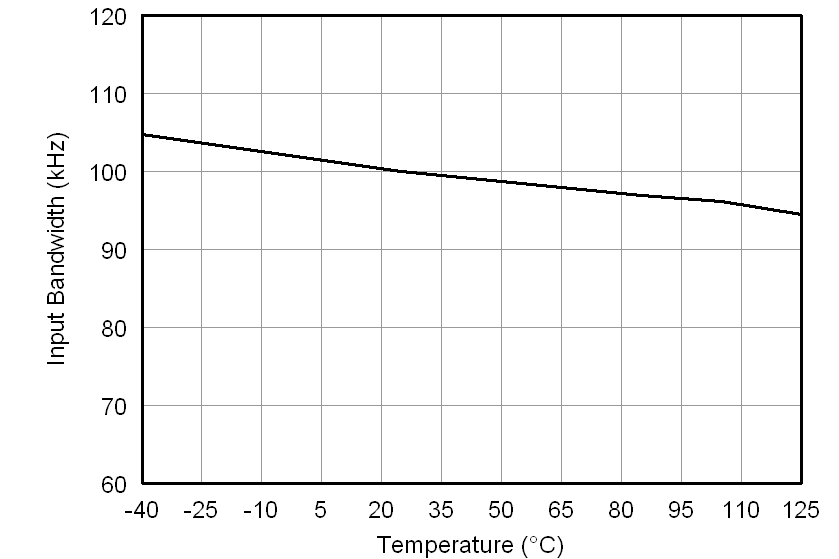
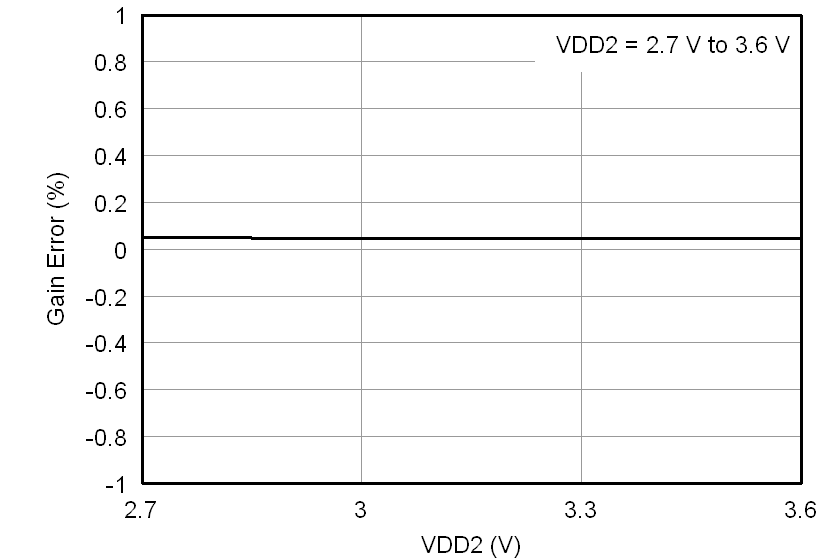
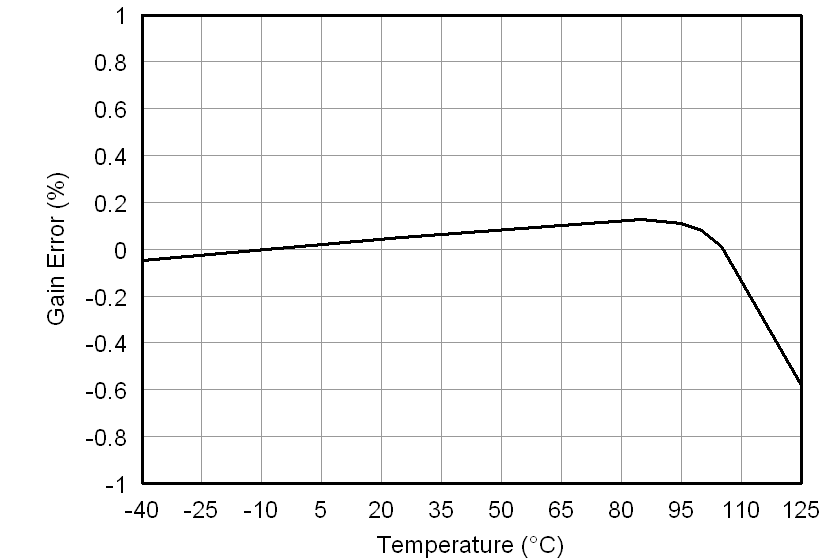
