ZHCSR27D August 2020 – September 2022 BQ79612-Q1 , BQ79614-Q1 , BQ79616-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Power Supplies
- 9.3.2 Measurement System
- 9.3.3 Cell Balancing
- 9.3.4 Integrated Hardware Protectors
- 9.3.5 GPIO Configuration
- 9.3.6
Communication, OTP, Diagnostic Control
- 9.3.6.1
Communication
- 9.3.6.1.1 Serial Interface
- 9.3.6.1.2 Daisy Chain Interface
- 9.3.6.1.3 Start Communication
- 9.3.6.1.4 Communication Timeout
- 9.3.6.1.5 Communication Debug Mode
- 9.3.6.1.6 Multidrop Configuration
- 9.3.6.1.7 SPI Master
- 9.3.6.1.8 SPI Loopback
- 9.3.6.2 Fault Handling
- 9.3.6.3 Nonvolatile Memory
- 9.3.6.4 Diagnostic Control/Status
- 9.3.6.1
Communication
- 9.3.7 Bus Bar Support
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Register Maps
- 9.5.1 OTP Shadow Register Summary
- 9.5.2 Read/Write Register Summary
- 9.5.3 Read-Only Register Summary
- 9.5.4
Register Field Descriptions
- 9.5.4.1 Device Addressing Setup
- 9.5.4.2 Device ID and Scratch Pad
- 9.5.4.3
General Configuration and Control
- 9.5.4.3.1 DEV_CONF
- 9.5.4.3.2 ACTIVE_CELL
- 9.5.4.3.3 BBVC_POSN1
- 9.5.4.3.4 BBVC_POSN2
- 9.5.4.3.5 PWR_TRANSIT_CONF
- 9.5.4.3.6 COMM_TIMEOUT_CONF
- 9.5.4.3.7 TX_HOLD_OFF
- 9.5.4.3.8 STACK_RESPONSE
- 9.5.4.3.9 BBP_LOC
- 9.5.4.3.10 COMM_CTRL
- 9.5.4.3.11 CONTROL1
- 9.5.4.3.12 CONTROL2
- 9.5.4.3.13 CUST_CRC_HI
- 9.5.4.3.14 CUST_CRC_LO
- 9.5.4.3.15 CUST_CRC_RSLT_HI
- 9.5.4.3.16 CUST_CRC_RSLT_LO
- 9.5.4.4 Operation Status
- 9.5.4.5 ADC Configuration and Control
- 9.5.4.6
ADC Measurement Results
- 9.5.4.6.1 VCELL16_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.2 VCELL15_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.3 VCELL14_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.4 VCELL13_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.5 VCELL12_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.6 VCELL11_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.7 VCELL10_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.8 VCELL9_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.9 VCELL8_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.10 VCELL7_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.11 VCELL6_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.12 VCELL5_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.13 VCELL4_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.14 VCELL3_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.15 VCELL2_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.16 VCELL1_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.17 BUSBAR_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.18 TSREF_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.19 GPIO1_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.20 GPIO2_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.21 GPIO3_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.22 GPIO4_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.23 GPIO5_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.24 GPIO6_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.25 GPIO7_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.26 GPIO8_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.27 DIETEMP1_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.28 DIETEMP2_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.29 AUX_CELL_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.30 AUX_GPIO_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.31 AUX_BAT_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.32 AUX_REFL_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.33 