ZHCSF03 March 2016 CDCM6208V2G
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 简化电路原理图
- 5 修订历史记录
- 6 说明 (续)
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information, Airflow = 0 LFM
- 8.5 Thermal Information, Airflow = 150 LFM
- 8.6 Thermal Information, Airflow = 250 LFM
- 8.7 Thermal Information, Airflow = 500 LFM
- 8.8 Single Ended Input Characteristics
- 8.9 Single Ended Input Characteristics (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 8.10 Differential Input Characteristics (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 8.11 Crystal Input Characteristics (SEC_REF)
- 8.12 Single Ended Output Characteristics (STATUS1, STATUS0, SDO, SDA)
- 8.13 PLL Characteristics
- 8.14 LVCMOS Output Characteristics
- 8.15 LVPECL (High-Swing CML) Output Characteristics
- 8.16 CML Output Characteristics
- 8.17 LVDS (Low-Power CML) Output Characteristics
- 8.18 HCSL Output Characteristics
- 8.19 Output Skew and Sync to Output Propagation Delay Characteristics
- 8.20 Device Individual Block Current Consumption
- 8.21 Worst Case Current Consumption
- 8.22 I2C TIMING
- 8.23 SPI Timing Requirements
- 8.24 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
- 10Detailed Description
-
11Application and Implementation
- 11.1 Application Information
- 11.2
Typical Applications
- 11.2.1
Design Requirements
- 11.2.1.1 Device Block-level Description
- 11.2.1.2 Device Configuration Control
- 11.2.1.3 Configuring the RESETN Pin
- 11.2.1.4 Preventing False Output Frequencies in SPI/I2C Mode at Startup:
- 11.2.1.5 Power Down
- 11.2.1.6 Device Power Up Timing:
- 11.2.1.7 Input Mux and Smart Input Mux
- 11.2.1.8 Universal INPUT Buffer (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 11.2.1.9 VCO Calibration
- 11.2.1.10 Reference Divider (R)
- 11.2.1.11 Input Divider (M)
- 11.2.1.12 Feedback Divider (N)
- 11.2.1.13 Prescaler Dividers (PS_A, PS_B)
- 11.2.1.14 Phase Frequency Detector (PFD)
- 11.2.1.15 Charge Pump (CP)
- 11.2.1.16
Programmable Loop Filter
- 11.2.1.16.1 Loop Filter Component Selection
- 11.2.1.16.2 Device Output Signaling
- 11.2.1.16.3 Integer Output Divider (IO)
- 11.2.1.16.4 Fractional Output Divider (FOD)
- 11.2.1.16.5 Output Synchronization
- 11.2.1.16.6 Output MUX on Y4 and Y5
- 11.2.1.16.7 Staggered CLK Output Powerup for Power Sequencing of a DSP
- 11.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 11.2.3 Application Performance Plots
- 11.2.1
Design Requirements
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14器件和文档支持
- 15机械、封装和可订购信息
7 Pin Configuration and Functions
RGZ Package
48 Pin VQFN
Top View
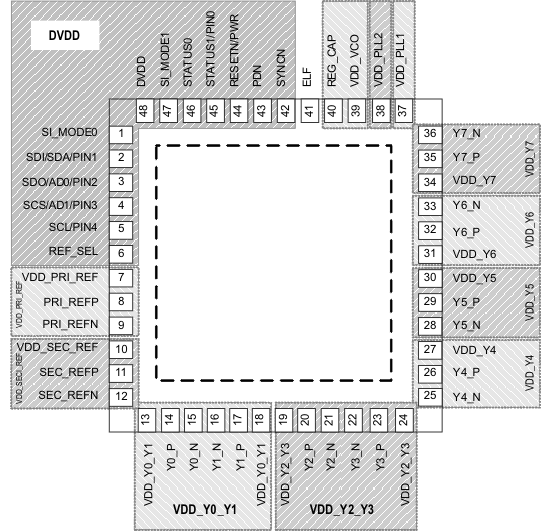
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||
| PRI_REFP | 8 | Input | Universal | Primary Reference Input + |
| PRI_REFN | 9 | Input | Universal | Primary Reference Input – |
| VDD_PRI_REF | 7 | PWR | Analog | Supply pin for reference inputs to set between 1.8 V, 2.5 V, or 3.3 V or connect to VDD_SEC_REF. |
