ZHCSJ56C February 2018 – September 2019 BQ25882
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Device Power-On-Reset
- 8.3.2 Device Power Up from Battery without Input Source
- 8.3.3 Device Power Up from Input Source
- 8.3.4 Input Current Optimizer (ICO)
- 8.3.5 Buck Mode Operation from Battery (OTG)
- 8.3.6 Power Path Management
- 8.3.7 Battery Charging Management
- 8.3.8 Integrated 16-Bit ADC for Monitoring
- 8.3.9 Status Outputs (PG, and INT)
- 8.3.10 Input Current Limit on ILIM Pin
- 8.3.11 Voltage and Current Monitoring
- 8.3.12 Thermal Regulation and Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.13 Battery Protection
- 8.3.14 Serial Interface
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Register Maps
- 8.5.1 Battery Voltage Regulation Limit Register (Address = 00h) [reset = A0h]
- 8.5.2 Charger Current Limit Register (Address = 01h) [reset = 54h]
- 8.5.3 Input Voltage Limit Register (Address = 02h) [reset = 85h]
- 8.5.4 Input Current Limit Register (Address = 03h) [reset = 39h]
- 8.5.5 Precharge and Termination Current Limit Register (Address = 04h) [reset = 22h]
- 8.5.6 Charger Control 1 Register (Address = 05h) [reset = 9Dh]
- 8.5.7 Charger Control 2 Register (Address = 06h) [reset = 7Dh]
- 8.5.8 Charger Control 3 Register (Address = 07h) [reset = 0Ah]
- 8.5.9 Charger Control 4 Register (Address = 08h) [reset = 0Dh]
- 8.5.10 OTG Control Register (Address = 09h) [reset = F6h]
- 8.5.11 ICO Current Limit Register (Address = 0Ah) [reset = XXh]
- 8.5.12 Charger Status 1 Register (Address = 0Bh) [reset = XXh]
- 8.5.13 Charger Status 2 Register (Address = 0Ch) [reset = XXh]
- 8.5.14 NTC Status Register (Address = 0Dh) [reset = 0Xh]
- 8.5.15 FAULT Status Register (Address = 0Eh) [reset = XXh]
- 8.5.16 Charger Flag 1 Register (Address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.17 Charger Flag 2 Register (Address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.18 FAULT Flag Register (Address = 11h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.19 Charger Mask 1 Register (Address = 12h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.20 Charger Mask 2 Register (Address = 13h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.21 FAULT Mask Register (Address = 14h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.22 ADC Control Register (Address = 15h) [reset = 30h]
- 8.5.23 ADC Function Disable Register (Address = 16h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.24 IBUS ADC 1 Register (Address = 17h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.25 IBUS ADC 0 Register (Address = 18h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.26 ICHG ADC 1 Register (Address = 19h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.27 ICHG ADC 0 Register (Address = 1Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.28 VBUS ADC 1 Register (Address = 1Bh) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.29 VBUS ADC 0 Register (Address = 1Ch) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.30 VBAT ADC 1 Register (Address = 1Dh) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.31 VBAT ADC 0 Register (Address = 1Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.32 VSYS ADC 1 Register (Address = 1Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.33 VSYS ADC 0 Register (Address = 20h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.34 TS ADC 1 Register (Address = 21h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.35 TS ADC 0 Register (Address = 22h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.36 TDIE ADC 1 Register (Address = 23h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.37 TDIE ADC 0 Register (Address = 24h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.38 Part Information Register (Address = 25h) [reset = 11h]
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.9.2 Interrupt to Host (INT)
In some applications, the host does not always monitor the charger operation. The INT pin notifies the system host on the device operation. By default, the following events will generate an active-low, 256-µs INT pulse.
- Good input source detected
- VVBUS < VVBUS_OV threshold
- VVBUS > VPOORSRC when IPOORSRC current is applied (not a poor source)
- VBUS_STAT changes state (VBUS_STAT any bit change)
- Good input source removed
- Entering IINDPM regulation
- Entering VINDPM regulation
- Entering IC junction temperature regulation (TREG)
- I2C Watchdog timer expired
- At initial power up, this INT gets asserted to signal I2C is ready for communication
- Charger status changes state (CHRG_STAT value change), including Charge Complete
- TS_STAT changes state (TS_STAT any bit change)
- VBUS overvoltage detected (VBUS_OVP)
- Junction temperature shutdown (TSHUT)
- Battery overvoltage detected (BATOVP)
- Charge safety timer expired
- A rising edge on any of the *_STAT bits
Each one of these INT sources can be masked off to prevent INT pulses from being sent out when they occur. Three bits exist for each one of these events:
- The STAT bit holds the current status of each INT source
- The FLAG bit holds information on which source produced an INT, regardless of the current status
- The MASK bit is used to prevent the device from sending out INT for each particular event
When one of the above conditions occurs (a rising edge on any of the *_STAT bits), the device sends out an INT pulse and keeps track of which source generated the INT via the FLAG registers. The FLAG register bits are automatically reset to zero after the host reads them, and a new edge on STAT bit is required to re-assert the FLAG.
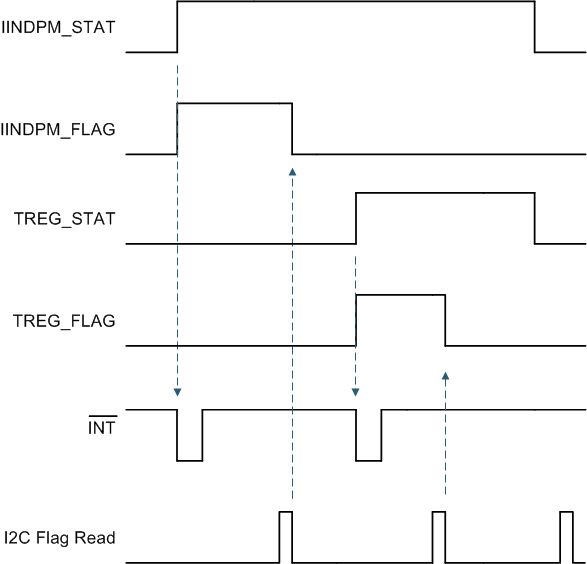 Figure 26. INT Generation Behavior Example
Figure 26. INT Generation Behavior Example