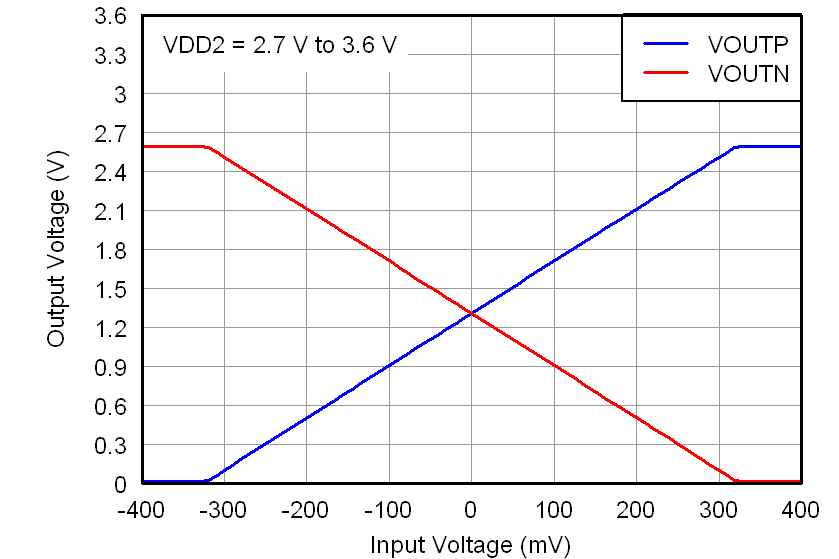
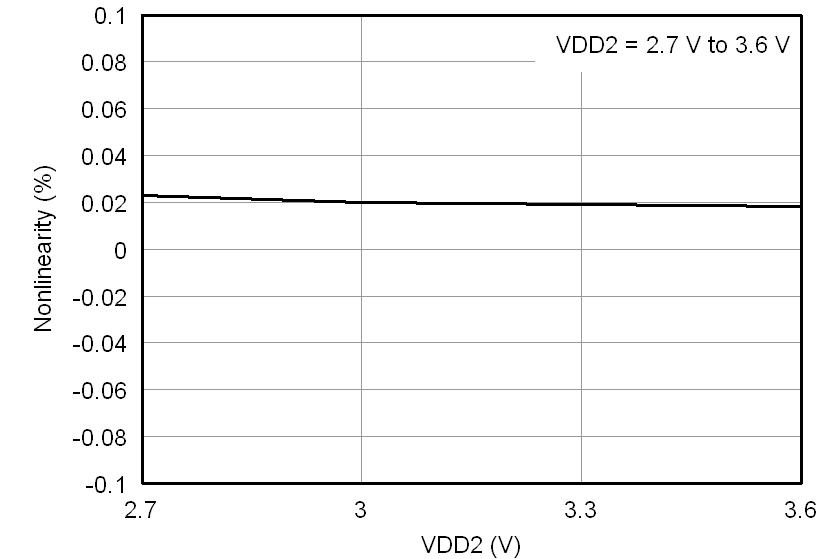
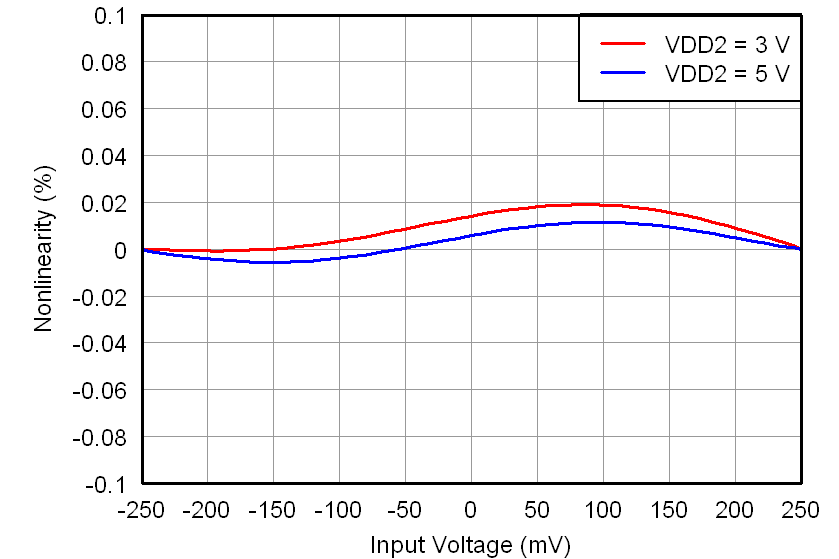