| SEC_REFP | 11 | Input | Universal | Secondary Reference Input + |
| SEC_REFN | 12 | Input | Universal | Secondary Reference Input – |
| VDD_SEC_REF | 10 | PWR | Analog | Supply pin for reference inputs to set between 1.8 V, 2.5 V, or 3.3 V or connect to VDD_PRI_REF(2). |
| REF_SEL | 6 | Input | LVCMOS 50kΩ pull-up |
Manual Reference Selection MUX for PLL. In SPI or I2C mode the reference selection is also controlled through Register 4 bit 12. REF_SEL = 0 (≤ VIL): selects PRI_REF REF_SEL = 1 (≥ VIH): selects SEC_REF (when Reg 4.12 = 1). See Table 35 for detail. |
| ELF | 41 | Output | Analog | External loop filter pin for PLL |
| Y0_P | 14 | Output | Universal | Output 0 Positive Terminal |
| Y0_N | 15 | Output | Universal | Output 0 Negative Terminal |
| Y1_P | 17 | Output | Universal | Output 1 Positive Terminal |
| Y1_N | 16 | Output | Universal | Output 1 Negative Terminal |
| VDD_Y0_Y1 (2 pins) | 13, 18 | PWR | Analog | Supply pin for outputs 0, 1 to set between 1.8 V, 2.5 V or 3.3 V |
| Y2_P | 20 | Output | Universal | Output 2 Positive Terminal |
| Y2_N | 21 | Output | Universal | Output 2 Negative Terminal |
| Y3_P | 23 | Output | Universal | Output 3 Positive Terminal |
| Y3_N | 22 | Output | Universal | Output 3 Negative Terminal |
| VDD_Y2_Y3 (2 pins) | 19, 24 | PWR | Analog | Supply pin for outputs 2, 3 to set between 1.8 V, 2.5 V or 3.3 V |
| Y4_P | 26 | Output | Universal | Output 4 Positive Terminal |
| Y4_N | 25 | Output | Universal | Output 4 Negative Terminal |
| VDD_Y4 | 27 | PWR | Analog | Supply pin for output 4 to set between 1.8 V, 2.5 V or 3.3 V |
| Y5_P | 29 | Output | Universal | Output 5 Positive Terminal |
| Y5_N | 28 | Output | Universal | Output 5 Negative Terminal |
| VDD_Y5 | 30 | PWR | Analog | Supply pin for output 5 to set between 1.8 V, 2.5 V or 3.3 V |
| Y6_P | 32 | Output | Universal | Output 6 Positive Terminal |
| Y6_N | 33 | Output | Universal | Output 6 Negative Terminal |
| VDD_Y6 | 31 | PWR | Analog | Supply pin for output 6 to set between 1.8 V, 2.5 V or 3.3 V |
| Y7_P | 35 | Output | Universal | Output 7 Positive Terminal |
| Y7_N | 36 | Output | Universal | Output 7 Negative Terminal |
| VDD_Y7 | 34 | PWR | Analog | Supply pin for output 7 to set between 1.8 V, 2.5 V or 3.3 V |
| VDD_VCO | 39 | PWR | Analog | Analog power supply for PLL/VCO; This pin is sensitive to power supply noise; The supply of this pin and the VDD_PLL2 supply pin can be combined as they are both analog and sensitive supplies |
| VDD_PLL1 | 37 | PWR | Analog | Analog Power Supply Connections |
| VDD_PLL2 | 38 | PWR | Analog | Analog Power Supply Connections; This pin is sensitive to power supply noise; The supply of VDD_PLL2 and VDD_VCO can be combined as these pins are both power-sensitive, analog supply pins |
| DVDD | 48 | PWR | Analog | Digital Power Supply Connections; This is also the reference supply voltage for all control inputs and must match the expected input signal swing of control inputs. |
