ZHCSFZ8B April 2013 – December 2016
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用范围
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Device Power Up
- 8.3.2 Power Path Management
- 8.3.3 Battery Charging Management
- 8.3.4 Status Outputs (PG, STAT, and INT)
- 8.3.5 Protections
- 8.3.6 Serial Interface
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Register Map
- 8.5.1
I2C Registers
- 8.5.1.1 Input Source Control Register REG00 (reset = 00111000, or 3D)
- 8.5.1.2 Power-On Configuration Register REG01 (reset = 00011011, or 1B)
- 8.5.1.3 Charge Current Control Register REG02 (reset = 00100000, or 20)
- 8.5.1.4 Pre-Charge/Termination Current Control Register REG 03 (reset = 00010001, or 11)
- 8.5.1.5 Charge Voltage Control Register REG04 (reset = 10011010, or 9A)
- 8.5.1.6 Charge Termination/Timer Control Register REG05 (reset = 10011010, or 9A)
- 8.5.1.7 IR Compensation / Thermal Regulation Control Register REG06 (reset = 00000011, or 03)
- 8.5.1.8 Misc Operation Control Register REG07 (reset = 01001011, or 4B)
- 8.5.1.9 System Status Register REG08
- 8.5.1.10 Fault Register REG09
- 8.5.1.11 Vender / Part / Revision Status Register REG0A
- 8.5.1
I2C Registers
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage range (with respect to GND) | VBUS | –2 | 20 | V |
| PMID, STAT, PG | –0.3 | 20 | V | |
| BTST | –0.3 | 26 | V | |
| SW | –2 | 20 | V | |
| BAT, SYS (converter not switching) | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| SDA, SCL, INT, OTG, ILIM, REGN, TS1, TS2, CE, PSEL | –0.3 | 7 | V | |
| BTST TO SW | –0.3 | 7 | V | |
| PGND to GND | –0.3 | 0.3 | V | |
| Output sink current | INT, STAT, PG | 6 | mA | |
| Junction temperature | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | 1000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | 250 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage | 3.9 | 17(1) | V |
| IIN | Input current | 3 | A | |
| ISYS | Output current (SYS) | 4.5 | A | |
| VBAT | Battery voltage | 4.4 | V | |
| IBAT | Fast charging current | 4.5 | A | |
| Discharging current with internal MOSFET | 6 (continuous) 9 (peak) (up to 1 sec duration) |
A | ||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature range | –40 | 85 | °C |
(1) The inherent switching noise voltage spikes should not exceed the absolute maximum rating on either the BTST or SW pins. A tight layout minimizes switching noise.
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | bq24292i | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGE (VQFN) | |||
