ZHCSDT8 May 2015 CDCM6208V1F
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 简化电路原理图
- 5 修订历史记录
- 6 Description (continued)
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information, Airflow = 0 LFM
- 8.5 Thermal Information, Airflow = 150 LFM
- 8.6 Thermal Information, Airflow = 250 LFM
- 8.7 Thermal Information, Airflow = 500 LFM
- 8.8 Single Ended Input Characteristics
- 8.9 Single Ended Input Characteristics (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 8.10 Differential Input Characteristics (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 8.11 Crystal Input Characteristics (SEC_REF)
- 8.12 Single Ended Output Characteristics (STATUS1, STATUS0, SDO, SDA)
- 8.13 PLL Characteristics
- 8.14 LVCMOS Output Characteristics
- 8.15 LVPECL (High-Swing CML) Output Characteristics
- 8.16 CML Output Characteristics
- 8.17 LVDS (Low-Power CML) Output Characteristics
- 8.18 HCSL Output Characteristics
- 8.19 Output Skew and Sync to Output Propagation Delay Characteristics
- 8.20 Device Individual Block Current Consumption
- 8.21 Worst Case Current Consumption
- 8.22 I2C TIMING
- 8.23 SPI Timing Requirements
- 8.24 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
- 10Detailed Description
-
11Application and Implementation
- 11.1 Application Information
- 11.2
Typical Applications
- 11.2.1
Design Requirements
- 11.2.1.1 Device Block-level Description
- 11.2.1.2 Device Configuration Control
- 11.2.1.3 Configuring the RESETN Pin
- 11.2.1.4 Preventing False Output Frequencies in SPI/I2C Mode at Startup:
- 11.2.1.5 Power Down
- 11.2.1.6 Device Power Up Timing:
- 11.2.1.7 Input Mux and Smart Input Mux
- 11.2.1.8 Universal INPUT Buffer (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 11.2.1.9 VCO Calibration
- 11.2.1.10 Reference Divider (R)
- 11.2.1.11 Input Divider (M)
- 11.2.1.12 Feedback Divider (N)
- 11.2.1.13 Prescaler Dividers (PS_A, PS_B)
- 11.2.1.14 Phase Frequency Detector (PFD)
- 11.2.1.15 Charge Pump (CP)
- 11.2.1.16
Programmable Loop Filter
- 11.2.1.16.1 Loop Filter Component Selection
- 11.2.1.16.2 Device Output Signaling
- 11.2.1.16.3 Integer Output Divider (IO)
- 11.2.1.16.4 Fractional Output Divider (FOD)
- 11.2.1.16.5 Output Synchronization
- 11.2.1.16.6 Output MUX on Y4 and Y5
- 11.2.1.16.7 Staggered CLK Output Powerup for Power Sequencing of a DSP
- 11.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 11.2.3 Application Performance Plots
- 11.2.1
Design Requirements
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14器件和文档支持
- 15机械、封装和可订购信息
10 Detailed Description
10.1 Overview
Supply Voltage: The CDCM6208V1F supply is internally regulated. Therefore each core and I/O supply can be mixed and matched in any order according to the application needs. The device jitter performance is independent of supply voltage.
Frequency Range: The PLL includes dual reference inputs with input multiplexer, charge pump, loop filter, and VCO that operates from 2.39 GHz to 2.55 GHz.
Reference inputs: The primary and secondary reference inputs support differential and single ended signals from 8 kHz to 250 MHz. The secondary reference input also supports crystals from 10 MHz to 50 MHz. There is a 4-bit reference divider available on the primary reference input. The input mux between the two references supports simply switching or can be configured as Smart MUX and supports glitchless input switching.
Divider and Prescaler: In addition to the 4-bit input divider of the primary reference a 14-b input divider at the output of input MUX and a cascaded 8-b and 10-b continuous feedback dividers are available. Two independent prescaler dividers offer divide by /4, /5 and /6 options of the VCO frequency of which any combination can then be chosen for a bank of 4 outputs (2 with fractional dividers and 2 that share an integer divider) through an output MUX. A total of 2 output MUXes are available.
Phase Frequency Detector and Charge Pump: The PFD input frequency can range from 8 kHz to 100 MHz. The charge pump gain is programmable and the loop filter consists of internal + partially external passive components and supports bandwidths from a few Hz up to 400kHz.
10.2 Functional Block Diagram
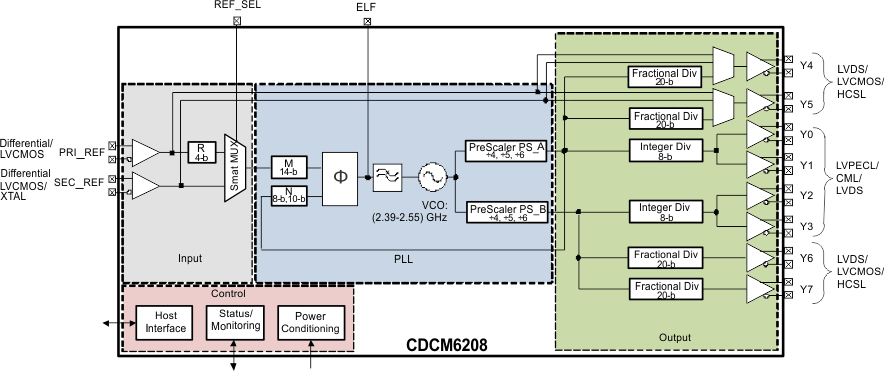 Figure 25. High-Level Block Diagram of CDCM6208V1F
Figure 25. High-Level Block Diagram of CDCM6208V1F
10.3 Feature Description
Phase Noise: The Phase Noise performance of the device can be summarized to:
Table 2. Synthesizer Mode (Loop filter BW >250 kHz)
| RANDOM JITTER (ALL OUTPUTS) | TOTAL JITTER | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYPICAL | MAXIMUM | MAXIMUM | ||
| 10k-20MHz | 12k-20MHz | 10k-100MHz | Integer divider DJ-unbound RJ 10k-20MHz |
Fractional divider DJ 10k-40MHz RJ 10k-20MHz |
| 0.27 ps-rms (Integer division) 0.7ps-rms (fractional div) |
0.3 ps-rms (int div)(2) | 0.625 ps-rms (int div) | 20 ps-pp (1) | 50-220 ps-pp, see Figure 3 |
Table 3. Jitter Cleaner Mode (Loop filter BW < 1 kHz)
| RANDOM JITTER (ALL OUTPUTS) | TOTAL JITTER | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYPICAL | MAXIMUM | MAXIMUM | ||
| 10k-20MHz | 10k-20MHz | 10k-100MHz | Integer divider DJ unbound RJ 10k-20MHz |
Fractional divider DJ 10k-40MHz RJ 10k-20MHz |
| 1.6 ps-rms (Integer division) 2.3 ps-rms (fractional div) 10k-20MHz |
2.1 ps-rms (int div) | 2.14 ps-rms (int div) | 40 ps-pp | 70-240 ps-pp, see Figure 3 |
Spurious Performance: The spurious performance is as follows:
- Less than -80 dBc spurious from PFD/reference clocks at 122.88 MHz output frequency in the Nyquist range.