| GND | PAD | PWR | Analog | Power Supply Ground and Thermal Pad |
| STATUS0 | 46 | Output | LVCMOS | Status pin 0 (see Table 6 for details) |
| STATUS1/PIN0 | 45 | Output/ Input |
LVCMOS no pull resistor |
STATUS1: Status pin in SPI/I2C modes. For details see Table 4 for pin modes and Table 6 for status mode. PIN0: Control pin 0 in pin mode. |
| SI_MODE1 | 47 | Input | LVCMOS 50kΩ pull-up |
Serial Interface Mode or Pin mode selection. SI_MODE[1:0]=00: SPI mode; SI_MODE[1:0]=01: I2C mode; SI_MODE[1:0]=10: Pin Mode (No serial programming); SI_MODE[1:0]=11: RESERVED |
| SI_MODE0 | 1 | Input | LVCMOS 50kΩ pull-down |
|
| SDI/SDA/PIN1 | 2 | Input/ Output |
LVCMOS in Open drain out LVCMOS in no pull resistor |
SDI: SPI Serial Data Input SDA: I2C Serial Data (Read/Write bi-directional), open drain output; requires a pull-up resistor in I2C mode; PIN1: Control pin 1 in pin mode |
| SDO/AD0/PIN2 | 3 | Output/ Input |
LVCMOS out LVCMOS in LVCMOS in no pull resistor |
SDO: SPI Serial Data AD0: I2C Address Offset Bit 0 input PIN2: Control pin 2 in pin mode |
| SCS/AD1/PIN 3 | 4 | Input | LVCMOS no pull resistor |
SCS: SPI Latch Enable AD1: I2C Address Offset Bit 1 input PIN3: Control pin 3 in pin mode |
| SCL/PIN4 | 5 | Input | LVCMOS no pull resistor |
SCL: SPI/I2C Clock PIN4: Control pin 4 in pin mode |
| RESETN/PWR | 44 | Input | LVCMOS 50kΩ pull-up |
In SPI/I2C programming mode, external RESETN signal (active low). RESETN = V IL: device in reset (registers values are retained) RESETN = V IH: device active. The device can be programmed via SPI while RESETN is held low (this is useful to avoid any false output frequencies at power up). (1) In Pin mode this pin controls device core and I/O supply voltage setting. 0 = 1.8 V, 1 = 2.5/3.3 V for the device core and I/O power supply voltage. In pin mode, it is not possible to mix and match the supplies. All supplies should either be 1.8 V or 2.5/3.3 V. |
| REG_CAP | 40 | Output | Analog | Regulator Capacitor; connect a 10 µF cap with ESR below 1 Ω to GND at frequencies above 100 kHz |
| PDN | 43 | Input | LVCMOS 50kΩ pull-up |
Power Down Active low. When PDN = VIH is normal operation. When PDN = VIL, the device is disabled and current consumption minimized. Exiting power down resets the entire device and defaults all registers. It is recommended to connect a capacitor to GND to hold the device in power-down until the digital and PLL related power supplies are stable. See section on power down in the application section. |
| SYNCN | 42 | Input | LVCMOS 50kΩ pull-up |
Active low. Device outputs are synchronized on a low-to-high transition on the SYNCN pin. SYNCN held low disables all outputs. |
(1) Note: the device cannot be programmed in I2C while RESETN is held low.
(2) If Secondary input buffer is disabled (Register 4 Bit 5 = 0), it is possible to connect VDD_SEC_REF to GND.