ZHCSHW7C february 2018 – july 2023 DLP3010
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Storage Conditions
- 6.3 ESD Ratings
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Timing Requirements
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics
- 6.9 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 6.10 Micromirror Array Physical Characteristics
- 6.11 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 6.12 Window Characteristics
- 6.13 Chipset Component Usage Specification
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.11 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micromirror tilt angle | DMD landed state(1) | 17 | degree | |||
| Micromirror tilt angle tolerance(2)(3)(4)(5) | –1.4 | 1.4 | degree | |||
| Micromirror tilt direction (6)(7) | Landed ON state | 180 | degree | |||
| Landed OFF state | 270 | |||||
| Micromirror crossover time(8) | Typical performance | 1 | 3 | µs | ||
| Micromirror switching time(9) | Typical performance | 10 | ||||
| Image performance(10) | Bright pixel(s) in active area (11) | Gray 10 Screen (12) | 0 | micromirrors | ||
| Bright pixel(s) in the POM (13) | Gray 10 Screen (12) | 1 | ||||
| Dark pixel(s) in the active area (14) | White Screen | 4 | ||||
| Adjacent pixel(s) (15) | Any Screen | 0 | ||||
| Unstable pixel(s) in active area (16) | Any Screen | 0 | ||||
(1) Measured relative to the plane formed by the overall micromirror array.
(2) Additional variation exists between the micromirror array and the package
datums.
(3) Represents the landed tilt angle variation relative to the nominal landed tilt
angle.
(4) Represents the variation that can occur between any two individual micromirrors,
located on the same device or located on different devices.
(5) For some applications, it is critical to account for the micromirror tilt angle
variation in the overall system optical design. With some system optical
designs, the micromirror tilt angle variation within a device may result in
perceivable non-uniformities in the light field reflected from the micromirror
array. With some system optical designs, the micromirror tilt angle variation
between devices may result in colorimetry variations, system efficiency
variations, or system contrast variations.
(6) When the micromirror array is
landed (not parked), the tilt direction of each individual micromirror is
dictated by the binary contents of the CMOS memory cell associated with each
individual micromirror. A binary value of 1 results in a micromirror landing in
the ON state direction. A binary value of 0 results in a micromirror landing in
the OFF state direction. See Figure 6-17.
(7) Micromirror tilt direction is measured as in a typical polar coordinate system:
Measuring counter-clockwise from a 0° reference which is aligned with the +X
Cartesian axis.
(8) The time required for a micromirror to nominally transition from one landed
state to the opposite landed state.
(9) The minimum time between successive transitions of a micromirror.
(10) Conditions of Acceptance: All DMD image quality returns will be evaluated using
the following projected image test conditions:
Test set degamma shall be linear
Test set brightness and contrast shall be set to nominal
The diagonal size of the projected image shall be a minimum of 20 inches
The projections screen shall be 1X gain
The projected image shall be inspected from a 38 inch minimum viewing distance
The image shall be in focus during all image quality tests
Test set degamma shall be linear
Test set brightness and contrast shall be set to nominal
The diagonal size of the projected image shall be a minimum of 20 inches
The projections screen shall be 1X gain
The projected image shall be inspected from a 38 inch minimum viewing distance
The image shall be in focus during all image quality tests
(11) Bright pixel definition: A single pixel or mirror that is stuck in the ON
position and is visibly brighter than the surrounding pixels
(12) Gray 10 screen definition: All areas of the screen are colored with the
following settings:
Red = 10/255
Green = 10/255
Blue = 10/255
Red = 10/255
Green = 10/255
Blue = 10/255
(13) POM definition: Rectangular border of off-state mirrors surrounding the active
area
(14) Dark pixel definition: A single pixel or mirror that is stuck in the OFF
position and is visibly darker than the surrounding pixels
(15) Adjacent pixel definition: Two or more stuck pixels sharing a common border or
common point, also referred to as a cluster
(16) Unstable pixel definition: A single pixel or mirror that does not operate in
sequence with parameters loaded into memory. The unstable pixel appears to be
flickering asynchronously with the image
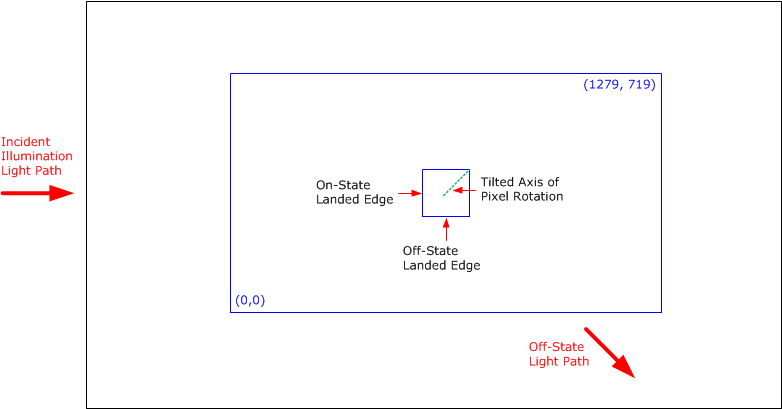 Figure 6-17 Landed Pixel Orientation and Tilt
Figure 6-17 Landed Pixel Orientation and Tilt