SLUSA49C April 2010 – June 2015
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Battery Voltage Regulation
- 8.3.2 Battery Current Regulation
- 8.3.3 Input Adapter Current Regulation
- 8.3.4 Precharge
- 8.3.5 Charge Termination, Recharge, and Safety Timer
- 8.3.6 Power Up
- 8.3.7 Enable and Disable Charging
- 8.3.8 System Power Selector
- 8.3.9 Automatic Internal Soft-Start Charger Current
- 8.3.10 Converter Operation
- 8.3.11 Synchronous and Nonsynchronous Operation
- 8.3.12 Cycle-by-Cycle Charge Undercurrent Protection
- 8.3.13 Input Overvoltage Protection (ACOV)
- 8.3.14 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 8.3.15 Battery Overvoltage Protection
- 8.3.16 Cycle-by-Cycle Charge Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.17 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 8.3.18 Temperature Qualification and JEITA Guideline
- 8.3.19 Timer Fault Recovery
- 8.3.20 PG Output
- 8.3.21 CE (Charge Enable)
- 8.3.22 Charge Status Outputs
- 8.3.23 Battery Detection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RGE|24
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RGE|24
订购信息
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)(2)(3)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | VCC, ACP, ACN, SRP, SRN, BATDRV, ACDRV, CE, STAT1, STAT2, PG | –0.3 | 33 | V | |
| PH | –2 | 36 | |||
| VFB | –0.3 | 16 | |||
| REGN, LODRV, ACSET, TS, TTC | –0.3 | 7 | |||
| BTST, HIDRV with respect to GND | –0.3 | 39 | |||
| VREF, ISET1, ISET2 | –0.3 | 3.6 | |||
| Maximum difference voltage | ACP–ACN, SRP–SRN | –0.5 | 0.5 | V | |
| TJ | Junction temperature | –40 | 155 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –55 | 155 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages are with respect to GND if not specified. Currents are positive into, negative out of the specified terminal. Consult the Packaging section of the data sheet for thermal limitations and considerations of packages.
(3) Must have a series resistor between battery pack and VFB if battery-pack voltage is expected to be greater than 16 V. Usually the resistor-divider top resistor takes care of this.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage range | VCC, ACP, ACN, SRP, SRN, BATDRV, ACDRV, CE, STAT1, STAT2, PG | –0.3 | 28 | V | |
| PH | –2 | 30 | |||
| VFB | –0.3 | 14 | |||
| REGN, LODRV, ACSET, TS, TTC | –0.3 | 6.5 | |||
| BTST, HIDRV with respect to GND | –0.3 | 34 | |||
| ISET1, ISET2 | –0.3 | 3.3 | |||
| VREF | 0 | 3.3 | |||
| Maximum difference voltage | ACP–ACN, SRP–SRN | –0.2 | 0.2 | V | |
| TJ | Junction temperature | 0 | 125 | °C | |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | bq24616 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGE [VQFN] | |||
| 24 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 43 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 54.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 20 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.6 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 19 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 4 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
5 V ≤ VVCC ≤ 28 V, 0°C < TJ < 125°C, typical values are at TA = 25°C, with respect to GND (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPERATING CONDITIONS | ||||||