| 24 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 32.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 29.8 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 9.1 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.3 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 9.1 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 2.2 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report (SPRA953).
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
VVBUS_UVLOZ < VVBUS < VACOV and VVBUS > VBAT + VSLEEP, TJ = –40°C to 125°C and TJ = 25°C for typical values unless other noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUIESCENT CURRENTS | ||||||
| IBAT | Battery discharge current (BAT, SW, SYS) | VVBUS < VUVLO, VBAT = 4.2 V, leakage between BAT and VBUS | 5 | µA | ||
| High-Z Mode, or no VBUS, BATFET disabled (REG07[5] = 1), TJ = –40°C – 85°C | 12 | 20 | µA | |||
| High-Z Mode, or no VBUS, REG07[5] = 0, TJ = –40°C – 85°C | 32 | 55 | µA | |||
| IVBUS | Input supply current (VBUS) | VVBUS = 5 V, High-Z mode | 15 | 30 | µA | |
| VVBUS = 17 V, High-Z mode | 30 | 50 | µA | |||
| VVBUS > VUVLO, VVBUS > VBAT, converter not switching | 1.5 | 3 | mA | |||
| VVBUS > VUVLO, VVBUS > VBAT, converter switching, VBAT=3.2V, ISYS=0A | 4 | mA | ||||
| VVBUS > VUVLO, VVBUS > VBAT, converter switching, VBAT=3.8V, ISYS=0A | 15 | mA | ||||
| IOTGBOOST | Battery Discharge Current in boost mode | VBAT=4.2V, Boost mode, IVBUS = 0A, converter switching | 4 | mA | ||
| VBUS/BAT POWER UP | ||||||
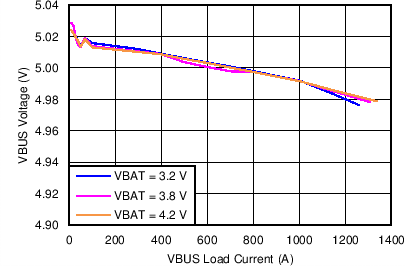
| VVBUS_OP | VBUS operating range | 3.9 | 17 | V | ||
| VVBUS_UVLOZ | VBUS for active I2C, no battery | VVBUS rising | 3.6 | V | ||
| VSLEEP | Sleep mode falling threshold | VVBUS falling, VVBUS-VBAT | 35 | 80 | 120 | mV |
| VSLEEPZ | Sleep mode rising threshold | VVBUS rising, VVBUS-VBAT | 170 | 250 | 350 | mV |
| VACOV | VBUS overvoltage rising threshold | VVBUS rising | 17.4 | 18 | V | |
| VACOV_HYST | VBUS Overvoltage Falling Hysteresis | VVBUS falling | 700 | mV | ||
| VBAT_UVLOZ | Battery for active I2C, no VBUS | VBAT rising | 2.3 | V | ||
| VBAT_DPL | Battery depletion threshold | VBAT falling | 2.4 | 2.6 | V | |
| VBAT_DPL_HY | Battery depletion rising hysteresis | VBAT rising | 200 | 260 | mV | |
| VVBUSMIN | Bad adapter detection threshold | VVBUS falling | 3.8 | V | ||
| IBADSRC | Bad adapter detection current source | 30 | mA | |||
| POWER PATH MANAGEMENT | ||||||
| VSYS_RANGE | Typical System regulation voltage | ISYS = 0A, Q4 off, VBAT up to 4.2 V, REG01[3:1]=101, VSYSMIN = 3.5 V |
3.5 | 4.35 | V | |
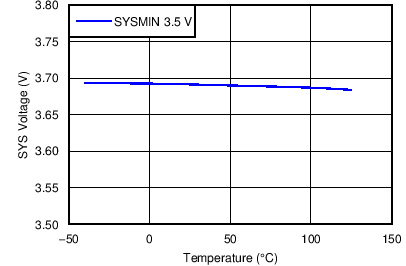
| VSYS_MIN | System voltage output | REG01[3:1]=101, VSYSMIN = 3.5 V | 3.55 | 3.65 | V | |
| RON(RBFET) | Internal top reverse blocking MOSFET on-resistance | Measured between VBUS and PMID | 23 | 38 | mΩ | |
| RON(HSFET) | Internal top switching MOSFET on-resistance between PMID and SW | TJ = –40°C – 85°C | 27 | 35 | mΩ | |