- Less than -68 dBc spurious from output channel-to-channel coupling on the victim output at differential signaling level operated at 122.88 MHz output frequency in the Nyquist range.
Device outputs:
The Device outputs offer multiple signaling formats: high-swing CML (LVPECL like), normal-swing CML (CML), low-swing CML (LVDS like), HCSL, and LVCMOS signaling.
Table 4. Device Outputs
| Outputs | LVPECL | CML | LVDS | HCSL | LVCMOS | OUTPUT DIVIDER | FREQUENCY RANGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y[3:0] | X | X | X | Integer only | 1.55 - 800 MHz | ||
| Y[7:4] | X | X | X | Integer | 1.55 - 800 MHz | ||
| Fractional | 1.00 - 400 MHz |
Outputs [Y0:Y3] are driven by 8-b continuous integer dividers per pair. Outputs [Y4:Y7] are each driven by 20-b fractional dividers that can achieve any frequency with better than 1ppm frequency accuracy. The output skew is typically less than 40 ps for differential outputs. The LVCMOS outputs support adjustable slew rate control to control EMI. Pairs of 2 outputs can be operated at 1.8 V, 2.5 V or 3.3 V power supply voltage.
Device Configuration:32 distinct pin modes are available that cover many common use cases without the need for any serial programming of the device. For maximum flexibility the device also supports SPI and I2C programming. I2C offers 4 distinct addresses to support up to 4 devices on the same programming lines.
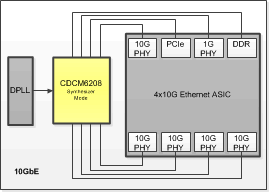 Figure 26. Typical Use Case: CDCM6208V1F Example in Wireless Infrastructure Baseband Application
Figure 26. Typical Use Case: CDCM6208V1F Example in Wireless Infrastructure Baseband Application
10.4 Device Functional Modes
10.4.1 Control Pins Definition
In the absence of a host interface, the CDCM6208V1F can be powered up in one of 32 pre-configured settings when the pins are SI_MODE[1:0] = 10. The CDCM6208V1F has 5 control pins identified to achieve commonly used networking frequencies, and change output types. The Smart Input MUX for the PLL is set in most configurations to manual mode in pin mode. Based on the control pins settings for the on-chip PLL, the device generates the appropriate frequencies and appropriate output signaling types at start-up. In the case of the PLL loop filter, "JC" denotes PLL bandwidths of ≤ 1 kHz and "Synth" denotes PLL bandwidths of ≥ 100 kHz.
Table 5. Pre-Configured Settings of CDCM6208V1F Accessible by PIN[4:0](1)(2)
| SI_MODE[1:0] | pin[4:0] | Use Case | fin(PRI_REF) | Type | fin(SEC_REF) | Type2 | REF_SEL | f(PFD) | f(VCO) | fout(Y0) | TYPE(Y0) | fout(Y1) | Type(Y1) | fout(Y2) | Type(Y2) | fout(Y3) | Type(Y3) | fout(Y4) | Type(Y4) | fout(Y5) | Type(Y5) | fout(Y6) | Type(Y6) | fout(Y7) | Type(Y7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | I/O | SPI Default | 25 | Disable | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 125 | PECL | 125 | PECL | 125 | PECL | 125 | PECL | 25 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL | 100 | Disable | 100 | Disable |
| 1 | I/O | I2C Default | 25 | Disable | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 125 | PECL | 125 | PECL | 125 | PECL | 125 | PECL | 25 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL | 100 | Disable | 100 | Disable |
| 11 | Reserved | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 0x00 | 1-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS |
| 10 | 0x01 | 2-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS |
| 10 | 0x02 | 3-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVCMOS-PN | 25 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x03 | 4-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 125 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x04 | 5-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 125 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x05 | 6-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 100 | PECL | 100 | PECL | 156.25 | PECL | 156.25 | PECL | 25 | LVDS | 100 | HCSL | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS |
| 10 | 0x06 | 7-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS |
| 10 | 0x07 | 8-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 156.25 | PECL | 156.25 | PECL | 25 | PECL | 25 | PECL | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 156.25 | LVDS | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL |
| 10 | 0x08 | 9-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 156.25 | PECL | 156.25 | PECL | 100 | PECL | 100 | PECL | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL |
| 10 | 0x09 | 10-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 100 | PECL | 100 | PECL | 156.25 | CML | 156.25 | CML | 25 | LVDS | 100 | HCSL | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS |
| 10 | 0x0A | 11-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 100 | PECL | 100 | PECL | 100 | PECL | 100 | PECL | 25 | LVCMOS-PN | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 50 | LVCMOS-PN | 12.0000001831055 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x0B | 12-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2400 | 25 | PECL | 25 | PECL | 100 | CML | 100 | CML | 25 | LVCMOS-PN | 25 | LVCMOS-PN | 100 | HCSL | 12 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x0C | 13-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 156.25 | PECL | 156.25 | PECL | 125 | PECL | 125 | PECL | 25 | LVCMOS-PN | 25 | LVCMOS-PN | 25 | LVDS | 100 | HCSL |
| 10 | 0x0D | 14-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 25 | PECL | 25 | PECL | 156.25 | PECL | 156.25 | PECL | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL | 156.25 | LVDS | 66.6666666666667 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x0E | 15-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 33.3333333333333 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x0F | 16-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 100 | PECL | 100 | PECL | 25 | LVCMOS-PN | 25 | LVDS | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL |
| 10 | 0x10 | 17-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 33.3333333333333 | LVCMOS-PN | 33.3333333333333 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x11 | 18-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | LVDS | 25 | PECL | 25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS |
| 10 | 0x12 | 19-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 100 | CML | 100 | CML | 100 | CML | 100 | CML | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL |
| 10 | 0x13 | 20-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 156.25 | PECL | 156.25 | PECL | 125 | PECL | 125 | PECL | 156.25 | HCSL | 156.25 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL |
| 10 | 0x14 | 21-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2400 | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 24 | LVCMOS-PN | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 133.333333333333 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x15 | 22-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 100 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x16 | 23-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 156.25 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x17 | 24-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 125 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 100 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x18 | 25-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 125 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x19 | 26-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL |
| 10 | 0x1A | 27-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | HCSL | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS |
| 10 | 0x1B | 28-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | HCSL | 100 | HCSL | 156.25 | LVDS |
| 10 | 0x1C | 29-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 23.9999992675781 | LVCMOS-PN | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 125 | LVDS | 83.3333333333333 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x1D | 30-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 23.9999992675781 | LVCMOS-PN | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 125 | LVDS | 100 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x1E | 31-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 23.9999992675781 | LVCMOS-PN | 125 | LVCMOS-PN | 125 | LVDS | 66.6666666666667 | LVCMOS-PN |
| 10 | 0x1F | 32-V1F | 25 | LVDS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2500 | 156.25 | LVDS | 156.25 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS | 125 | LVDS | 25 | LVCMOS-PN | 100 | LVDS | 100 | LVDS |
For all pin modes, STATUS0 outputs the PLL_LOCK signal and STATUS1 the LOSS OF REFERENCE.