AUX_VBG2_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.34 AUX_AVAO_REF_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.35 AUX_AVDD_REF_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.36 AUX_OV_DAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.37 AUX_UV_DAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.38 AUX_OT_OTCB_DAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.39 AUX_UT_DAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.40 AUX_VCBDONE_DAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.41 AUX_VCM_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.42 REFOVDAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.43 DIAG_MAIN_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.44 DIAG_AUX_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.7 Balancing Configuration, Control and Status
- 9.5.4.8 Protector Configuration and Control
- 9.5.4.9 GPIO Configuration
- 9.5.4.10 SPI Master
- 9.5.4.11 Diagnostic Control
- 9.5.4.12 Fault Configuration and Reset
- 9.5.4.13
Fault Status
- 9.5.4.13.1 FAULT_SUMMARY
- 9.5.4.13.2 FAULT_COMM1
- 9.5.4.13.3 FAULT_COMM2
- 9.5.4.13.4 FAULT_COMM3
- 9.5.4.13.5 FAULT_OTP
- 9.5.4.13.6 FAULT_SYS
- 9.5.4.13.7 FAULT_PROT1
- 9.5.4.13.8 FAULT_PROT2
- 9.5.4.13.9 FAULT_OV1
- 9.5.4.13.10 FAULT_OV2
- 9.5.4.13.11 FAULT_UV1
- 9.5.4.13.12 FAULT_UV2
- 9.5.4.13.13 FAULT_OT
- 9.5.4.13.14 FAULT_UT
- 9.5.4.13.15 FAULT_COMP_GPIO
- 9.5.4.13.16 FAULT_COMP_VCCB1
- 9.5.4.13.17 FAULT_COMP_VCCB2
- 9.5.4.13.18 FAULT_COMP_VCOW1
- 9.5.4.13.19 FAULT_COMP_VCOW2
- 9.5.4.13.20 FAULT_COMP_CBOW1
- 9.5.4.13.21 FAULT_COMP_CBOW2
- 9.5.4.13.22 FAULT_COMP_CBFET1
- 9.5.4.13.23 FAULT_COMP_CBFET2
- 9.5.4.13.24 FAULT_COMP_MISC
- 9.5.4.13.25 FAULT_PWR1
- 9.5.4.13.26 FAULT_PWR2
- 9.5.4.13.27 FAULT_PWR3
- 9.5.4.14
Debug Control and Status
- 9.5.4.14.1 DEBUG_CTRL_UNLOCK
- 9.5.4.14.2 DEBUG_COMM_CTRL1
- 9.5.4.14.3 DEBUG_COMM_CTRL2
- 9.5.4.14.4 DEBUG_COMM_STAT
- 9.5.4.14.5 DEBUG_UART_RC
- 9.5.4.14.6 DEBUG_UART_RR_TR
- 9.5.4.14.7 DEBUG_COMH_BIT
- 9.5.4.14.8 DEBUG_COMH_RC
- 9.5.4.14.9 DEBUG_COMH_RR_TR
- 9.5.4.14.10 DEBUG_COML_BIT
- 9.5.4.14.11 DEBUG_COML_RC
- 9.5.4.14.12 DEBUG_COML_RR_TR
- 9.5.4.14.13 DEBUG_UART_DISCARD
- 9.5.4.14.14 DEBUG_COMH_DISCARD
- 9.5.4.14.15 DEBUG_COML_DISCARD
- 9.5.4.14.16 DEBUG_UART_VALID_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.14.17 DEBUG_COMH_VALID_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.14.18 DEBUG_COML_VALID_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.14.19 DEBUG_OTP_SEC_BLK
- 9.5.4.14.20 DEBUG_OTP_DED_BLK
- 9.5.4.15
OTP Programming Control and Status
- 9.5.4.15.1 OTP_PROG_UNLOCK1A through OTP_PROG_UNLOCK1D
- 9.5.4.15.2 OTP_PROG_UNLOCK2A through OTP_PROG_UNLOCK2D
- 9.5.4.15.3 OTP_PROG_CTRL
- 9.5.4.15.4 OTP_ECC_TEST
- 9.5.4.15.5 OTP_ECC_DATAIN1 through OTP_ECC_DATAIN9
- 9.5.4.15.6 OTP_ECC_DATAOUT1 through OTP_ECC_DATAOUT9
- 9.5.4.15.7 OTP_PROG_STAT
- 9.5.4.15.8 OTP_CUST1_STAT
- 9.5.4.15.9 OTP_CUST2_STAT
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1
Base
Device Application Circuit
- 10.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.1.3 Application Curve
- 10.2.2 Daisy Device Application Circuit
- 10.2.1
Base
Device Application Circuit
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.3.6.1.1.2.1.6 Calculating Frame CRC Value
The CRC calculation by the transmitter is in bit-stream order across the entire transmission frame (except for the CRC). When determining bit-stream order for implementing the CRC algorithm, it is important to note that protocol bytes transmit serially, least-significant bit first. Figure 9-27 illustrates the bit-stream order concept.