| TJ = –40°C – 125°C | 27 | 45 | ||||
| RON(LSFET) | Internal bottom switching MOSFET on-resistance between SW and PGND | TJ = –40°C – 85°C | 32 | 45 | mΩ | |
| TJ = –40°C – 125°C | 32 | 48 | ||||
| VFWD | BATFET forward voltage in supplement mode | BAT discharge current 10mA | 30 | mV | ||
| VSYS_BAT | SYS/BAT Comparator | VSYS falling | 90 | mV | ||
| VBATGD | Battery good comparator rising threshold | VBAT rising | 3.55 | V | ||
| VBATGD_HYST | Battery good comparator falling threshold | VBAT falling | 100 | mV | ||
| BATTERY CHARGER | ||||||
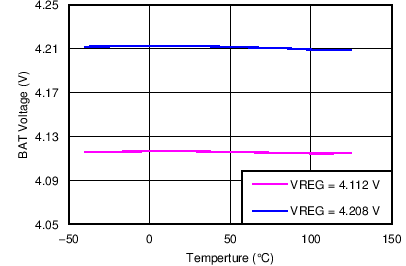
| VBAT_REG_ACC | Charge voltage regulation accuracy | VBAT = 4.112V and 4.208V | –0.5% | 0.5% | ||
| IICHG_REG_ACC | Fast charge current regulation accuracy | VBAT = 3.8V, ICHG = 1792mA, TJ = 25°C | –4% | 4% | ||
| VBAT = 3.8V, ICHG = 1792mA, TJ = –20°C – 125°C | –7% | 7% | ||||
| ICHG_20pct | Charge current with 20% option on | VBAT = 3.1V, ICHG = 104mA, REG02=03 | 75 | 150 | mA | |
| VBATLOWV | Battery LOWV falling threshold | Fast charge to precharge, REG04[1] = 1 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 2.9 | V |
| VBATLOWV_RISE | Battery LOWV rising threshold | Precharge to fast charge, REG04[1] = 1 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.1 | V |
| IPRECHG_ACC | Precharge current regulation accuracy | VBAT = 2.6V, ICHG = 256mA | –20% | 20% | ||
| ITERM_ACC | Termination current accuracy | ITERM = 256mA, ICHG = 960mA | –20% | 20% | ||
| VSHORT | Battery Short Voltage | VBAT falling | 2 | V | ||
| VSHORT_HYST | Battery Short Voltage hysteresis | VBAT rising | 200 | mV | ||
| ISHORT | Battery short current | VBAT<2.2V | 100 | mA | ||
| VRECHG | Recharge threshold below VBAT_REG | VBAT falling, REG04[0] = 0 | 100 | mV | ||
| RON_BATFET | SYS-BAT MOSFET on-resistance | TJ = 25°C | 12 | 15 | mΩ | |
| TJ = –40°C – 125°C | 12 | 20 | ||||
| INPUT VOLTAGE/CURRENT REGULATION | ||||||
| VINDPM_REG_ACC | Input voltage regulation accuracy | REG00[6:3]=0110 (4.36V) or 1011 (4.76V) | –2% | 2% | ||
| IUSB_DPM | USB Input current regulation limit, VBUS = 5V, current pulled from SW | USB100 | 85 | 100 | mA | |
| USB150 | 125 | 150 | mA | |||
| USB500 | 440 | 500 | mA | |||
| USB900 | 750 | 900 | mA | |||
| IADPT_DPM | Input current regulation accuracy | Input current limit 1.5A, REG00[2:0] = 101 | 1.30 | 1.55 | A | |
| IIN_START | Input current limit during system start up | VSYS<2.2V | 100 | mA | ||
| KILIM | IIN = KILIM/RILIM | IINDPM = 1.5A | 485 | 530 | A x Ω | |
| BAT OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION | ||||||
| VBATOVP | Battery overvoltage threshold | VBAT rising, as percentage of VBAT_REG | 104% | |||
