ZHCSI52G August 2016 – March 2019 DRA780 , DRA781 , DRA782 , DRA783 , DRA785 , DRA786 , DRA787 , DRA788
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Device Comparison
-
4Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 Pin Diagram
- 4.2 Pin Attributes
- 4.3
Signal Descriptions
- 4.3.1 VIP
- 4.3.2 DSS
- 4.3.3 SD_DAC
- 4.3.4 ADC
- 4.3.5 Camera Control
- 4.3.6 CPI
- 4.3.7 CSI2
- 4.3.8 EMIF
- 4.3.9 GPMC
- 4.3.10 Timers
- 4.3.11 I2C
- 4.3.12 UART
- 4.3.13 McSPI
- 4.3.14 QSPI
- 4.3.15 McASP
- 4.3.16 DCAN and MCAN
- 4.3.17 GMAC_SW
- 4.3.18 SDIO Controller
- 4.3.19 GPIO
- 4.3.20 ePWM
- 4.3.21 ATL
- 4.3.22 Test Interfaces
- 4.3.23 System and Miscellaneous
- 4.3.24 Power Supplies
- 4.4 Pin Multiplexing
- 4.5 Connections for Unused Pins
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power on Hour (POH) Limits
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Operating Performance Points
- 5.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.7
Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-6 LVCMOS DDR DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-7 Dual Voltage LVCMOS I2C DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-8 IQ1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-9 IHHV1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-10 LVCMOS Analog OSC Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-11 Dual Voltage LVCMOS DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-12 Analog-to-Digital ADC Subsystem Electrical Specifications
- 5.8 Thermal Characteristics
- 5.9
Timing Requirements and Switching Characteristics
- 5.9.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 5.9.2 Interface Clock Specifications
- 5.9.3 Power Supply Sequences
- 5.9.4 Clock Specifications
- 5.9.5 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 5.9.6
Peripherals
- 5.9.6.1 Timing Test Conditions
- 5.9.6.2 VIP
- 5.9.6.3 DSS
- 5.9.6.4 EMIF
- 5.9.6.5 GPMC
- 5.9.6.6 GP Timers
- 5.9.6.7 I2C
- 5.9.6.8 UART
- 5.9.6.9 McSPI
- 5.9.6.10 QSPI
- 5.9.6.11
McASP
- Table 5-50 Timing Requirements for McASP1
- Table 5-51 Timing Requirements for McASP2
- Table 5-52 Timing Requirements for McASP3
- Table 5-53 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McASP1
- Table 5-54 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McASP2
- Table 5-55 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McASP3
- 5.9.6.12 DCAN and MCAN
- 5.9.6.13
GMAC_SW
- 5.9.6.13.1 GMAC MDIO Interface Timings
- 5.9.6.13.2
GMAC RGMII Timings
- Table 5-63 Timing Requirements for rgmiin_rxc - RGMIIn Operation
- Table 5-64 Timing Requirements for GMAC RGMIIn Input Receive for 10/100/1000 Mbps
- Table 5-65 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for rgmiin_txctl - RGMIIn Operation for 10/100/1000 Mbit/s
- Table 5-66 Switching Characteristics for GMAC RGMIIn Output Transmit for 10/100/1000 Mbps
- 5.9.6.14 SDIO Controller
- 5.9.6.15 GPIO
- 5.9.6.16 ATL
- 5.9.7
Emulation and Debug Subsystem
- 5.9.7.1
JTAG Electrical Data/Timing
- Table 5-78 Timing Requirements for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- Table 5-79 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- Table 5-80 Timing Requirements for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG With RTCK
- Table 5-81 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG With RTCK
- 5.9.7.2 Trace Port Interface Unit (TPIU)
- 5.9.7.1
JTAG Electrical Data/Timing
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Description
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 DSP Subsystem
- 6.4 IPU
- 6.5 EVE
- 6.6 Memory Subsystem
- 6.7 Interprocessor Communication
- 6.8 Interrupt Controller
- 6.9 EDMA
- 6.10 Peripherals
- 6.11 On-Chip Debug
-
7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7.1 Introduction
- 7.2 Power Optimizations
- 7.3 Core Power Domains
- 7.4 Single-Ended Interfaces
- 7.5 Differential Interfaces
- 7.6 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 7.7 DDR2 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 7.8
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 7.8.1 DDR3 General Board Layout Guidelines
- 7.8.2
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 7.8.2.1 Board Designs
- 7.8.2.2 DDR3 Device Combinations
- 7.8.2.3 DDR3 Interface Schematic
- 7.8.2.4 Compatible JEDEC DDR3 Devices
- 7.8.2.5 PCB Stackup
- 7.8.2.6 Placement
- 7.8.2.7 DDR3 Keepout Region
- 7.8.2.8 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 7.8.2.9 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 7.8.2.10 Net Classes
- 7.8.2.11 DDR3 Signal Termination
- 7.8.2.12 VTT
- 7.8.2.13 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies and Routing Definition
- 7.8.2.14 Data Topologies and Routing Definition
- 7.8.2.15 Routing Specification
- 7.9 CVIDEO/SD-DAC Guidelines and Electrical Data/Timing
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.2.3.1 PDN Resistance and IR Drop
Lumped methodology consists of grouping all of the power pins on both the PMIC (voltage source) and processor (current sink) devices. Then the PMIC source is set to an expected Use Case voltage level and the processor load has its Use Case current sink value set as well. Now the lumped/effective resistance for the power rail trace/plane routes can be determine based upon the actual layout’s power rail etch wide, shape, length, via count and placement Figure 7-5 illustrates the pin-grouping/lumped concept.
The lumped methodology consists of importing the PCB layout database (from Cadence Allegro tool or any other layout design tool) into the static IR drop modeling and simulation tool of preference for the PCB designer. This is followed by applying the correct PCB stack-up information (thickness, material properties) of the PCB dielectric and metallization layers. The material properties of dielectric consist of permittivity (Dk) and loss tangent (Df).
For the conductor layers, the correct conductivity needs to be programmed into the simulation tool. This is followed by pin-grouping of the power and ground nets, and applying appropriate voltage/current sources. The current and voltage information can be obtained from the power and voltage specifications of the device under different operating conditions / Use Cases.
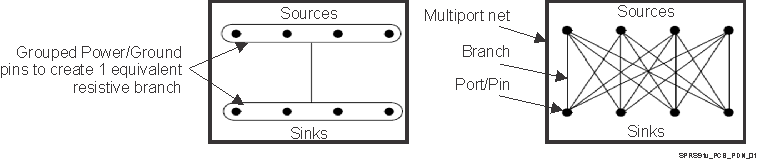 Figure 7-5 Pin-grouping concept: Lumped and Distributed Methodologies
Figure 7-5 Pin-grouping concept: Lumped and Distributed Methodologies