General Note: in all pin mode, all voltage supplies must either be 1.8 V or 2.5/3.3 V and the PWR pin number 44 must be set to 0 or 1 accordingly. In SPI and I2C mode, the supply voltages can be "mixed and matched" as long as the corresponding register bits reflect the supply voltage setting for each desired 1.8 V or 2.5/3.3 V supply. Exception: inputs configured for LVDS signaling (Type = LVDS) are supply agnostic, and therefore can be powered from 2.5 V/3.3 V or 1.8 V regardless of the supply select setting of pin number 44.
10.4.2 Loop Filter Recommendations for Pin Modes
The following two tables provide the internal charge pump and R3/C3 settings for pin modes. The designer can either design their own optimized loop filter, or use the suggested loop filter in the Table 6.
Table 6. CDCM6208V1F Loop Filter Recommendation for Pin Mode
| SI_MODE[1:0] | pin [4:0] | Use Case | PRI_REF | SEC_REF | REF_SEL | f(PFD) (MHz) |
ICP (mA) |
Recommended Loop Filter C1/R2/C2 |
Internal LPF Components | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freq (MHz) |
Type | Freq (MHz) |
Type | R3 (Ohm) |
C3 (pF) |
|||||||
| 0 | I/O | SPI Default | 25 | Disable | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 1 | I/O | I2C Default | 25 | Disable | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 11 | Reserved | |||||||||||
| 10 | 0x00 | 1-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x01 | 2-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x02 | 3-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x03 | 4-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x04 | 5-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x05 | 6-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x06 | 7-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x07 | 8-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x08 | 9-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 337.5 |
| 10 | 0x09 | 10-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x0A | 11-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x0B | 12-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x0C | 13-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x0D | 14-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x0E | 15-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x0F | 16-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x10 | 17-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x11 | 18-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x12 | 19-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x13 | 20-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x14 | 21-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x15 | 22-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x16 | 23-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x17 | 24-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x18 | 25-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x19 | 26-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x1A | 27-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x1B | 28-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x1C | 29-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x1D | 30-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x1E | 31-V1F | 25 | LVCMOS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
| 10 | 0x1F | 32-V1F | 25 | LVDS | 25 | Crystal | MAN-SEC | 25 | 2.5m | 100pF/500Ohm/22nF | 100 Ohm | 242.5 |
10.4.3 Status Pins Definition
The device vitals such as input signal quality, smart mux input selection, and PLL lock can be monitored by reading device registers or at the status pins STATUS1, and STATUS0. Register 3[12:7] allows for customization of which vitals are mapped to these two pins. Table 7 lists the three events that can be mapped to each status pin and which can also be read in the register space.
Table 7. CDCM6208V1F Status Pin Definition List
| STATUS SIGNAL NAME | SIGNAL TYPE | SIGNAL NAME | REGISTER BIT NO. | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEL_REF | LVCMOS | STATUS0, 1 | Reg 3.12 Reg 3.9 |
Indicates Reference Selected for PLL: 0 → Primary input selected to drive PLL 1 → Secondary input selected to drive PLL |
| LOS_REF | LVCMOS | STATUS0, 1 | Reg 3.11 Reg 3.8 |
Loss of selected reference input observed at active input: 0 → Reference input present 1 → Loss of reference input Important Note 1: For LOS_REF to operate properly, the secondary input SEC_IN must be enabled. Set register Q4.5=1. If register Q4.5 is set to zero, LOS_REF will output a static high signal regardless of the actual input signal status on PRI_IN. |
| PLL_UNLOCK | LVCMOS | STATUS0, 1 | Reg 3.10 Reg 3.7 |
Indicates unlock status for PLL (digital): PLL locked → Q21.02 = 0 and VSTATUS0/1= VIH PLL unlocked → Q21.2 = 1 and VSTATUS0/1= VILSee note (1) Note 2: I f the smartmux is enabled and both reference clocks stall, the STATUSx output signal will 98% of the time indicate the LOS condition with a static high signal. However, in 2% of the cases, the LOS detection engine erroneously stalls at a state where the STATUSx output PLL lock indicator will signalize high for 511 out of every 512 PFD clock cycles. |
NOTE
It is recommended to assert only one out of the three register bits for each of the status pins. For example, to monitor the PLL lock status on STATUS0 and the selected reference clock sources on STATUS1 output, the device register settings would be Q3.12 = Q3.7 = 1 and Q3.11 = Q3.10 = Q3.9 = Q3.8 = 0. If a status pin is unused, it is recommended to set the according 3 register bits to zero (e.g. Q3[12:9] = 0 for STATUS0 = 0). If more than one bit is enabled for each STATUS signal, the function becomes OR'ed. For example, if Q3.11 = Q3.10 = 1 and Q3.12 = 0, the STATUS0 output would be high either if the device goes out of lock or the selected reference clock signal is lost.
