ZHCSDC6D November 2014 – February 2018 AMC7836
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: DAC
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: ADC and Temperature Sensor
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 6.8 Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: DAC
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics: ADC
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics: Reference
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics: Temperature Sensor
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 Interface Configuration: Address 0x00 – 0x02
- 7.6.2
Device Identification: Address 0x03 – 0x0D
- 7.6.2.1 Chip Type Register (address = 0x03) [reset = 0x08]
- 7.6.2.2 Chip ID Low Byte Register (address = 0x04) [reset = 0x36]
- 7.6.2.3 Chip ID High Byte Register (address = 0x05) [reset = 0x0C]
- 7.6.2.4 Version ID Register (address = 0x06) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.5 Manufacturer ID Low Byte Register (address = 0x0C) [reset = 0x51]
- 7.6.2.6 Manufacturer ID High Byte Register (address = 0x0D) [reset = 0x04]
- 7.6.3 Register Update (Buffered Registers): Address 0x0F
- 7.6.4
General Device Configuration: Address 0x10 through 0x17
- 7.6.4.1 ADC Configuration Register (address = 0x10) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.4.2 False Alarm Configuration Register (address = 0x11) [reset = 0x70]
- 7.6.4.3 GPIO Configuration Register (address = 0x12) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.4.4 ADC MUX Configuration 0 Register (address = 0x13) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.4.5 ADC MUX Configuration 1 Register (address = 0x14) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.4.6 ADC MUX Configuration 2 Register (address = 0x15) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.4.7 DAC Clear Enable 0 Register (address = 0x18) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.4.8 DAC Clear Enable 1 Register (address = 0x19) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.5 DAC Clear and ALARMOUT Source Select: Address 0x1A through 0x1D
- 7.6.6 DAC Range: Address 0x1E
- 7.6.7
ADC and Temperature Data: Address 0x20 through 0x4B
- 7.6.7.1 ADCn-Data (Low Byte) Register (address = 0x20 through 0x49) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.7.2 ADCn-Data (High Byte) Register (address = 0x20 through 0x49) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.7.3 Temperature Data (Low Byte) Register (address = 0x4A) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.7.4 Temperature Data (High Byte) Register (address = 0x4B) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.8 DAC Data: Address 0x50 through 0x6F
- 7.6.9 Status Registers: Address 0x70 through 0x72
- 7.6.10 GPIO: Address 0x7A
- 7.6.11
Out-Of-Range ADC Thresholds: Address 0x80 through 0x93
- 7.6.11.1 ADCn-Upper-Thresh (Low Byte) Register (address = 0x80 through 0x93) [reset = 0xFF]
- 7.6.11.2 ADCn-Upper-Thresh (High Byte) Register (address = 0x80 through 0x93) [reset = 0x0F]
- 7.6.11.3 ADCn-Lower-Thresh (Low Byte) Register (address = 0x80 through 0x93) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.11.4 ADCn-Lower-Thresh (High Byte) Register (address = 0x80 through 0x93) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.11.5 LT-Upper-Thresh (Low Byte) Register (address = 0x94) [reset = 0xFF]
- 7.6.11.6 LT-Upper-Thresh (High Byte) Register (address = 0x95) [reset = 0x07]
- 7.6.11.7 LT-Lower-Thresh (Low Byte) Register (address = 0x96) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.11.8 LT-Lower-Thresh (High Byte) Register (address = 0x97) [reset = 0x08]
- 7.6.12 Alarm Hysteresis Configuration: Address 0xA0 and 0xA5
- 7.6.13
Clear and Power-Down Registers: Address 0xB0 through 0XB4
- 7.6.13.1 DAC Clear 0 Register (address = 0xB0) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.13.2 DAC Clear 1 Register (address = 0xB1) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.13.3 Power-Down 0 Register (address = 0xB2) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.13.4 Power-Down 1 Register (address = 0xB3) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.13.5 Power-Down 2 Register (address = 0xB4) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.14 ADC Trigger: Address 0xC0
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.1.2 Current Sensing Applications
In applications that require current sensing of the power amplifier, an external high-side current sense amplifier can be added and configured to the unipolar ADC inputs. Figure 117 shows this design.
The LMP8480 device is a precision current sense device that amplifies the small differential voltage developed across a current-sense resistor in the presence of high input common-mode voltages. The LMP8480 device accepts input signals with a common-mode voltage range from 4 V to 76 V with a bandwidth of 270 kHz. The LMP8480 device offers different fixed gain settings. The optimal gain setting is dependent on the accuracy requirement of the application. To maintain precision over temperature, the output of the LMP8480 device should be directly connected to the AMC7836 unipolar ADC inputs. If the output range of the LMP8480 device is scaled by a voltage divider, as shown in Figure 117, an output amplifier may be required to drive the ADC unipolar input to ensure a low impedance source. If the series resistance, in this case R4, is low enough then the buffer may not be required because the LMP8480 device is capable of driving the input of the AMC7836 unipolar ADC channel.
NOTE
The external resistors will cause some small error because of temperature drift and the input bias current of the operation amplifier.
Figure 117 also shows a simple method to ensure proper power sequencing of the power amplifier by adding a series PMOS transistor to the PA drain terminal. The activation of the PMOS transistor connects the PAVDD voltage supply to the drain pin of the power amplifier. The PMOS transistor is driven with a voltage divider that swings from the PAVDD voltage to PAVDD × (R2 / (R1 + R2)). The NMOS shown in Figure 117 is connected to a microcontroller output that controls the state of the PMOS transistor.
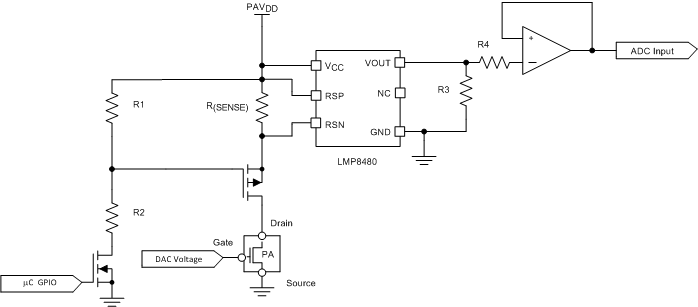 Figure 117. Current-Sense Application With PMOS ON and OFF
Figure 117. Current-Sense Application With PMOS ON and OFF