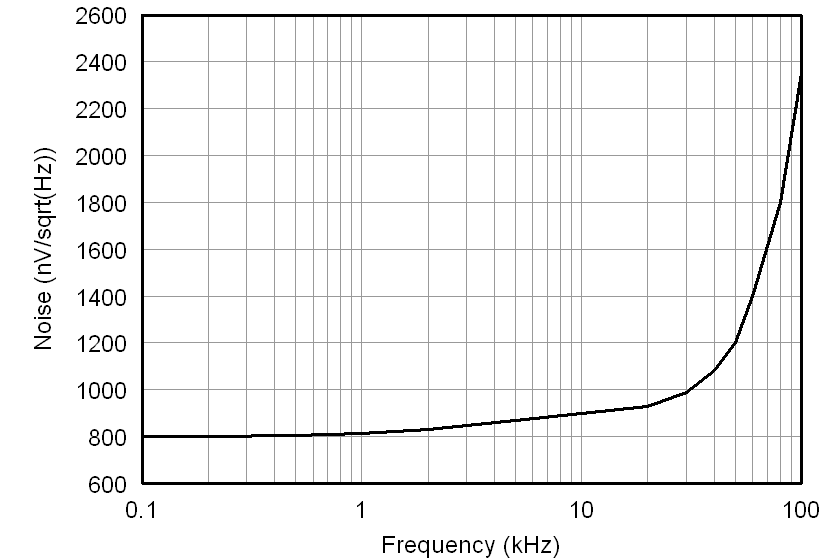
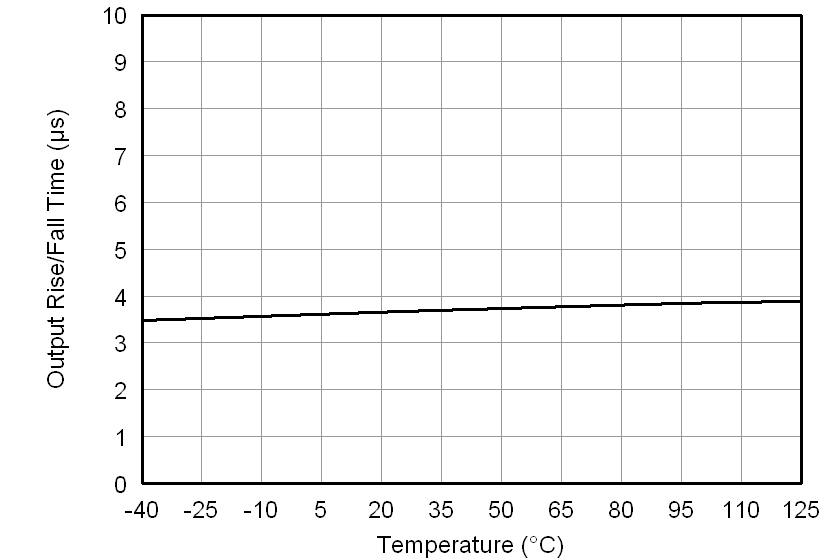
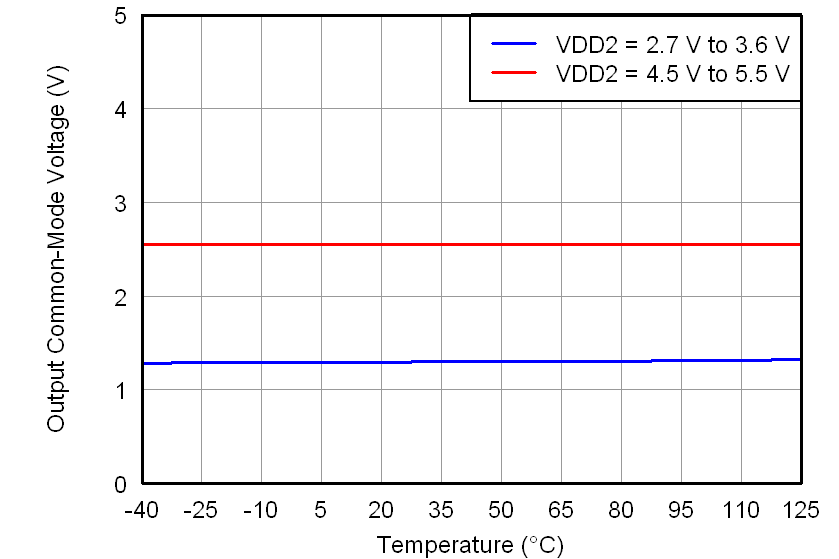
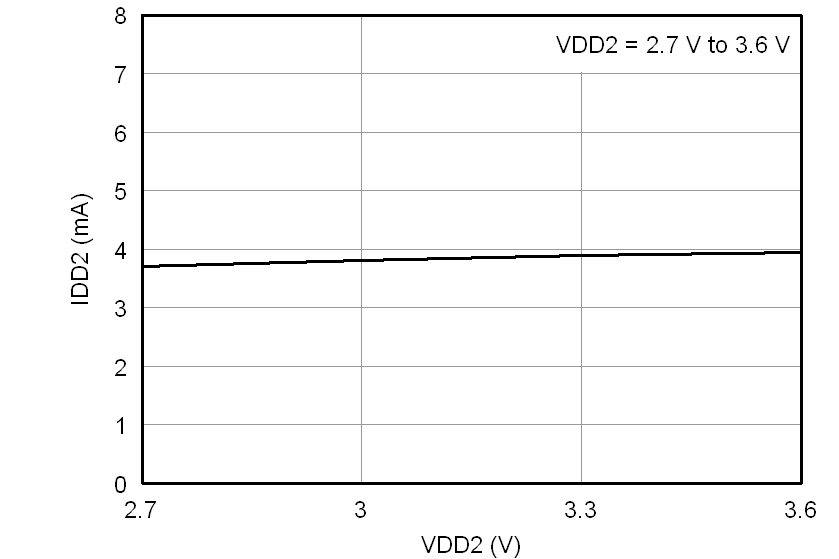