10.4.4 PLL Lock Detect
The PLL lock detection circuit is a digital detection circuit which detects any frequency error, even a single cycle slip. The PLL unlock is signalized when a certain number of cycle slips have been exceeded, at which point the counter is reset. A frequency error of 2% will cause PLL unlock to stay low. A 0.5% frequency error shows up as toggling the PLL lock output with roughly 50% duty cycle at roughly 1/1000 th of the PFD update frequency to the device. A frequency error of 1ppm would show up as rare toggling low for a duration of approximately 1000 PFD update clock cycles. If the system plans using PLL lock to toggle a system reset, then consider adding an RC filter on the PLL LOCK output (Status 1 or Status 0) to avoid rare cycle slips from triggering an entire system reset.
10.4.5 Interface and Control
The host (DSP, Microcontroller, FPGA, etc) configures and monitors the CDCM6208V1F via the SPI or I2C port. The host reads and writes to a collection of control/status bits called the register file. Typically, a hardware block is controlled and monitored via a specific grouping of bits located within the register file. The host controls and monitors certain device-wide critical parameters directly, via control/status pins. In the absence of a host, the CDCM6208V1F can be configured to operate in pin mode where the control pins [PIN0-PIN4] can be set appropriately to generate the necessary clock outputs out of the device.
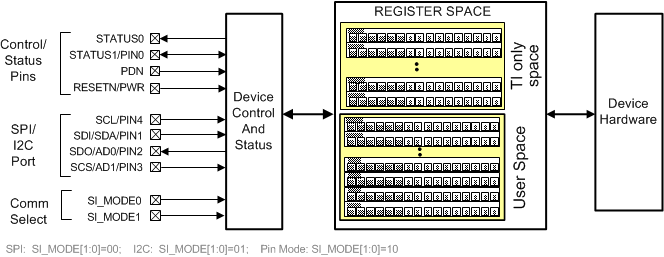 Figure 27. CDCM6208V1F Interface and Control Block
Figure 27. CDCM6208V1F Interface and Control Block
Within this register space, there are certain bits that have read/write access. Other bits are read-only (an attempt to write to a read only bit will not change the state of the bit).
10.4.5.1 Register File Reference Convention
Figure 28 shows the method this document employs to refer to an individual register bit or a grouping of register bits. If a drawing or text references an individual bit, the format is to specify the register number first and the bit number second. The CDCM6208V1F contains 21 registers that are 16 bits wide. The register addresses and the bit positions both begin with the number zero (0). A period separates the register address and bit address. The first bit in the register file is address 'R0.0' meaning that it is located in Register 0 and is bit position 0. The last bit in the register file is address R31.15 referring to the 16thbit of register address 31 (the 32ndregister in the device
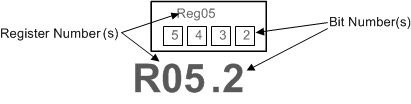 Figure 28. CDCM6208V1F Register Reference Format
Figure 28. CDCM6208V1F Register Reference Format
10.4.5.2 SPI - Serial Peripheral Interface
To enable the SPI port, tie the communication select pins SI_MODE[1:0] to ground. SPI is a master/slave protocol in which the host system is always the master; therefore, the host always initiates communication to/from the device. The SPI interface consists of four signal pins. The device SPI address is 0000.
Table 8. Serial Port Signals in SPI Mode
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NUMBER | ||
| SDI/SDA/PIN1 | 2 | Input | SDI: SPI Serial Data Input |
| SDO/AD0/PIN2 | 3 | Output | SDO: SPI Serial Data |
| SCS/AD1/PIN3 | 4 | Input | SCS: SPI Latch Enable |
| SCL/PIN4 | 5 | Input | SCL: SPI/I2C Clock |
The host must present data to the device MSB first. A message includes a transfer direction bit, an address field, and a data field as depicted in Figure 29
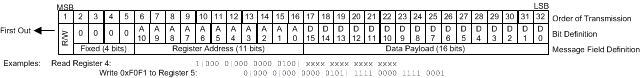 Figure 29. CDCM6208V1F SPI Message Format
Figure 29. CDCM6208V1F SPI Message Format
10.4.5.2.1 Configuring the PLL
The CDCM6208V1F allows configuring the PLL to accommodate various input and output frequencies either through an I2C or SPI programming interface or in the absence of programming, the PLL can be configured through control pins. The PLL can be configured by setting the Smart Input MUX, Reference Divider, PLL Loop Filter, Feedback Divider, Prescaler Divider, and Output Dividers.
For the PLL to operate in closed loop mode, the following condition in Equation 2 has to be met when using primary input for the reference clock, and the condition in Equation 3 has to be met when using secondary input for the reference clock.
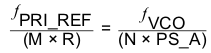
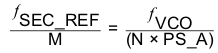
In Equation 2 and Equation 3, ƒPRI_REF is the reference input frequency on the primary input and ƒSEC_REF is the reference input frequency on the secondary input, R is the reference divider, M is the input divider, N is the feedback divider, and PS_A the prescaler divider A.
The output frequency, ƒOUT, is a function of ƒVCO, the prescaler A, and the output divider (O), and is given by Equation 4. (Use PS_B in for outputs 2, 3, 6, and 7).
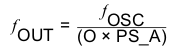
When the output frequency plan calls for the use of some output dividers as fractional values, the following steps are needed to calculate the closest achievable frequencies for those using fractional output dividers and the frequency errors (difference between the desired frequency and the closest achievable frequency).
- Based on system needs, decide the frequencies that need to have best possible jitter performance.
- Once decided, these frequencies need to be placed on integer output dividers.
- Then a frequency plan for these frequencies with strict jitter requirements can be worked out using the common divisor algorithm.
- Once the integer divider plans are worked out, the PLL settings (including VCO frequency, feedback divider, input divider and prescaler divider) can be worked out to map the input frequency to the frequency out of the prescaler divider.
- Then calculate the fractional divider values (whose values must be greater than 2) that are needed to support the output frequencies that are not part of the common frequency plan from the common divisor algorithm already worked out.
- For each fractional divider value, try to represent the fractional portion in a 20 bit binary scheme, where the first fractional bit is represented as 0.5, the second fractional bit is represented as 0.25, third fractional bit is represented as 0.125 and so on. Continue this process until the entire 20 bit fractional binary word is exhausted.
- Once exhausted, the fraction can be calculated as a cumulative sum of the fractional bit x fractional value of the fractional bit. Once this is done, the closest achievable output frequency can be calculated with the mathematical function of the frequency out of the prescaler divider divided by the achievable fractional divider.
- The frequency error can then be calculated as the difference between the desired frequency and the closest achievable frequency.