| VVCC_OP | VCC input voltage operating range | 5 | 28 | V | ||
| QUIESCENT CURRENTS | ||||||
| IBAT | Total battery discharge current (sum of currents into VCC, BTST, PH, ACP, ACN, SRP, SRN, VFB), VFB ≤ VFB_REG | VVCC < VSRN, VVCC > VUVLO (SLEEP) | 15 | μA | ||
| Battery discharge current (sum of currents into BTST, PH, SRP, SRN, VFB), VFB ≤ VFB_REG | VVCC > VSRN, VVCC > VUVLO CE = LOW | 5 | µA | |||
| VVCC > VSRN, VVCC > VVCCLOW CE = HIGH, charge done | 5 | µA | ||||
| IAC | Adapter supply current (current into VCC,ACP,ACN pin) | VVCC > VSRN, VVCC > VUVLO CE = LOW (IC quiescent current) | 1 | 1.5 | mA | |
| VVCC > VSRN, VVCC > VVCCLOW, CE = HIGH, charge done | 2 | 5 | ||||
| VVCC > VSRN, VVCC > VVCCLOW, CE = HIGH, charging, Qg_total = 20 nC | 25 | |||||
| CHARGE VOLTAGE REGULATION | ||||||
| VFB_REG | Feedback regulation voltage | VT3 < VTS < VT1 | 2.1 | V | ||
| VT4 < VTS < VT3 | 2.05 | |||||
| VT5 < VTS < VT4 | 2.025 | |||||
| Charge voltage regulation accuracy | TJ = 0 to 85°C | –0.5% | –0.5% | |||
| TJ = –40 to 125°C | –0.7% | –0.7% | ||||
| IVFB | Leakage current into VFB pin | VFB = 2.1 V, 2.05 V, 2.025 V | 100 | nA | ||
| CURRENT REGULATION – FAST-CHARGE | ||||||
| VISET1 | ISET1 voltage range | 2 | V | |||
| VIREG_CHG | SRP-SRN current-sense voltage range | VIREG_CHG = VSRP – VSRN | 100 | mV | ||
| KISET1 | Charge current set factor (amps of charge current per volt on ISET1 pin) | RSENSE = 10 mΩ | 5 | A/V | ||
| Charge current regulation accuracy | VIREG_CHG = 40 mV | –3% | 3% | |||
| VIREG_CHG = 20 mV | –4% | 4% | ||||
| VIREG_CHG = 5 mV | –25% | 25% | ||||
| VIREG_CHG = 1.5 mV (VSRN > 3.1 V) | –40% | 40% | ||||
| IISET1 | Leakage current into ISET1 pin | VISET1 = 2 V | 100 | nA | ||
| CURRENT REGULATION – PRECHARGE | ||||||
| VISET2 | ISET2 voltage range | 2 | V | |||
| KISET2 | Precharge current-set factor (amps of precharge current per volt on ISET2 pin) | RSENSE = 10 mΩ | 1 | A/V | ||
| Precharge current-regulation accuracy | VIREG_PRECH = 20 mV | –4% | 4% | |||
| VIREG_PRECH = 5 mV | –25% | 25% | ||||
| VIREG_PRECH = 1.5 mV (VSRN < 3.1 V) | –55% | 55% | ||||
| IISET2 | Leakage current into ISET2 pin | VISET2 = 2 V | 100 | nA | ||
| CHARGE TERMINATION | ||||||
| KTERM | Termination current-set factor (amps of termination current per volt on ISET2 pin) | RSENSE = 10 mΩ | 1 | A/V | ||
| Termination-current accuracy | VITERM = 20 mV | –4% | 4% | |||
| VITERM = 5 mV | –25% | 25% | ||||
| VITERM = 1.5 mV | –45% | 45% | ||||
| Deglitch time for termination (both edge) | 100 | ms | ||||
| tQUAL | Termination qualification time | VBAT> VRECH and ICHG< ITERM | 250 | ms | ||
| IQUAL | Termination qualification current | Discharge current once termination is detected | 2 | mA | ||
| INPUT CURRENT REGULATION | ||||||
| VACSET | ACSET voltage range | 2 | V | |||
| VIREG_DPM | ACP-ACN current sense voltage range | VIREG_DPM = VACP – VACN | 100 | mV | ||
| KACSET | Input current set factor (amps of input current per volt on ACSET pin) | RSENSE = 10 mΩ | 5 | A/V | ||
| IACSET | Input current regulation accuracy leakage current in to ACSET pin | VIREG_DPM = 40 mV | –3% | 3% | ||
| VIREG_DPM = 20 mV | –4% | 4% | ||||
| VIREG_DPM = 5 mV | –25% | 25% | ||||
| IISET1 | Leakage current in to ACSET pin | VACSET = 2 V | 100 | nA | ||
