ZHCSBK4G March 2013 – March 2019
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Maximum Power Point Tracking
- 7.3.2 Battery Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.3 Battery Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.4 Battery Voltage within Operating Range (VBAT_OK Output)
- 7.3.5 Storage Element / Battery Management
- 7.3.6 Programming OUT Regulation Voltage
- 7.3.7 Step Down (Buck) Converter
- 7.3.8 Nano-Power Management and Efficiency
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.1.2 Storage Element Selection
In order for the charge management circuitry to protect the storage element from over-charging or discharging, the storage element must be connected to VBAT pin and the system load tied to the VSTOR pin. Many types of elements can be used, such as capacitors, super capacitors or various battery chemistries. A storage element with 100 µF equivalent capacitance is required to filter the pulse currents of the PFM switching charger. The equivalent capacitance of a battery can be computed as computed as
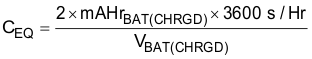
In order for the storage element to be able to charge VSTOR capacitor (CSTOR) within the tVB_HOT_PLUG (50 ms typical) window at hot-plug; therefore preventing the IC from entering cold start, the time constant created by the storage element's series resistance (plus the resistance of the internal PFET switch) and equivalent capacitance must be less than tVB_HOT_PLUG . For example, a battery's resistance can be computed as:
The storage element must be sized large enough to provide all of the system load during periods when the harvester is no longer providing power. The harvester is expected to provide at least enough power to fully charge the storage element while the system is in low power or sleep mode. Assuming no load on VSTOR (i.e., the system is in low power or sleep mode), the following equation estimates charge time from voltage VBAT1 to VBAT2 for given input power is:
Refer to SLUC461 for a design example that sizes the storage element.
Note that if there are large load transients or the storage element has significant impedance then it may be necessary to increase the CSTOR capacitor from the 4.7 µF minimum or add additional capacitance to VBAT in order to prevent a droop in the VSTOR voltage. Refer to Inductor Selection for sizing capacitors.