10.5 Programming
10.5.1 Writing to the CDCM6208V1F
To initiate a SPI data transfer, the host asserts the SCS (serial chip select) pin low. The first rising edge of the clock signal (SCL) transfers the bit presented on the SDI pin of the CDCM6208V1F. This bit signals if a read (first bit high) or a write (first bit low) will transpire. The SPI port shifts data to the CDCM6208V1F with each rising edge of SCL. Following the W/R bit are 4 fixed bits followed by 11 bits that specify the address of the target register in the register file. The 16 bits that follow are the data payload. If the host sends an incomplete message, (i.e. the host de-asserts the SCS pin high prior to a complete message transmission), then the CDCM6208V1F aborts the transfer, and device makes no changes to the register file or the hardware. Figure 31 shows the format of a write transaction on the CDCM6208V1F SPI port. The host signals the CDCM6208V1F of the completed transfer and disables the SPI port by de-asserting the SCS pin high.
10.5.2 Reading from the CDCM6208V1F
As with the write operation, the host first initiates a SPI transfer by asserting the SCS pin low. The host signals a read operation by shifting a logical high in the first bit position, signaling the CDCM6208V1F that the host is imitating a read data transfer from the device. During the portion of the message in which the host specifies the CDCM6208V1F register address, the host presents this information on the SDI pin of the device (for the first 15 clock cycles after the W/R bit). During the 16 clock cycles that follow, the CDCM6208V1F presents the data from the register specified in the first half of the message on the SDO pin. The SDO output is 3-stated anytime SCS is high, so that multiple SPI slave devices can be connected to the same serial bus. The host signals the CDCM6208V1F that the transfer is complete by de-asserting the SCS pin high.
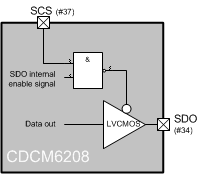 Figure 30.
Figure 30.
10.5.3 Block Write/Read Operation
The device supports a block write and block read operation. The host need only specify the lowest address of the sequence of addresses that the host needs to access. The CDCM6208V1F will automatically increment the internal register address pointer if the SCS pin remains low after the SPI port finishes the initial 32-bit transmission sequence. Each transmission of 16 bits (a data payload width) results in the device automatically incrementing the address pointer (provided the SCS pin remains active low for all sequences).
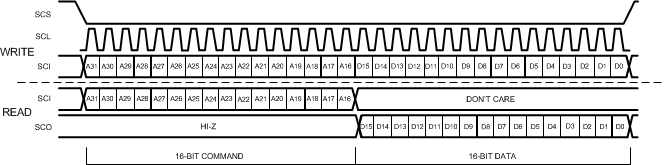 Figure 31. CDCM6208V1F SPI Port Message Sequencing
Figure 31. CDCM6208V1F SPI Port Message Sequencing
10.5.4 I2C Serial Interface
With SI_MODE1=0 and SI_MODE0=1 the CDCM6208V1F enters I 2C mode. The I2C port on the CDCM6208V1F works as a slave device and supports both the 100 kHz standard mode and 400 kHz fast mode operations. Fast mode imposes a glitch tolerance requirement on the control signals. Therefore, the input receivers ignore pulses of less than 50 ns duration. The inputs of the device also incorporates a Schmitt trigger at the SDA and SCL inputs to provide receiver input hysteresis for increased noise robustness.
NOTE
Communication through I2C is not possible while RESETN is held low.
In an I2C bus system, the CDCM6208V1F acts as a slave device and is connected to the serial bus (data bus SDA and clock bus SCL). The SDA port is bidirectional and uses an open drain driver to permit multiple devices to be connected to the same serial bus. The CDCM6208V1F allows up to four unique CDCM6208V1F slave devices to occupy the I2C bus in addition to any other I2C slave device with a different I2C address. These slave devices are accessed via a 7-bit slave address transmitted as part of an I2C packet. Only the device with a matching slave address responds to subsequent I2C commands. The device slave address is 10101xx (the two LSBs are determined by the AD1 and AD0 pins). The five MSBs are hard-wired, while the two LSBs are set through pins on device powerup.
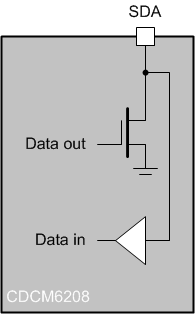 Figure 32.
Figure 32.
During the data transfer through the I2C port interface, one clock pulse is generated for each data bit transferred. The data on the SDA line must be stable during the high period of the clock. The high or low state of the data line can change only when the clock signal on the SCL line is low. The start data transfer condition is characterized by a high-to-low transition on the SDA line while SCL is high. The stop data transfer condition is characterized by a low-to-high transition on the SDA line while SCL is high. The start and stop conditions are always initiated by the master. Every byte on the SDA line must be eight bits long. Each byte must be followed by an acknowledge bit and bytes are sent MSB first.
The acknowledge bit (A) or non-acknowledge bit (A) is the 9thbit attached to any 8-bit data byte and is always generated by the receiver to inform the transmitter that the byte has been received (when A = 0) or not (when A = 1). A = 0 is done by pulling the SDA line low during the 9thclock pulse and A = 1 is done by leaving the SDA line high during the 9thclock pulse.
The I2C master initiates the data transfer by asserting a start condition which initiates a response from all slave devices connected to the serial bus. Based on the 8-bit address byte sent by the master over the SDA line (consisting of the 7-bit slave address (MSB first) and an R/W bit), the device whose address corresponds to the transmitted address responds by sending an acknowledge bit. All other devices on the bus remain idle while the selected device waits for data transfer with the master. The CDCM6208V1F slave address bytes are given in below table.
After the data transfer has occurred, stop conditions are established. In write mode, the master asserts a stop condition to end data transfer during the 10 thclock pulse following the acknowledge bit for the last data byte from the slave. In read mode, the master receives the last data byte from the slave but does not pull SDA low during the 9thclock pulse. This is known as a non-acknowledge bit. By receiving the non-acknowledge bit, the slave knows the data transfer is finished and enters the idle mode. The master then takes the data line low during the low period before the 10 thclock pulse, and high during the 10 thclock pulse to assert a stop condition.
For "Register Write/Read" operations, the I2C master can individually access addressed registers, that are made of two 8-bit data bytes.
