SWRS045F January 2006 – November 2018 CC1021
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 RF Transmit
- 4.5 RF Receive
- 4.6 RSSI / Carrier Sense
- 4.7 Intermediate Frequency (IF)
- 4.8 Crystal Oscillator
- 4.9 Frequency Synthesizer
- 4.10 Digital Inputs / Outputs
- 4.11 Current Consumption
- 4.12 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for VQFNP Package
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 5.3 Configuration Overview
- 5.4 Microcontroller Interface
- 5.5 4-wire Serial Configuration Interface
- 5.6 Signal Interface
- 5.7 Data Rate Programming
- 5.8 Frequency Programming
- 5.9
Receiver
- 5.9.1 IF Frequency
- 5.9.2 Receiver Channel Filter Bandwidth
- 5.9.3 Demodulator, Bit Synchronizer and Data Decision
- 5.9.4 Receiver Sensitivity versus Data Rate and Frequency Separation
- 5.9.5 RSSI
- 5.9.6 Image Rejection Calibration
- 5.9.7 Blocking and Selectivity
- 5.9.8 Linear IF Chain and AGC Settings
- 5.9.9 AGC Settling
- 5.9.10 Preamble Length and Sync Word
- 5.9.11 Carrier Sense
- 5.9.12 Automatic Power-Up Sequencing
- 5.9.13 Automatic Frequency Control
- 5.9.14 Digital FM
- 5.10 Transmitter
- 5.11 Input and Output Matching and Filtering
- 5.12 Frequency Synthesizer
- 5.13 VCO and LNA Current Control
- 5.14 Power Management
- 5.15 On-Off Keying (OOK)
- 5.16 Crystal Oscillator
- 5.17 Built-in Test Pattern Generator
- 5.18 Interrupt on Pin DCLK
- 5.19 PA_EN and LNA_EN Digital Output Pins
- 5.20 System Considerations and Guidelines
- 5.21 Antenna Considerations
- 5.22 Configuration Registers
- 6Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
5.9.1 IF Frequency
The IF frequency is derived from the crystal frequency as shown in Equation 12.
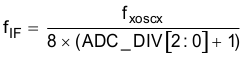
Where: ADC_DIV[2:0] is set in the MODEM register.
The analog filter succeeding the mixer is used for wideband and anti-alias filtering which is important for the blocking performance at 1 MHz and larger offsets. This filter is fixed and centered on the nominal IF frequency of 307.2 kHz. The bandwidth of the analog filter is about 160 kHz.
Using crystal frequencies which gives an IF frequency within 300 to 320 kHz means that the analog filter can be used (assuming low frequency deviations and low data rates).
Large offsets, however, from the nominal IF frequency will give an un-symmetric filtering (variation in group delay and different attenuation) of the signal, resulting in decreased sensitivity and selectivity.
For IF frequencies other than 300 to 320 kHz and for high frequency deviation and high data rates (typically ≥ 76.8 kBaud), the analog filter must be bypassed by setting FILTER_BYPASS = 1 in the FILTER register. In this case the blocking performance at 1 MHz and larger offsets will be degraded.
The IF frequency is always the ADC clock frequency divided by 4. The ADC clock frequency should therefore be as close to 1.2288 MHz as possible.