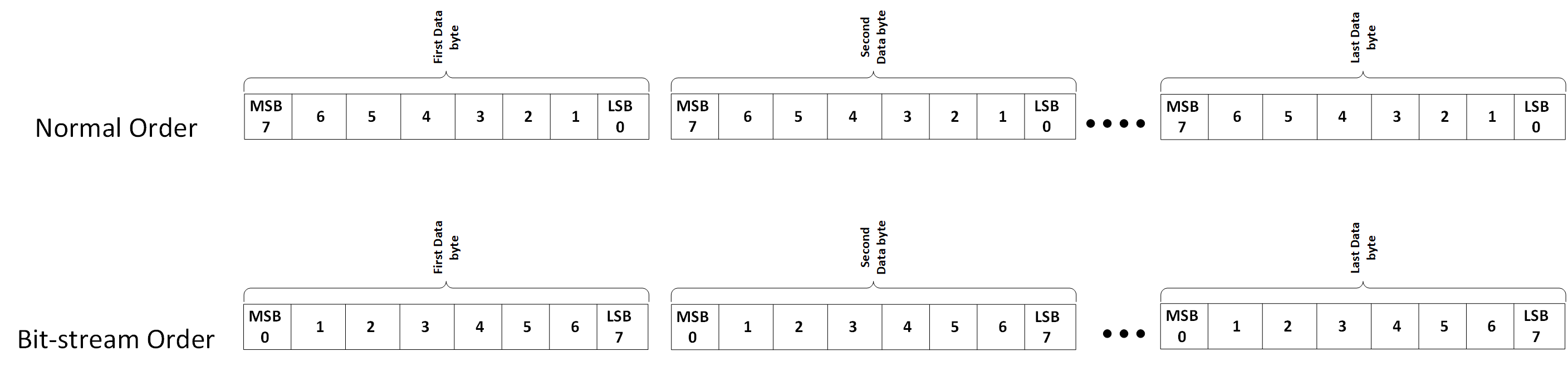
Figure 9-27 Bit-Stream Order Explanation
The CRC (0x0000) is appended to the end of the bit-stream. This bit-stream is then initialized by XOR'ing with 0xFFFF to catch any leading 0 errors. This new bit-stream is then divided by the polynomial (0xC002) until only the 2-byte CRC remains. During this process, the most significant 17 bits of the bit stream are XOR’d with the polynomial. The leading zeroes of the result are removed and that result is XOR’d with the polynomial once again. The process is repeated until only the 2-byte CRC remains. For example:
Example 1: CRC Calculation Using Polynomial Division
Command Frame = 0x80 00 02 0F 0B (0b1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 0000 1111 0000 1011)
Command Frame in bit stream order = 0x01 00 40 F0 D0 (0b0000 0001 0000 0000 0100 0000 1111 0000 1101 0000)
After Initialization (XOR with 0xFFFF) = 0b1111 1110 1111 1111 0100 0000 1111 0000 1101 0000
1111 1110 1111 1111 0100 0000 1111 0000 1101 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 #append 0x0000 for CRC
1100 0000 0000 0010 1 #XOR with polynomial
0011 1110 1111 1101 1100 0000 1111 0000 1101 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
11 1110 1111 1101 1100 0000 1111 0000 1101 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 #delete leading zeros from previous result
11 0000 0000 0000 101 #XOR with polynomial
00 1110 1111 1101 0110 0000 1111 0000 1101 0000
……
……
……
1100 0110 0000 0001 0000 0000
1100 0000 0000 0010 1 #XOR with polynomial
0000 0110 0000 0011 1000 0000
110 0000 0011 1000 0000
110 0000 0000 0001 01 #XOR with polynomial
000 0000 0011 1001 0100
0000 0011 1001 0100 #CRC result in bit stream order
1100 0000 0010 1001 #final CRC result in normal order
CRC final 0xC029