ZHCSJL4A February 2019 – March 2019 BQ25883
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Device Power-On-Reset
- 8.3.2 Device Power Up from Battery without Input Source
- 8.3.3 Device Power Up from Input Source
- 8.3.4 Input Current Optimizer (ICO)
- 8.3.5 Buck Mode Operation from Battery (OTG)
- 8.3.6 Power Path Management
- 8.3.7 Battery Charging Management
- 8.3.8 Integrated 16-Bit ADC for Monitoring
- 8.3.9 Status Outputs
- 8.3.10 Input Current Limit on ILIM Pin
- 8.3.11 Voltage and Current Monitoring
- 8.3.12 Thermal Regulation and Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.13 Battery Protection
- 8.3.14 Serial Interface
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Register Maps
- 8.5.1 Battery Voltage Regulation Limit Register (Address = 00h) [reset = A0h]
- 8.5.2 Charger Current Limit Register (Address = 01h) [reset = 5Eh]
- 8.5.3 Input Voltage Limit Register (Address = 02h) [reset = 84h]
- 8.5.4 Input Current Limit Register (Address = 03h) [reset = 39h ]
- 8.5.5 Precharge and Termination Current Limit Register (Address = 04h) [reset = 22h]
- 8.5.6 Charger Control 1 Register (Address = 05h) [reset = 9Dh]
- 8.5.7 Charger Control 2 Register (Address = 06h) [reset = 7Dh]
- 8.5.8 Charger Control 3 Register (Address = 07h) [reset = 02h]
- 8.5.9 Charger Control 4 Register (Address = 08h) [reset = 0Dh]
- 8.5.10 OTG Control Register (Address = 09h) [reset = F6h]
- 8.5.11 ICO Current Limit in Use Register (Address = 0Ah) [reset = XXh]
- 8.5.12 Charger Status 1 Register (Address = 0Bh) [reset = XXh]
- 8.5.13 Charger Status 2 Register (Address = 0Ch) [reset = XXh]
- 8.5.14 NTC Status Register (Address = 0Dh) [reset = 0Xh]
- 8.5.15 FAULT Status Register (Address = 0Eh) [reset = XXh]
- 8.5.16 Charger Flag 1 Register (Address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.17 Charger Flag 2 Register (Address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.18 FAULT Flag Register (Address = 11h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.19 Charger Mask 1 Register (Address = 12h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.20 Charger Mask 2 Register (Address = 13h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.21 FAULT Mask Register (Address = 14h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.22 ADC Control Register (Address = 15h) [reset = 30h]
- 8.5.23 ADC Function Disable Register (Address = 16h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.24 IBUS ADC 1 Register (Address = 17h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.25 IBUS ADC 0 Register (Address = 18h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.26 ICHG ADC 1 Register (Address = 19h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.27 ICHG ADC 0 Register (Address = 1Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.28 VBUS ADC 1 Register (Address = 1Bh) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.29 VBUS ADC 0 Register (Address = 1Ch) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.30 VBAT ADC 1 Register (Address = 1Dh) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.31 VBAT ADC 0 Register (Address = 1Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.32 VSYS ADC 1 Register (Address = 1Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.33 VSYS ADC 0 Register (Address = 20h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.34 TS ADC 1 Register (Address = 21h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.35 TS ADC 0 Register (Address = 22h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.36 TDIE ADC 1 Register (Address = 23h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.37 TDIE ADC 0 Register (Address = 24h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.38 Part Information Register (Address = 25h) [reset = 18h]
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
RGE Package
24-Pin VQFN
Top View
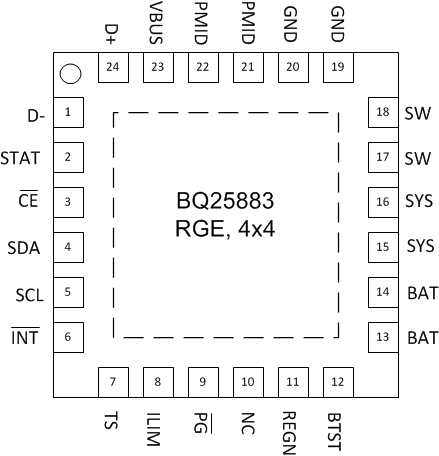
