DLPS119B December 2018 – May 2022 DLP2010NIR
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Storage Conditions
- 6.3 ESD Ratings
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Timing Requirements
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics
- 6.9 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 6.10 Physical Characteristics of the Micromirror Array
- 6.11 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 6.12 Window Characteristics
- 6.13 Chipset Component Usage Specification
- 6.14 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.3 Application Curve
In a reflective spectroscopy application, a broadband light source illuminates a sample and the reflected light spectrum is dispersed onto the DLP2010NIR. A microprocessor in conjunction with the DLPC150/3470 controls individual DLP2010NIR micromirrors to reflect specific wavelengths of light to a single point detector. The microprocessor uses an analog-to-digital converter to sample the signal received by the detector into a digital value. By sequentially selecting different wavelengths of light and capturing the values at the detector, the microprocessor can then plot a spectral response to the light. This systems allows the measurement of the collected light and derive the wavelengths absorbed by the sample. This process leads to the absorption spectrum shown in Figure 8-2.
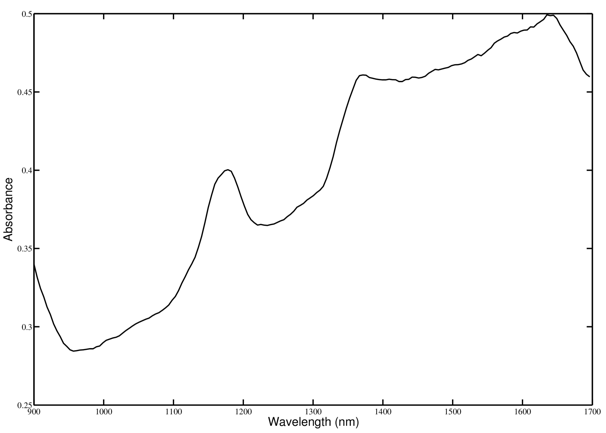 Figure 8-2 Sample DLP2010NIR Based
Spectrometer Output
Figure 8-2 Sample DLP2010NIR Based
Spectrometer Output