| INPUT UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT COMPARATOR (UVLO) | ||||||
| VUVLO | AC undervoltage rising threshold | Measure on VCC | 3.65 | 3.85 | 4 | V |
| VUVLO_HYS | AC undervoltage hysteresis, falling | 350 | mV | |||
| VCC LOWV COMPARATOR | ||||||
| Falling threshold, disable charge | Measure on VCC | 4.1 | V | |||
| Rising threshold, resume charge | 4.35 | 4.5 | V | |||
| SLEEP COMPARATOR (REVERSE DISCHARGING PROTECTION) | ||||||
| VSLEEP _FALL | SLEEP falling threshold | VVCC – VSRN to enter SLEEP | 40 | 100 | 150 | mV |
| VSLEEP_HYS | SLEEP hysteresis | 500 | mV | |||
| SLEEP rising delay | VCC falling below SRN, Delay to turn off ACFET | 1 | μs | |||
| SLEEP falling delay | VCC rising above SRN, Delay to turn on ACFET | 30 | ms | |||
| SLEEP rising shutdown deglitch | VCC falling below SRN, Delay to enter SLEEP mode | 100 | ms | |||
| SLEEP falling powerup deglitch | VCC rising above SRN, Delay to exit SLEEP mode | 30 | ms | |||
| ACN / SRN COMPARATOR | ||||||
| VACN-SRN_FALL | ACN to SRN falling threshold | VACN – VSRN to turn on BATFET | 100 | 200 | 310 | mV |
| VACN-SRN_HYS | ACN to SRN rising hysteresis | 100 | mV | |||
| ACN to SRN rising deglitch | VACN – VSRN > VACN-SRN_RISE | 2 | ms | |||
| ACN to SRN falling deglitch | VACN – VSRN < VACN-SRN_FALL | 50 | μs | |||
| BAT LOWV COMPARATOR | ||||||
| VLOWV | Precharge to fast-charge transition (LOWV threshold) | Measured on VFB pin, rising | 1.534 | 1.55 | 1.566 | V |
| VLOWV_HYS | LOWV hysteresis | 100 | mV | |||
| LOWV rising deglitch | VFB falling below VLOWV | 25 | ms | |||
| LOWV falling deglitch | VFB rising above VLOWV + VLOWV_HYS | 25 | ms | |||
| RECHARGE COMPARATOR | ||||||
| VRECHG | Recharge threshold (with-respect-to VREG) | Measured on VFB pin, falling | 35 | 50 | 65 | mV |
| Recharge rising deglitch | VFB decreasing below VRECHG | 10 | ms | |||
| Recharge falling deglitch | VFB decreasing above VRECHG | 10 | ms | |||
| BAT OVERVOLTAGE COMPARATOR | ||||||
| VOV_RISE | Overvoltage rising threshold | As percentage of VFB ,T1 – T5 | 104% | |||
| VOV_FALL | Overvoltage falling threshold | As percentage of VFB,T1 – T5 | 102% | |||
| INPUT OVERVOLTAGE COMPARATOR (ACOV) | ||||||
| VACOV | AC overvoltage rising threshold on VCC | 31.04 | 32 | 32.96 | V | |
| VACOV_HYS | AC overvoltage falling hysteresis | 1 | V | |||
| AC overvoltage deglitch (both edges) | Delay to changing the STAT pins | 1 | ms | |||
| AC overvoltage rising deglitch | Delay to turn off ACFET, disable charge | 1 | ms | |||
| AC overvoltage falling deglitch | Delay to turn on ACFET, resume charge | 20 | ms | |||
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN COMPARATOR | ||||||
| TSHUT | Thermal shutdown rising temperature | Temperature increasing | 145 | °C | ||
| TSHUT_HYS | Thermal shutdown hysteresis | 15 | °C | |||
| Thermal shutdown rising deglitch | Temperature increasing | 100 | μs | |||
| Thermal shutdown falling deglitch | Temperature decreasing | 10 | ms | |||
| THERMISTOR COMPARATOR | ||||||
| VT1 | T1 (0 °C) threshold, charge suspended below this temperature | VTS rising, as percentage of VVREF | 70.2% | 70.8% | 71.4% | |
| VT1-HYS | Charge back to ICHARGE/2 and VFB = 2.1 V above this temperature. | Hysteresis, VTS falling | 0.6% | |||
