ZHCSE90D September 2015 – September 2020 DLPC910
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5
Register Map
- 7.5.1
Register Table Overview
- 7.5.1.1 DESTOP_INTERRUPT Register
- 7.5.1.2 MAIN_STATUS Register
- 7.5.1.3 DESTOP_CAL Register
- 7.5.1.4 DESTOP_DMD_ID_REG Register
- 7.5.1.5 DESTOP_CATBITS_REG Register
- 7.5.1.6 DESTOP_VERSION Register
- 7.5.1.7 DESTOP_RESET_REG Register
- 7.5.1.8 DESTOP_INFIFO_STATUS Register
- 7.5.1.9 DESTOP_BUS_SWAP Register
- 7.5.1.10 DESTOP_DMDCTRL Register
- 7.5.1.11 DESTOP_BIT_FLIP Register
- 7.5.1
Register Table Overview
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.4 Interface Training
The DLPC910 detects the phase differences between the ½ speed clock (used in the device driving the LVDS data) and the internally generated ½ speed data clocks to select a clock phase for data capture. This is done by supplying a simple repeating pattern on all of the data inputs while the INIT_ACTIVE output of the DLPC910 is high/active. The details of the training pattern are described below.
Figure 7-1 shows a simple block diagram of the training pattern insertion logic.
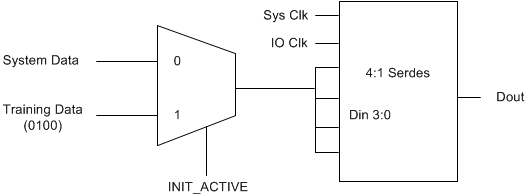 Figure 7-1 Block Diagram of Training Pattern Logic
Figure 7-1 Block Diagram of Training Pattern LogicThe expected training pattern is 0100. In Figure 7-2, the data input to the 4:1 SERDES cells is captured on the rising edge of the ½ speed system clock. The output latency shown is based on the documentation for the Xilinx SERDES cells. Individual implementation may vary depending on the type of cells, technology, and design technique used.
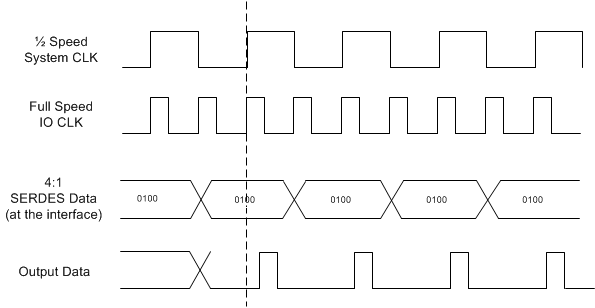 Figure 7-2 Training Pattern Alignment
Figure 7-2 Training Pattern AlignmentIn Xilinx FPGAs (due to the construction of the ISERDES and OSERDES cells) a pattern of 0010 needs to be applied to the output/transmitting SERDES cells data pins (D1 = 0, D2 = 0, D3 = 1, D4 = 0) in order to receive a result of 0100 (Q1 = 0, Q2 = 1, Q3 = 0, Q4 = 0) at the input/receiving SERDES cell.
The patterns should be applied on all of the data and DVALID pins. In this respect, the interface is treated as a 17 bit interface with DVALID being the 17th data bit. The receiving logic in the DLPC910 adjusts the clock phase until the correct pattern is seen at the inputs. This allows DLPC910 to correctly select a clock phase for data capture and will contribute to a more robust interface. It is important that the training pattern is applied to the DVALID and data inputs of the DLPC910 before reset to the device is de-asserted, as training commences immediately on the de-assertion of reset. The INIT_ACTIVE signal is asserted while the device is held in reset in order to help facilitate this behavior.