ZHCSGA3A march 2017 – march 2023 BQ25601
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Power-On-Reset (POR)
- 9.3.2 Device Power Up from Battery without Input Source
- 9.3.3 Power Up from Input Source
- 9.3.4 Boost Mode Operation From Battery
- 9.3.5 Host Mode and Standalone Power Management
- 9.3.6 Power Path Management
- 9.3.7 Battery Charging Management
- 9.3.8 Protections
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6 Register Maps
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.3.7.5 JEITA Guideline Compliance During Charging Mode
To improve the safety of charging Li-ion batteries, JEITA guideline was released on April 20, 2007. The guideline emphasized the importance of avoiding a high charge current and high charge voltage at certain low and high temperature ranges.
To initiate a charge cycle, the voltage on TS pin must be within the VT1 to VT5 thresholds. If TS voltage exceeds the T1-T5 range, the controller suspends charging and waits until the battery temperature is within the T1 to T5 range.
At cool temperature (T1-T2), JEITA recommends the charge current to be reduced to half of the charge current or lower. At warm temperature (T3-T5), JEITA recommends charge voltage less than 4.1 V. Charge termination is disabled for cool and warm conditions.
The charger provides flexible voltage/current settings beyond the JEITA requirement. The voltage setting at warm temperature (T3-T5) can be VREG or 4.1V (configured by JEITA_VSET). The current setting at cool temperature (T1-T2) can be further reduced to 20% of fast charge current (JEITA_ISET).
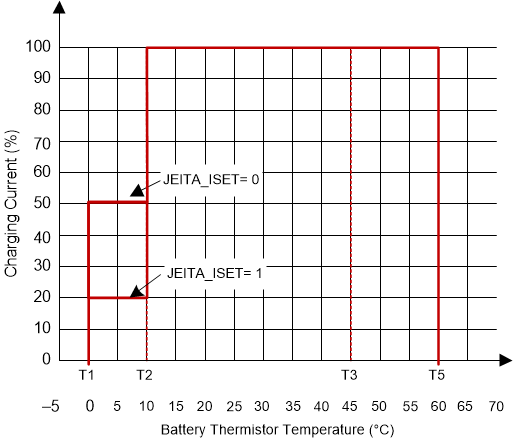 Figure 9-3 JEITA
Profile: Charging Current
Figure 9-3 JEITA
Profile: Charging Current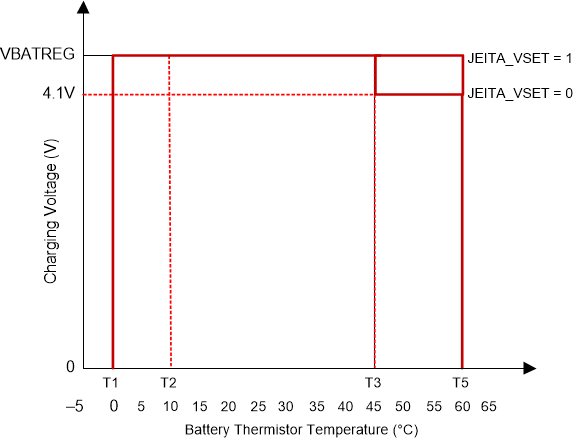 Figure 9-4 JEITA
Profile: Charging Voltage
Figure 9-4 JEITA
Profile: Charging Voltage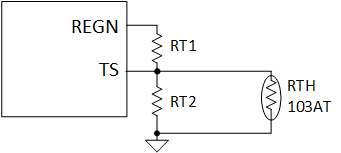 Figure 9-5 TS Resistor Network
Figure 9-5 TS Resistor NetworkEquation 1 through Equation 2 describe updates to the resistor bias network.
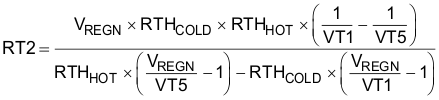
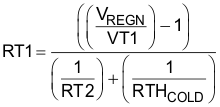
Select 0°C to 60°C range for Li-ion or Li-polymer battery:
- RTHCOLD = 27.28 KΩ
- RTHHOT = 3.02 KΩ
- RT1 = 5.23 KΩ
- RT2 = 30.9 KΩ