| VT2 | T2 (10 °C) threshold, charge back to ICHARGE/2 and VFB = 2.1 V below this temperature. | VTS rising, as percentage of VVREF | 68.0% | 68.6% | 69.2% | |
| VT2-HYS | Charge back to ICHARGE and VFB = 2.1 V above this temperature. | Hysteresis, VTS falling | 0.8% | |||
| VT3 | T3 (45 °C) threshold, charge back to ICHARGE and VFB = 2.05 V above this temperature. | VTS falling, as percentage of VVREF | 55.5% | 56.1% | 56.7% | |
| VT3-HYS | Charge back to ICHARGE and VFB = 2.1 V below this temperature. | Hysteresis, VTS rising | 0.8% | |||
| VT4 | T4 (50 °C) threshold, charge back to ICHARGE and VFB = 2.025 V above this temperature. | VTS falling, as percentage of VVREF | 53.2% | 53.7% | 54.2% | |
| VT4-HYS | Charge back to ICHARGE and VFB = 2.05 V below this temperature. | Hysteresis, VTS rising | 0.8% | |||
| VT5 | T5 (60 °C) threshold, charge suspended above this temperature. | VTS falling, as percentage of VVREF | 47.6% | 48.1% | 48.6% | |
| VT5-HYS | Charge back to ICHARGE and VFB = 2.025 V below this temperature. | Hysteresis, VTS rising | 1.2% | |||
| Deglitch time for temperature out-of-valid-charge-range detection | VTS < VT5 or VTS > VT1 | 400 | ms | |||
| Deglitch time for temperature in-valid-range detection | VTS > VT5 + VT5_HYS or VTS < VT1 - VT1_HYS | 20 | ms | |||
| Deglitch time for temperature detection above/below T2, T3, T4 threshold | 25 | ms | ||||
| Charge current when VTS between VT1 and VT2 range | ICHARGE/2 | |||||
| CHARGE OVERCURRENT COMPARATOR (CYCLE-BY-CYCLE) | ||||||
| VOC | Charge overcurrent falling threshold | Current rising in nonsynchronous mode, measure on V(SRP-SRN), VSRP < 2 V | 45.5 | mV | ||
| Current rising, as percentage of V(IREG_CHG), in synchronous mode, VSRP > 2.2V | 160% | |||||
| Charge overcurrent threshold floor | Minimum OCP threshold in synchronous mode, measure on V(SRP-SRN), VSRP > 2.2 V | 50 | mV | |||
| Charge overcurrent threshold ceiling | Maximum OCP threshold in synchronous mode, measure on V(SRP-SRN), VSRP > 2.2 V | 180 | mV | |||
| CHARGE UNDERCURRENT COMPARATOR (CYCLE-BY-CYCLE) | ||||||
| VISYNSET | Charge undercurrent falling threshold | Switch from SYNCH to NON-SYNCH, VSRP > 2.2 V | 1 | 5 | 9 | mV |
| BATTERY SHORTED COMPARATOR (BATSHORT) | ||||||
| VBATSHT | BAT short falling threshold, forced nonsynchronous mode | VSRP falling | 2 | V | ||
| VBATSHT_HYS | BAT short rising hysteresis | 200 | mV | |||
| VBATSHT_DEG | Deglitch on both edges | 1 | μs | |||
| LOW CHARGE CURRENT COMPARATOR | ||||||
| VLC | Low charge current (average) falling threshold to force into nonsynchronous mode | Measure on V(SRP-SRN) | 1.25 | mV | ||
| VLC_HYS | Low charge current, rising hysteresis | 1.25 | mV | |||
| VLC_DEG | Deglitch on both edge | 1 | μs | |||
| VREF REGULATOR | ||||||
| VVREF_REG | VREF regulator voltage | VVCC > VUVLO, (0–35 mA load) | 3.267 | 3.3 | 3.333 | V |
| IVREF_LIM | VREF current limit | VVREF = 0 V, VVCC > VUVLO | 35 | mA | ||
| REGN REGULATOR | ||||||
| VREGN_REG | REGN regulator voltage | VVCC > 10 V, CE = HIGH, (0–40 mA load) | 5.7 | 6 | 6.3 | V |
| IREGN_LIM | REGN current limit | VREGN = 0 V, VVCC > VUVLO, CE = HIGH | 40 | mA | ||
| TTC INPUT AND SAFETY TIMER | ||||||
| TPRECHG | Precharge safety timer range(1) | Precharge time before fault occurs | 1440 | 1800 | 2160 | s |