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| D+ | 24 | AIO | Positive USB data line – D+/D– based USB host/charging port detection. The detection includes data contact detection (DCD) and secondary detection in BC1.2. |
| D– | 1 | AIO | Negative USB data line – D+/D– based USB host/charging port detection. The detection includes data contact detection (DCD) and secondary detection in BC1.2. |
| STAT | 2 | DO | Open drain charge status indicator – Connect to the pull-up rail via 10-kΩ resistor. LOW indicates charge in progress. HIGH indicates charge complete or charge disabled. When any fault occurs, the STAT pin blinks at 1Hz. The STAT function can be disabled when the STAT_DIS bit is set. |
| CE | 3 | DI | Active Low Charge Enable Pin – Battery charging is enabled when EN_CHG bit is 1 and CE pin is LOW. CE pin is internally pulled low with 900k-Ω resistor. |
| SDA | 4 | DIO | I2C Interface Data – Connect SDA to the pull up rail through a 10-kΩ resistor. |
| SCL | 5 | DI | I2C Interface Clock – Connect SCL to the pull up rail through a 10-kΩ resistor. |
| INT | 6 | DO | Open drain active Interrupt Output – Connect INT to the pull up rail via a 10-kΩ resistor. The INT pin sends active low, 256-µs pulse to the host to report charger device status and fault. |
| TS | 7 | AI | Temperature Qualification Voltage – Connect a negative temperature coefficient thermistor. Program temperature window with a resistor divider from REGN to TS to GND. Charge suspends when TS pin is out of range. Recommend 103AT-2 thermistor. |
| ILIM | 8 | AI | Input Current Limit (IINDPM) – ILIM pin sets the maximum input current and can be used to monitor input current. IINDPM loop regulates ILIM pin voltage at 0.8V. When ILIM pin is less than 0.8V, the input current can be calculated by IIN = KILIM x VILIM / (RILIM x 0.8V). A resistor connected from ILIM pin to ground sets the input current limit as maximum (IINMAX = KILIM / RILIM). When ILIM pin is short to GND, the input current limit is set to maximum by ILIM. The actual input current limit is the lower limit set by ILIM pin (when EN_ILIM bit is HIGH) or IINDPM register bits. Input current limit less than 500mA is not supported on ILIM pin. The ILIM pin function can be disabled when EN_ILIM bit is 0. If ILIM pin is not used, pull this pin to GND.Do not float this pin.
|
| PG | 9 | DO | Open drain active low power good indicator – Connect to the pull up rail via 10-kΩ resistor. LOW indicates a good input source if the input voltage is within VVBUS_OP (3.9 V), and can provide more than IPOORSRC (30 mA). |
| REGN | 11 | P | Gate Drive Supply – Bias supply for internal MOSFETs driver and IC. Bypass REGN to GND with a 4.7-µF ceramic capacitor. REGN current limit is 50 mA. |
| BTST | 12 | P | PWM High-side Driver Supply – Internally, BTST is connected to the cathode of the boot-strap diode. Connect a 47nF bootstrap capacitor from SW to BTST. |
| BAT | 13, 14 | P | Battery Power Connection – Connect minimum recommended 10-µF capacitance after derating closely to the BAT pin and GND. |
| SYS | 15, 16 | P | System Connection – The internal BATFET is connected between SYS and BAT. When the battery falls below the minimum system voltage, the switch-mode converter keeps SYS above the minimum system voltage. Connect a 2x22-µF capacitance after derating closely to the SYS pin and PGND. |
| SW | 17, 18 | P | Inductor Connection – Connect to the switched side of the external inductor. |
| GND | 19, 20, | – | Ground Return |
| PMID | 21, 22 | P | Blocking MOSFET Connection – The minimum recommended total input low-ESR capacitance on VBUS and PMID, after applied derating, is 10 uF. At least 1-uF is recommended at VBUS with the remainder at PMID. Typical value for PMID is 10 uF. |
| VBUS | 23 | P | Input Supply – VBUS is connected to the external DC supply. Bypass VBUS to GND with at least 1-µF ceramic capacitor, placed as close to the IC as possible. |
| NC | 10 | – | No Connect – Leave these pins floating or tie to ground. |