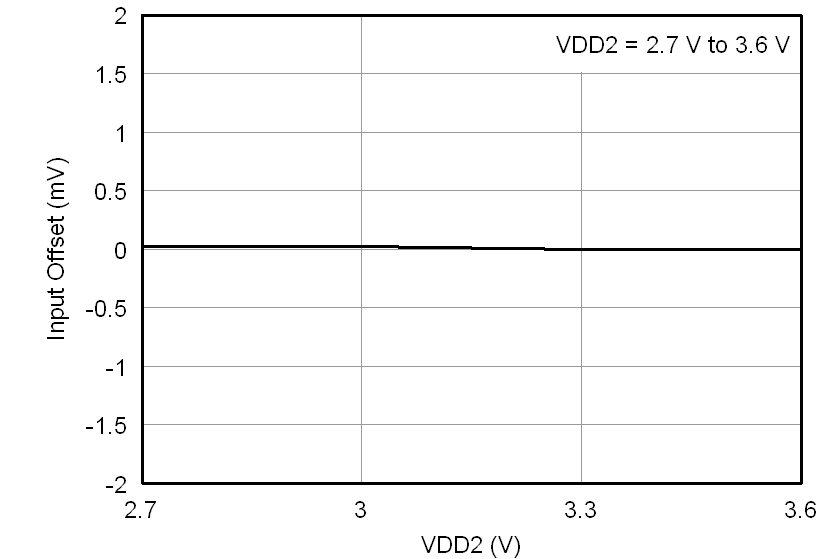
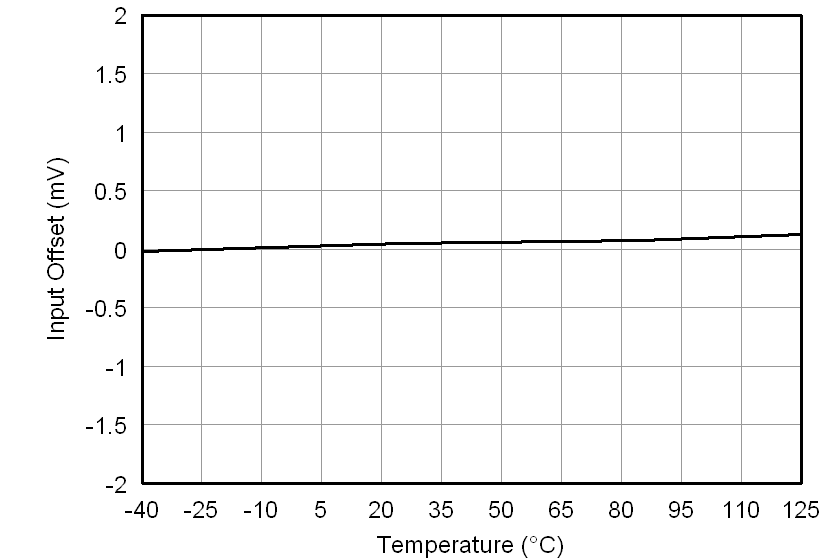
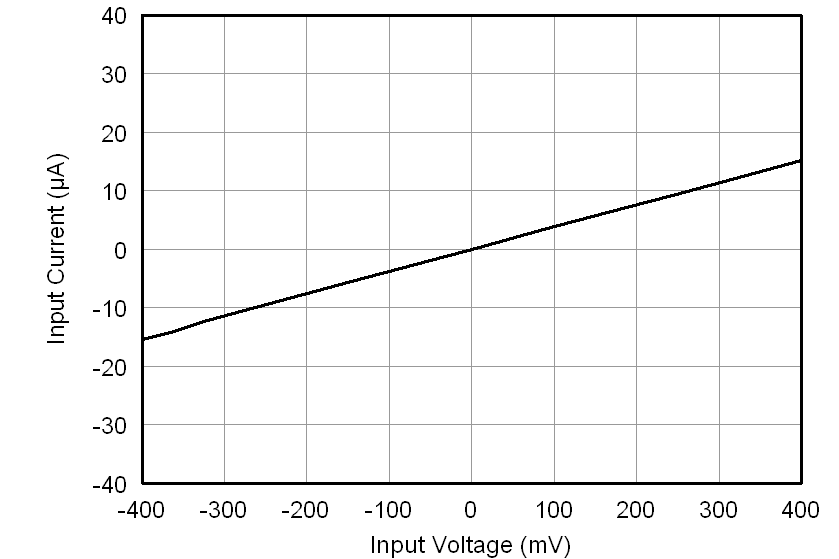