Table 9. I2C Slave Address Byte
| A6 | A5 | A4 | A3 | A2 | AD1 | AD0 | R/W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1/0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1/0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1/0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1/0 |
Table 10. Generic Programming Sequence
| S | Start Condition | ||||||||||||||
| Sr | Repeated Condition | ||||||||||||||
| R/W | 1 = Read (Rd) from slave; 0 = Write (Wr) to slave | ||||||||||||||
| A | Acknowledge (ACK = 0 and NACK = 1) | ||||||||||||||
| P | Stop Condition | ||||||||||||||
| Master to Slave Transmission | |||||||||||||||
| Slave to Master Transmission | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| S | SLAVE Address | Wr | A | Register Address | A | Register Address | A | Data Byte | A | Data Byte | A | P |
| 1 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| S | SLAVE Address | Wr | A | Register Address | A | Register Address | A | S | Slave Address | Rd | A | Data Byte | A | Data Byte | A | P |
10.6 Register Maps
In SPI/I2C mode the device can be configured through twenty registers. Register 4 configures the input, Reg 0-3 the PLL and dividers, and Register 5 - 20 configures the 8 different outputs.
 Figure 35. Device Register Map
Figure 35. Device Register Map
Table 11. Register 0
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | These bits must be set to 0 | |
| 9:7 | LF_C3[2:0] | PLL Internal Loop Filter (C3) | PLL Internal Loop Filter Capacitor (C3) Selection 000 → 35 pF 001→ 112.5 pF 010 → 177.5 pF 011 → 242.5 pF 100 → 310 pF 101 → 377.5 pF 110 → 445 pF 111 → 562.5 pF |
| 6:4 | LF_R3[2:0] | PLL Internal Loop Filter (R3) | PLL Internal Loop Filter Resistor (R3) Selection 000 → 10 Ω 001 → 30 Ω 010 → 60 Ω 011 → 100 Ω 100 → 530 Ω 101→ 1050 Ω 110 → 2080 Ω 111 → 4010 Ω |
| 3:1 | PLL_ICP[2:0] | PLL Charge Pump | PLL Charge Pump Current Setting 000 → 500 µA 001 → 1.0 mA 010 → 1.5 mA 011 → 2.0 mA 100 → 2.5 mA 101 → 3.0 mA 110 → 3.5 mA 111→ 4.0 mA |
| 0 | RESERVED | This bit is tied to zero statically, and it is recommended to set to 0 when writing to register. |
Table 12. Register 1
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15:2 | PLL_REFDIV[13:0] | PLL Reference Divider | PLL Reference 14-b Divider Selection (Divider value is register value +1) |
| 1:0 | PLL_FBDIV1[9:8] | PLL Feedback Divider 1 | PLL Feedback 10-b Divider Selection, Bits 9:8 |
Table 13. Register 2
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15:8 | PLL_FBDIV1[7:0] | PLL Feedback Divider 1 | PLL Feedback 10-b Divider Selection, Bits 7:0 (Divider value is register value +1) |
| 7:0 | PLL_FBDIV0[7:0] | PLL Feedback Divider 0 | PLL Feedback 8-b Divider Selection (Divider value is register value +1) |
Table 14. Register 3
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15:13 | RESERVED | These bits must be set to 0 | |
| 12 | ST1_SEL_REFCLK | Device Status | Reference clock status enable on Status 1 pin: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable (See Table 7 for full description) |
| 11 | ST1_LOR_EN | Loss-of-reference Enable on Status 1 pin: 0 → Disable" 1 → Enable (See Table 7 for full description) |
|
| 10 | ST1_PLLLOCK_EN | PLL Lock Indication Enable on Status 1 pin: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable (See Table 7 for full description) |
|
| 9 | ST0_SEL_REFCLK | Reference clock status enable on Status 0 pin: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable (See Table 7 for full description) |
|
| 8 | ST0_LOR_EN | Loss-of-reference Enable on Status 0 pin: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable (See Table 7 for full description) |
|
| 7 | ST0_PLLLOCK_EN | PLL Lock Indication Enable on Status 0 pin:" 0 → Disable 1 → Enable (See Table 7 for full description) |
|
| 6 | RSTN | Device Reset | Device Reset Selection: 0 → Device In Reset (retains register values) 1 → Normal Operation |
| 5 | SYNCN | Output Divider | Output Channel Dividers Synchronization Enable: 0 → Forces synchronization 1 → Exits synchronization |
| 4 | ENCAL | PLL/VCO | PLL/VCO Calibration Enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable |
| 3:2 | PS_B[1:0] | PLL Prescaler Divider B | PLL Prescaler 1 Integer Divider Selection: 00 → Divide-by-4 01→ Divide-by-5 10 → Divide-by-6 11 → RESERVED used for Y2, Y3, Y6, and Y7 |
| 1:0 | PS_A[1:0] | PLL Prescaler Divider A | PLL Prescaler 0 Integer Divider Selection: 00 → Divide-by-4 01 → Divide-by-5 10 → Divide-by-6 11 → RESERVED used in PLL feedback, Y0, Y1, Y4, and Y5 |
Table 15. Register 4
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | SMUX_PW[1:0] | Reference Input Smart MUX | Smart MUX Pulse Width Selection. This bit controls the Smart MUX delay and waveform reshaping. 00 → PLL Smart MUX Clock Delay and Reshape Disabled (default in all pin modes) 01 → PLL Smart MUX Clock Delay Enable 10 → PLL Smart MUX Clock Reshape Enable 11 → PLL Smart MUX Clock Delay and Reshape Enable |
| 13 | SMUX_MODE_SEL | Smart MUX Mode Selection: 0 → Auto select 1 → Manual select Note: in Auto select mode, both input buffers must be enabled. Set R4.5 = 1 and R4.2 = 1 |
|
| 12 | SMUX_REF_SEL | Smart MUX Selection for PLL Reference: 0 → Primary 1 → Secondary (only if REF_SEL pin is high) This bit is ignored when smartmux is set to auto select (e.g. R4.13 = 0). See Table 7 for details. |
|
| 11:8 | CLK_PRI_DIV[3:0] | Primary Input Divider | Primary Input (R) Divider Selection: 0000 → Divide by 1 1111 → Divide by 16 |
| 7:6 | SEC_SELBUF[1:0] | Secondary Input | Secondary Input Buffer Type Selection: 00 → CML 01 → LVDS 10 → LVCMOS 11 → Crystal |
| 5 | EN_SEC_CLK | Secondary input enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable |
|
| 4:3 | PRI_SELBUF[1:0] | Primary Input | Primary Input Buffer Type Selection: 00 → CML 01 → LVDS 10 → LVCMOS 11 → LVCMOS |
| 2 | EN_PRI_CLK | Primary input enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable |
|
| 1 | SEC_SUPPLY (1) | Secondary Input | Supply voltage for secondary input: 0 → 1.8 V 1 → 2.5/3.3 V |
| 0 | PRI_SUPPLY (2) | Primary Input | Supply voltage for primary input: 0 → 1.8 V 1 → 2.5/3.3 V |