| VBATOVP_HYST | Battery overvoltage hysteresis | VBAT falling, as percentage of VBAT_REG | 2% | |||
| THERMAL REGULATION AND THERMAL SHUTDOWN | ||||||
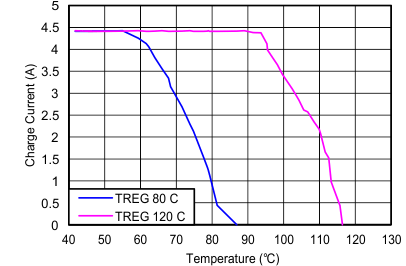
| TJunction_REG | Junction temperature regulation accuracy | REG06[1:0] = 11 | 115 | 120 | 125 | °C |
| TSHUT | Thermal shutdown rising temperature | Temperature increasing | 160 | °C | ||
| TSHUT_HYS | Thermal shutdown hysteresis | 30 | °C | |||
| COLD/HOT THERMISTER COMPARATOR | ||||||
| VLTF | Cold temperature threshold, TS pin voltage rising threshold | Charger suspends charge. As Percentage to VREGN | 73% | 73.5% | 74% | |
| VLTF_HYS | Cold temperature hysteresis, TS pin voltage falling | As Percentage to VREGN | 0.2% | 0.4% | 0.6% | |
| VHTF | Hot temperature TS pin voltage falling threshold | As Percentage to VREGN | 46.6% | 47.2% | 48.8% | |
| VTCO | Cut-off temperature TS pin voltage falling threshold | As Percentage to VREGN | 44.2% | 44.7% | 45.2% | |
| CHARGE OVERCURRENT COMPARATOR | ||||||
| IHSFET_OCP | HSFET overcurrent threshold | 5.3 | 7 | A | ||
| IBATFET_OCP | System over load threshold | 9 | A | |||
| CHARGE UNDERCURRENT COMPARATOR (CYCLE-BY-CYCLE) | ||||||
| VLSFET_UCP | LSFET charge undercurrent falling threshold | From sync mode to non-sync mode | 100 | mA | ||
| PWM OPERATION | ||||||
| DMAX | Maximum PWM duty cycle | 97% | ||||
| VBTST_REFRESH | Bootstrap refresh comparator threshold | VBTST-VSW when LSFET refresh pulse is requested, VBUS=5V | 3.6 | V | ||
| VBTST-VSW when LSFET refresh pulse is requested, VBUS>6V | 4.5 | |||||
| BOOST MODE OPERATION | ||||||
| VOTG_REG | OTG output voltage | I(VBUS) = 0 | 5 | V | ||
| VOTG_REG_ACC | OTG output voltage accuracy | I(VBUS) = 0 | –2.5% | 2% | ||
| IOTG | OTG mode output current | REG01[0] = 0 | 0.5 | A | ||
| REG01[0] = 1 | 1.3 | A | ||||
| VOTG_OVP | OTG overvoltage threshold | 5.3 | 5.5 | V | ||
| IOTG_ILIM | LSFET cycle-by-cycle current limit | 3.2 | 4.6 | A | ||
| IOTG_HSZCP | HSFET under current falling threshold | 100 | mA | |||
| IRBFET_OCP | RBFET overcurrent threshold | REG01[0] = 1 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 2.7 | A |
| REG01[0] = 0 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 1.8 | |||
| REGN LDO | ||||||
| VREGN | REGN LDO output voltage | VVBUS = 10V, IREGN = 40mA | 5.6 | 6 | 6.4 | V |
| VVBUS = 5V, IREGN = 20mA | 4.75 | 4.8 | V | |||
| IREGN | REGN LDO current limit | VVBUS = 10V, VREGN = 3.8V | 50 | mA | ||
| LOGIC I/O PIN CHARACTERISTICS (OTG, CE, PSEL, STAT, PG) | ||||||
| VILO | Input low threshold | 0.4 | V | |||
| VIH | Input high threshold | 1.3 | V | |||
| VOUT_LO | Output low saturation voltage | Sink current = 5 mA | 0.4 | V | ||
| IBIAS | High level leakage current | Pull up rail 1.8V | 1 | µA | ||