| TCHARGE | Fast-charge safety-timer range, with ±10% accuracy(1) | Tchg = CTTC × KTTC | 1 | 10 | h | |
| Fast-charge timer accuracy(1) | 0.01 μF ≤ CTTC ≤ 0.11 μF | –10% | 10% | |||
| KTTC | Timer multiplier | 5.6 | min/nF | |||
| TTC low threshold | VTTC below this threshold disables the safety timer and termination | 0.4 | V | |||
| TTC oscillator high threshold | 1.5 | V | ||||
| TTC oscillator low threshold | 1 | V | ||||
| TTC source/sink current | 45 | 50 | 55 | μA | ||
| BATTERY SWITCH (BATFET) DRIVER | ||||||
| RDS_BAT_OFF | BATFET turnoff resistance | VACN > 5 V | 150 | Ω | ||
| RDS_BAT_ON | BATFET turnon resistance | VACN > 5 V | 20 | kΩ | ||
| VBATDRV_REG | BATFET drive voltage | VBATDRV_REG = VACN – VBATDRV when VACN > 5 V and BATFET is on | 4.2 | 7 | V | |
| AC SWITCH (ACFET) DRIVER | ||||||
| RDS_AC_OFF | ACFET turnoff resistance | VVCC > 5 V | 30 | Ω | ||
| RDS_AC_ON | ACFET turnon resistance | VVCC > 5 V | 20 | kΩ | ||
| VACDRV_REG | ACFET drive voltage | VACDRV_REG = VVCC – VACDRV when VVCC > 5 V and ACFET is on | 4.2 | 7 | V | |
| AC / BAT MOSFET DRIVERS TIMING | ||||||
| Driver dead time | Dead time when switching between AC and BAT | 10 | μs | |||
| BATTERY DETECTION | ||||||
| tWAKE | Wake time | Maximum time charge is enabled | 500 | ms | ||
| IWAKE | Wake current | RSENSE = 10 mΩ | 50 | 125 | 200 | mA |
| tDISCHARGE | Discharge time | Maximum time discharge current is applied | 1 | sec | ||
| IDISCHARGE | Discharge current | 8 | mA | |||
| IFAULT | Fault current after a time-out fault | 2 | mA | |||
| VWAKE | Wake threshold (with respect to VREG) | Voltage on VFB to detect battery absent during wake | 50 | mV | ||
| VDISCH | Discharge threshold | Voltage on VFB to detect battery absent during discharge | 1.55 | V | ||
| PWM HIGH-SIDE DRIVER (HIDRV) | ||||||
| RDS_HI_ON | High-side driver (HSD) turnon resistance | VBTST – VPH = 5.5 V | 3.3 | 6 | Ω | |
| RDS_HI_OFF | HSD turnoff resistance | VBTST – VPH = 5.5 V | 1 | 1.3 | Ω | |
| VBTST_REFRESH | Bootstrap refresh comparator threshold voltage | VBTST – VPH when low-side refresh pulse is requested | 4 | 4.2 | V | |
| PWM LOW-SIDE DRIVER (LODRV) | ||||||
| RDS_LO_ON | Low-side driver (LSD) turnon resistance | 4.1 | 7 | Ω | ||
| RDS_LO_OFF | LSD turnoff resistance | 1 | 1.4 | Ω | ||
| PWM DRIVER TIMING | ||||||
| Driver dead time | Dead time when switching between LSD and HSD, no load at LSD and HSD | 30 | ns | |||
| PWM OSCILLATOR | ||||||
| VRAMP_HEIGHT | PWM ramp height | As percentage of VCC | 7 | % | ||
| PWM switching frequency | 510 | 600 | 690 | kHz | ||
| INTERNAL SOFT-START (8 steps to regulation current ICHG) | ||||||
| Soft-start steps | 8 | step | ||||
| Soft-start step time | 1.6 | ms | ||||
| CHARGER SECTION POWER-UP SEQUENCING | ||||||
| Charge-enable delay after power up | Delay from CE = 1 until charger is allowed to turn on | 1.5 | s | |||
| LOGIC IO PIN CHARACTERISTICS (CE, STAT1, STAT2, PG) | ||||||
| VIN_LO | CE input low-threshold voltage | 0.8 | V | |||
| VIN_HI | CE input high-threshold voltage | 2.1 | ||||
| VBIAS_CE | CE input bias current | V = 3.3 V (CE has internal 1-MΩ pulldown resistor) | 6 | μA | ||
| VOUT_LO | STAT1, STAT2, PG output low saturation voltage | Sink current = 5 mA | 0.5 | V | ||
| IOUT_HI | Leakage current | V = 32 V | 1.2 | µA | ||
(1) Verified by design.
