ZHCSR80A June 2009 – January 2023 AMC6821-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.2 Feature Description
- 8.3 Device Functional Modes
- 8.4 Programming
- 8.5 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.8.2 Fan Spin-Up
The PWM duty cycle controls the cooling fan speed. To spin up a fan from a stopped state or under-speed status, the spin-up process is applied to overcome the fan inertia. During the first third of spin-up, the duty cycle of the PWM gradually increases from 33.3% to 100%, and then maintains at 100% through the rest of the process. At the end of the spin-up process, the duty cycle is adjusted to 33.3%. After starting, the fan speed is controlled normally. Figure 8-14 shows the spin-up process. The bits [STIME2:STIME0] (bits 2:0 of 0x20) define the spin-up time, from 0.2 seconds to 8 seconds, as shown in Table 8-3. Fan speed is monitored immediately after the spin-up process.
Spin-up is disabled by setting the FSPD bit of the Fan Characteristics Register to '1'. If disabled, the spin-up process is not applied when the fan stops or an RPM is detected below the minimum speed. The TACH low limit register defines the minimum speed. After power-on or reset, the FSPD bit is cleared and the spin-up is always performed, regardless of the state of the FANS bit (bit 1 of 0x02).
Note that no FANS (fan-slow) detections are performed during spin-up. This bit is cleared ('0') only after reading it, and reasserts '1' in the next monitoring if a fan-slow condition is detected. After spin-up, FANS is set ('1') even if the TACH data are less than the TACH low limit until the flag is read.
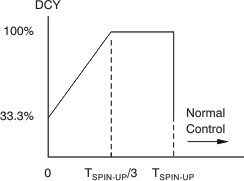 Figure 8-14 Spin-Up
Process
Figure 8-14 Spin-Up
Process| STIME2 | STIME1 | STIME0 | SPIN-UP TIME (SECONDS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.4 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.6 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 (default) |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 |