| I2C INTERFACE (SDA, SCL, INT) | ||||||
| VIH | Input high threshold level | VPULLUP = 1.8V, SDA and SCL | 1.3 | V | ||
| VIL | Input low threshold level | VPULLUP = 1.8V, SDA and SCL | 0.4 | V | ||
| VOL | Output low threshold level | Sink current = 5mA | 0.4 | V | ||
| IBIAS | High-level leakage current | VPULLUP = 1.8V, SDA and SCL | 1 | µA | ||
7.6 Timing Requirements
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBUS/BAT POWER UP | ||||||
| tBADSRC | Bad source detection duration | 30 | ms | |||
| BOOST MODE OPERATION | ||||||
| tOTG_DLY | OTG mode enable delay | I(VBUS) = 0 From OTG pin high to VBUS=VOTG_REG Specified by Design |
22 | 50 | ms | |
| tOTG_OCP_OFF | OTG mode overcurrent protection off cycle time | 32 | ms | |||
| tOTG_OCP_ON | OTG mode overcurrent protection on cycle time | 100 | µs | |||
| DIGITAL CLOCK AND WATCHDOG TIMER | ||||||
| fHIZ | Digital crude clock | REGN LDO disabled | 15 | 35 | 50 | kHz |
| fDIG | Digital clock | REGN LDO enabled | 1300 | 1500 | 1700 | kHz |
| tWDT | Watchdog timer | REGN LDO enabled REG05[5:4]=11 | 136 | 160 | s | |
| I2C INTERFACE (SDA, SCL, INT) | ||||||
| fSCL | SCL clock frequency | 400 | kHz | |||
7.7 Switching Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BATTERY CHARGER | ||||||
| tRECHG | Recharge deglitch time | VBAT falling, REG04[0]=0 | 20 | ms | ||
| BAT OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION | ||||||
| tBATOVP | Battery overvoltage deglitch time to disable charge | 1 | µs | |||
| THERMAL REGULATION AND THERMAL SHUTDOWN | ||||||
| Thermal shutdown rising deglitch | Temperature increasing delay | 1 | ms | |||
| Thermal shutdown falling deglitch | Temperature decreasing delay | 1 | ms | |||
| PWM OPERATION | ||||||
| FSW | PWM Switching frequency, and digital clock | 1300 | 1500 | 1700 | kHz | |
| COLD/HOT THERMISTER COMPARATOR | ||||||
| Deglitch time for temperature out of range detection | VTS > VLTF, or VTS < VTCO, or VTS < VHTF | 10 | ms | |||
7.8 Typical Characteristics
Table 1. Tables of Figures
| FIGURE NO. | |
|---|---|
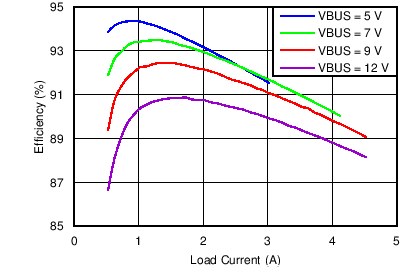
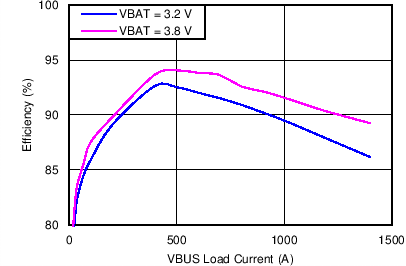
| Charging Efficiency vs. Charging Current | Figure 1 |
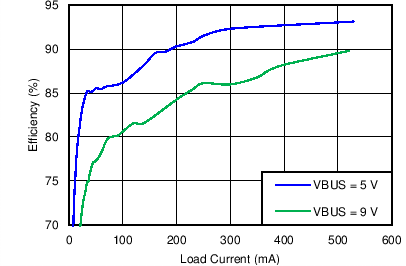
| System Light Load Efficiency vs System Load current | Figure 2 |
| Boost Mode Efficiency vs VBUS Load Current | Figure 3 |
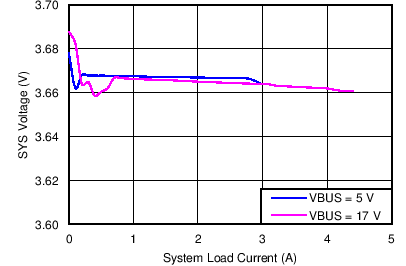
| SYS Voltage Regulation vs System Load | Figure 4 |
| Boost Mode VBUS Voltage Regulation vs VBUS Load Current | Figure 5 |
| SYS Voltage vs Temperature | Figure 6 |
| BAT Voltage vs Temperature | Figure 7 |
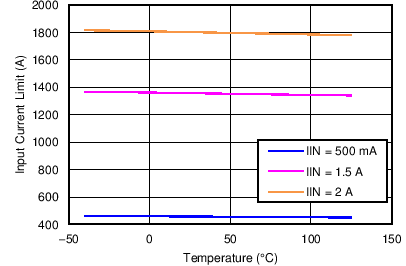
| Input Current Limit vs Temperature | Figure 8 |
| Charge Current vs Temperature | Figure 9 |