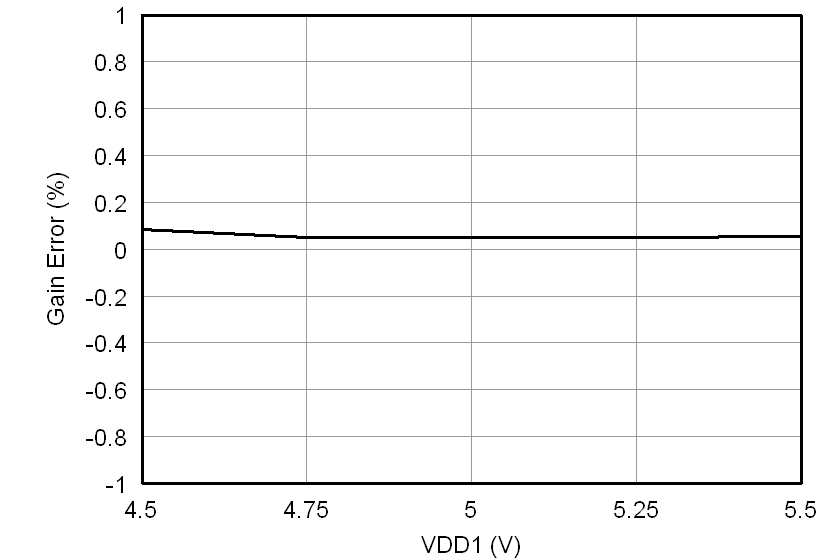
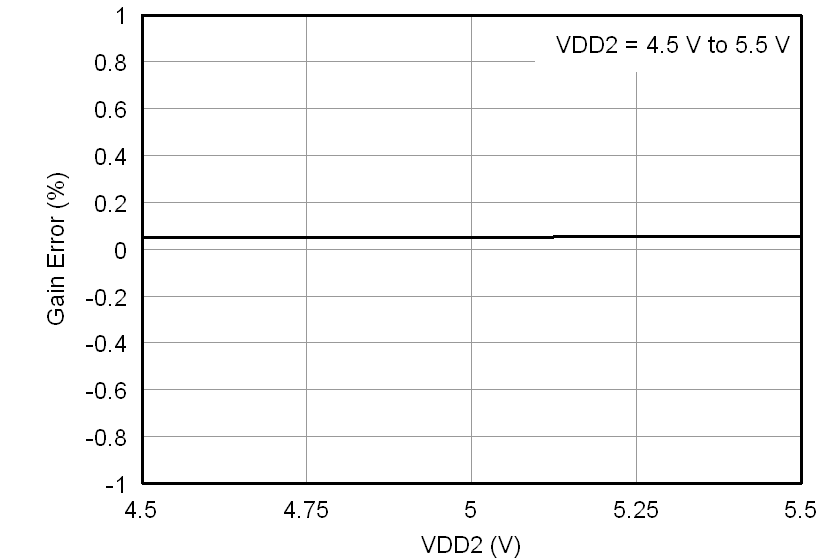
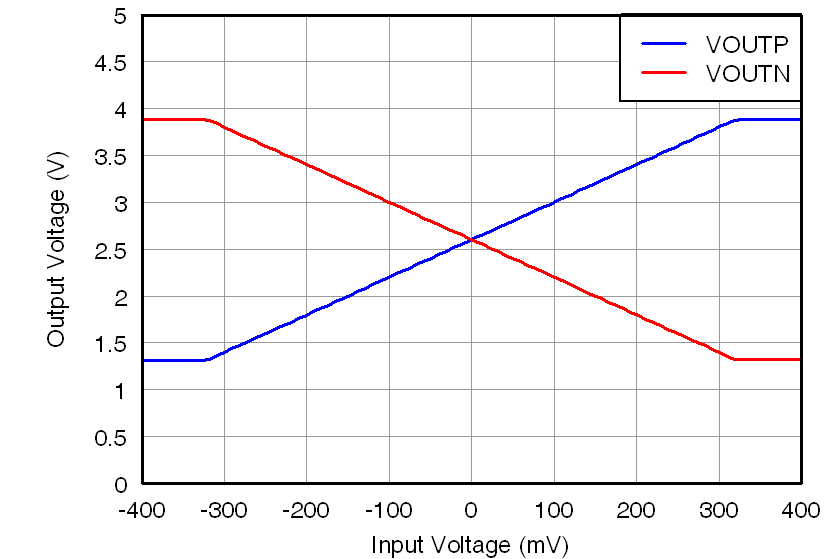