Table 16. Register 5
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 12 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 11 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 10 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 9 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 8:7 | SEL_DRVR_CH1[1:0] | Output Channel 1 | Output Channel 1 Type Selection: 00, 01 → LVDS 10 → CML 11 → PECL |
| 6:5 | EN _CH1[1:0] | Output channel 1 enable: 00 → Disable 01 → Enable 10 → Drive static 0 11 → Drive static 1 |
|
| 4:3 | SEL_DRVR_CH0[1:0] | Output Channel 0 | Output Channel 0 Type Selection: 00, 01 → LVDS 10 → CML 11 → PECL |
| 2:1 | EN_CH0[1:0] | Output channel 0 enable: 00 → Disable 01 → Enable 10 → Drive static 0 11 → Drive static 1 |
|
| 0 | SUPPLY_CH0_1 (1) | Output Channels 0 and 1 |
Output Channels 0 and 1 Supply Voltage Selection: 0 → 1.8 V 1 → 2.5/3.3 V |
Table 17. Register 6
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 12 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 11 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 10 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 9 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 8 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 7:0 | OUTDIV0_1[7:0] | Output Channels 0 and 1 |
Output channels 0 and 1 8-b output integer divider setting (Divider value is register value +1) |
Table 18. Register 7
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 12 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 11 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 10 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 9 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 8:7 | SEL_DRVR_CH3[1:0] | Output Channel 3 | Output Channel 3 Type Selection: 00, 01 → LVDS 10 → CML 11 → PECL |
| 6:5 | EN_CH3[1:0] | Output channel 3 enable: 00 → Disable 01 → Enable 10 → Drive static 0 11 → Drive static 1 |
|
| 4:3 | SEL_DRVR_CH2[1:0] | Output Channel 2 | Output Channel 2 Type Selection: 00, 01 → LVDS 10 → CML" 11 → PECL |
| 2:1 | EN_CH2[1:0] | Output channel 2 enable: 00 → Disable 01 → Enable 10 → Drive static 0 11 → Drive static 1 |
|
| 0 | SUPPLY_CH2_3 (1) | Output Channels 2 and 3 |
Output Channels 2 and 3 Supply Voltage Selection: 0 → 1.8 V 1 → 2.5/3.3 V |
Table 19. Register 8
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 12 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 11 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 10 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 9 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 8 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 7:0 | OUTDIV2_3[7:0] | Output Channels 2 and 3 |
Output channels 2 and 3 8-b output integer divider setting (Divider value is register value +1) |
Table 20. Register 9
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14:13 | OUTMUX_CH4[1:0] | Output Channel 4 | Output MUX setting for output channel 4: 00 and 11 → PLL 01 → Primary input 10 → Secondary input |
| 12:10 | PRE_DIV_CH4[2:0] | Output channel 4 fractional divider's 3-b pre-divider setting (this pre-divider is bypassed if Q9.9 = 0) 000 → Divide by 2 001 → Divide by 3 111 → Divide by 1 All other combinations reserved |
|
| 9 | EN_FRACDIV_CH4 | Output channel 4 fractional divider enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable |
|
| 8 | LVCMOS_SLEW_CH4 | Output channel 4 LVCMOS output slew: 0 → Normal 1 → Slow |
|
| 7 | EN_LVCMOS_N_CH4 | Output channel 4 negative-side LVCMOS enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable (Negative side can only be enabled if positive side is enabled) |
|
| 6 | EN_LVCMOS_P_CH4 | Output channel 4 positive-side LVCMOS enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable |
|
| 5 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 4:3 | SEL_DRVR_CH4[2:0] | Output channel 4 type selection: 00 or 01 → LVDS 10 → LVCMOS 11 → HCSL |
|
| 2:1 | EN_CH4[1:0] | Output channel 4 enable: 00 → Disable 01 → Enable 10 → Drive static 0 11 → Drive static 1 |
|
| 0 | SUPPLY_CH4 (1) | Output channel 4 Supply Voltage Selection: 0 → 1.8 V 1 → 2.5/3.3 V |
Table 21. Register 10
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 12 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 11:4 | OUTDIV4[7:0] | Output Channel 4 | Output channel 4 8-b integer divider setting (Divider value is register value +1) |
| 3:0 | FRACDIV4[19:16] | Output channel 4 20-b fractional divider setting, bits 19 - 16 |
Table 22. Register 11
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | FRACDIV4[15:0] | Output Channel 4 | Output channel 4 20-b fractional divider setting, bits 15 - 0 |
Table 23. Register 12
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14:13 | OUTMUX_CH5[1:0] | Output Channel 5 | Output MUX setting for output channel 5: 00 and 11 → PLL 01 → Primary input 10 → Secondary input |
| 12:10 | PRE_DIV_CH5[2:0] | Output channel 5 fractional divider's 3-b pre-divider setting (this pre-divider is bypassed if Q12.9 = 0) 000 → Divide by 2 001 → Divide by 3 111 → Divide by 1 All other combinations reserved |
|
| 9 | EN_FRACDIV_CH5 | Output channel 5 fractional divider enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable |
|
| 8 | LVCMOS_SLEW_CH5 | Output channel 5 LVCMOS output slew: 0 → Normal 1 → Slow |
|
| 7 | EN_LVCMOS_N_CH5 | Output channel 5 negative-side LVCMOS enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable (Negative side can only be enabled if positive side is enabled) |
|
| 6 | EN_LVCMOS_P_CH5 | Output channel 5 positive-side LVCMOS enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable |
|
| 5 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 4:3 | SEL_DRVR_CH5[2:0] | Output channel 5 type selection: 00 or 01 → LVDS 10 → LVCMOS 11 → HCSL |
|
| 2:1 | EN_CH5[1:0] | Output channel 5 enable: 00 → Disable 01 → Enable 10 → Drive static 0 11 → Drive static 1 |
|
| 0 | SUPPLY_CH5 (1) | Output channel 5Supply Voltage Selection: 0 → 1.8 V 1 → 2.5/3.3 V |
Table 24. Register 13
