ZHCSR80A June 2009 – January 2023 AMC6821-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.2 Feature Description
- 8.3 Device Functional Modes
- 8.4 Programming
- 8.5 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.2 Temperature Sensor
The AMC6821-Q1 has an integrated temperature sensor (shown in Figure 8-2) to measure the ambient temperature, and one remote diode sensor (such as a Pentium thermal diode) input to measure external (CPU) temperature. The measurement relies on the characteristics of a semiconductor junction operation at a fixed current level. The forward voltage of the diode (VBE) depends on the current through it and the ambient temperature. The change in VBE when the diode is operated at two different currents, I1 and I2, is shown in Equation 1:
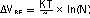
where
- k is Boltzmann’s constant,
- q is the charge of the carrier,
- T is the absolute temperature in degrees Kelvin, and
- N is the ratio of the two currents.
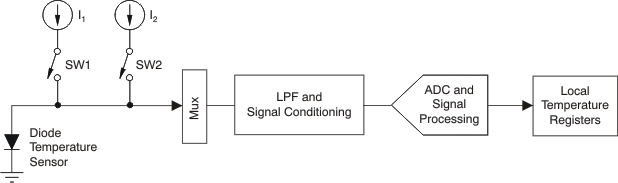 Figure 8-2 Integrated Local Temperature Sensor
Figure 8-2 Integrated Local Temperature SensorThe remote sensing transistor can be a substrate transistor built within the microprocessor (as in a Pentium-IV), or a discrete small-signal type transistor. This architecture is shown in Figure 8-3. The internal bias diode biases the IN– terminal above ground to prevent the ground noise from interfering with the measurement. An external capacitor (up to 1000pF) may be placed between IN+ and IN– to further reduce the noise from interfering.
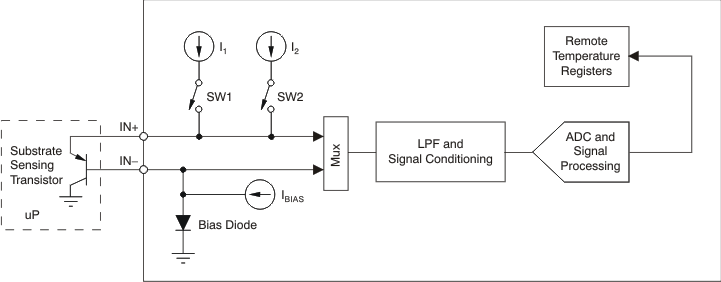 Figure 8-3 Remote Temperature Sensor
Figure 8-3 Remote Temperature SensorThe analog sensing signal is pre-processed by a low-pass filter and signal conditioning circuitry, then digitized by the ADC. The resulting digital signal is further processed by the digital filter and processing unit. The final result is stored in the local temperature data register and remote temperature data register, respectively. The eight MSBs are stored in the corresponding Temp-DATA-HByte register, and the three LSBs are stored in the Temp-DATA-LByte register. Refer to the Temperature Data Registers section for details.
The format of the final result is in two’s complement; see Table 8-1. It should be noted that the device measures the temperature from –40°C to +125°C, although the code represents temperature from –128°C to +127°C.