7.6 Typical Characteristics
Table 1. Table of Graphs
| FIGURE | ||
|---|---|---|
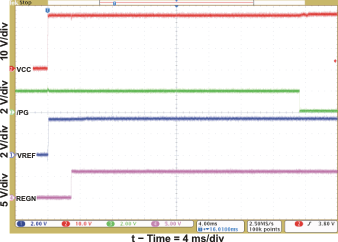
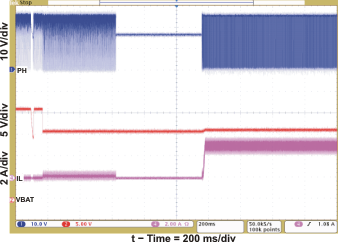
| VREF, REGN, and PG Power Up (CE = 1) | Figure 1 | |
| Charge Enable | Figure 2 | |
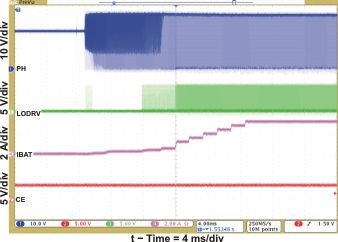
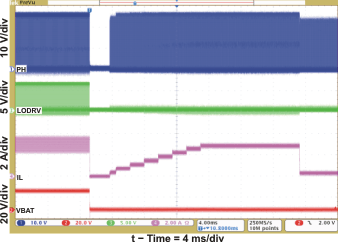
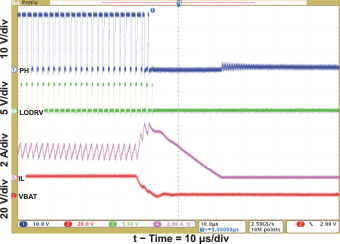
| Current Soft-Start (CE = 1) | Figure 3 | |
| Charge Disable | Figure 4 | |
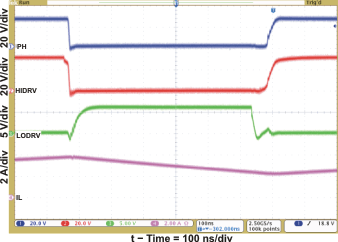
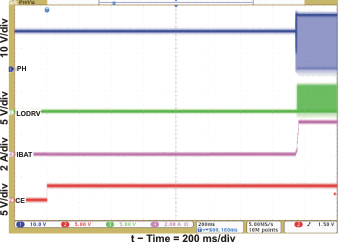
| Continuous-Conduction Mode Switching Waveform | Figure 5 | |
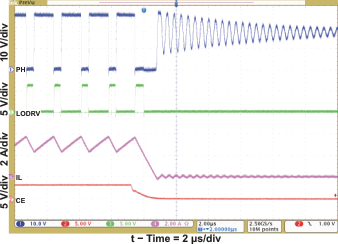
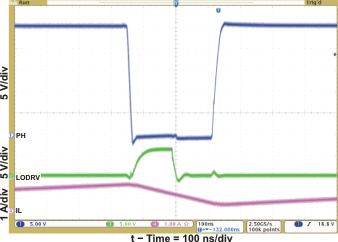
| Cycle-by-Cycle Synchronous to Nonsynchronous | Figure 6 | |
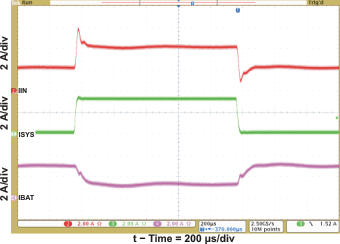
| Transient System Load (DPM) | Figure 7 | |
| Battery Insertion | Figure 8 | |
| Batter- to-Ground Short Protection | Figure 9 | |
| Battery-to-Ground Short Transition | Figure 10 | |
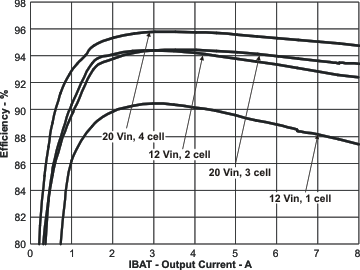
| Efficiency vs Output Current | Figure 11 | |