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 12 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 11:4 | OUTDIV5[7:0] | Output Channel 5 | Output channel 5 8-b integer divider setting (Divider value is register value +1) |
| 3:0 | FRACDIV5[19:16] | Output channel 5 20-b fractional divider setting, bits 19-16 |
Table 25. Register 14
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | FRACDIV5[15:0] | Output Channel 5 | Output channel 5 20-b fractional divider setting, bits 15-0 |
Table 26. Register 15
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 12:10 | PRE_DIV_CH6[2:0] | Output Channel 6 | Output channel 6 fractional divider's 3-b pre-divider setting (this pre-divider is bypassed if Q15.9 = 0) 000 → Divide by 2 001 → Divide by 3 111 → Divide by 1 All other combinations reserved |
| 9 | EN_FRACDIV_CH6 | Output channel 6 fractional divider enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable |
|
| 8 | LVCMOS_SLEW_CH6 | Output channel 6 LVCMOS output slew: 0 → Normal 1 → Slow |
|
| 7 | EN_LVCMOS_N_CH6 | Output channel 6 negative-side LVCMOS enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable (Negative side can only be enabled if positive side is enabled) |
|
| 6 | EN_LVCMOS_P_CH6 | Output channel 6 positive-side LVCMOS enable: 0 → Disable 1 → Enable |
|
| 5 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 4:3 | SEL_DRVR_CH6[1:0] | Output channel 6 type selection: 00 or 01 → LVDS 10 → LVCMOS 11 → HCSL |
|
| 2:1 | EN_CH6[1:0] | Output channel 6 enable: 00 → Disable 01 → Enable 10 → Drive static 0 11 → Drive static 1 |
|
| 0 | SUPPLY_CH6 (1) | Output channel 6 Supply Voltage Selection: 0 → 1.8 V 1 → 2.5/3.3 V |
Table 27. Register 16
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 12 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 11:4 | OUTDIV6[7:0] | Output Channel 6 | Output channel 6 8-b integer divider setting (Divider value is register value +1) |
| 3:0 | FRACDIV6[19:16] | Output channel 6 20-b fractional divider setting, bits 19-16 |
Table 28. Register 17
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | FRACDIV6[15:0] | Output Channel 6 | Output channel 6 20-b fractional divider setting, bits 15-0 |
Table 29. Register 18
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 12:10 | PRE_DIV_CH7[2:0] | Output Channel 7 | Output channel 7 fractional divider's 3-b pre-divider setting (this pre-divider is bypassed if Q18.9 = 0) 000 → Divide by 2 001 → Divide by 3 111 → Divide by 1 All other combinations reserved |
| 9 | EN_FRACDIV_CH7 | Output channel 7 fractional divider enable: 0 → Disable, 1 → Enable | |
| 8 | LVCMOS_SLEW_CH7 | Output channel 7 LVCMOS output slew: 0 → Normal, 1 → Slow | |
| 7 | EN_LVCMOS_N_CH7 | Output channel 7 negative-side LVCMOS enable: 0 → Disable, 1 → Enable (Negative side can only be enabled if positive side is enabled) | |
| 6 | EN_LVCMOS_P_CH7 | Output channel 7 positive-side LVCMOS enable: 0 → Disable, 1 → Enable | |
| 5 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 4:3 | SEL_DRVR_CH7[2:0] | Output channel 7 type selection:00 or 01 → LVDS, 10 → LVCMOS, 11 → HCSL | |
| 2:1 | EN_CH7[1:0] | Output channel 7 enable: 00 → Disable, 01 → Enable, 10 → Drive static low, 11 → Drive static high | |
| 0 | SUPPLY_CH7 (1) | Output channel 7 Supply Voltage Selection: 0 → 1.8 V, 1 → 2.5/3.3 V |
Table 30. Register 19
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 12 | RESERVED | This bit must be set to 0 | |
| 11:4 | OUTDIV7[7:0] | Output Channel 7 | Output channel 7 8-b integer divider setting (Divider value is register value +1) |
| 3:0 | FRACDIV7[19:16] | Output channel 7 20-b fractional divider setting, bits 19-16 |
Table 31. Register 20
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | FRACDIV7[15:0] | Output Channel 7 | Output channel 7 20-b fractional divider setting, bits 15-0 |
Table 32. Register 21 (Read Only)
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 14 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 13 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 12 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 11 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 10 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 9 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 8 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 7 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 6 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 5 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 4 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 3 | RESERVED | This bit will read a 0 | |
| 2 | PLL_UNLOCK | Device Status Monitoring | Indicates unlock status for PLL (digital): 0 → PLL locked 1 → PLL unlocked Note: the external output signal on Status 0 or Status 1 uses a reversed logic, and indicates "lock" with a VOH signal and unlock with a VOL signaling level. |
| 1 | LOS_REF | Loss of reference input observed at input Smart MUX output in observation window for PLL: 0 → Reference input present 1 → Loss of reference input |
|
| 0 | SEL_REF | Indicates Reference Selected for PLL: 0 → Primary 1 → Secondary |
Table 33. Register 40 (Read Only)
| BIT | BIT NAME | RELATED BLOCK | DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | Ignore | |
| 14 | RESERVED | Ignore | |
| 13 | RESERVED | Ignore | |
| 12 | RESERVED | Ignore | |
| 11 | RESERVED | Ignore | |
| 10 | RESERVED | Ignore | |
| 9 | RESERVED | Ignore | |
| 8 | RESERVED | Ignore | |
| 7 | RESERVED | Ignore | |
| 6 | RESERVED | Ignore | |
| 5:3 | VCO_VERSION | Device Information | Indicates the device version (Read only): 000 → CDCM6208V1F |
| 2:0 | DIE_REVISION | Indicates the silicon die revision (Read only): 00X --> Engineering Prototypes 010 --> Production Material |
Table 34. Default Register Setting For SPI/I2C Modes
| Register | CDCM6208V1F |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0x01B9 |
| 1 | 0x0000 |
| 2 | 0x0018 |
| 3 | 0x08F4 |
| 4 | 0x20B7 |
| 5 | 0x01BA |
| 6 | 0x0003 |
| 7 | 0x0002 |
| 8 | 0x0003 |
| 9 | 0x0000 |
| 10 | 0x0040 |
| 11 | 0x0000 |
| 12 | 0x0000 |
| 13 | 0x0040 |
| 14 | 0x0000 |
| 15 | 0x0000 |
| 16 | 0x0040 |
| 17 | 0x0000 |
| 18 | 0x0002 |
| 19 | 0x0040 |
| 20 | 0x7940 |
| . | . |
| . | . |
| . | . |
| 40 | 0x0001 |