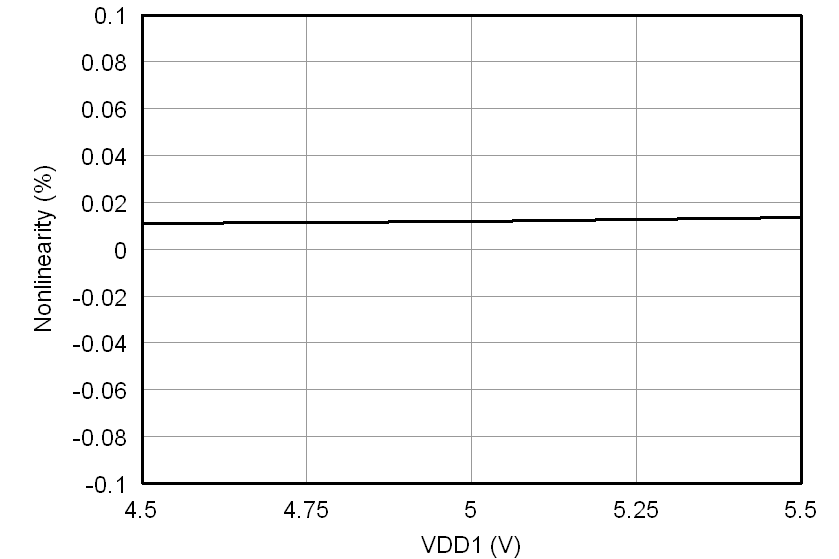
At VDD1 = VDD2 = 5 V, VINP = –250 mV to 250 mV, and VINN = 0 V, unless otherwise noted.