ZHCSN40K February 2019 – April 2024 DRA829J , DRA829J-Q1 , DRA829V , DRA829V-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Device Comparison
-
5 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 5.1 Pin Diagram
- 5.2 Pin Attributes
- 5.3
Signal Descriptions
- 5.3.1 ADC
- 5.3.2 DDRSS
- 5.3.3 GPIO
- 5.3.4 I2C
- 5.3.5 I3C
- 5.3.6 MCAN
- 5.3.7 MCSPI
- 5.3.8 UART
- 5.3.9 MDIO
- 5.3.10 CPSW2G
- 5.3.11 CPSW9G
- 5.3.12 ECAP
- 5.3.13 EQEP
- 5.3.14 EHRPWM
- 5.3.15 USB
- 5.3.16 SERDES
- 5.3.17 OSPI
- 5.3.18 Hyperbus
- 5.3.19 GPMC
- 5.3.20 MMC
- 5.3.21 CPTS
- 5.3.22 UFS
- 5.3.23 PRU_ICSSG [Currently Not Supported]
- 5.3.24 MCASP
- 5.3.25 DSS
- 5.3.26 DP
- 5.3.27 Camera Streaming Interface Receiver (CSI_RX_IF) Subsystem
- 5.3.28 DSI_TX
- 5.3.29 VPFE
- 5.3.30 DMTIMER
- 5.3.31 Emulation and Debug
- 5.3.32 System and Miscellaneous
- 5.3.33 Power Supply
- 5.4 Pin Multiplexing
- 5.5 Pin Connectivity Requirements
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Power-On-Hour (POH) Limits
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Operating Performance Points
- 6.6
Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.1 I2C, Open-Drain, Fail-Safe (I2C OD FS) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.2 Fail-Safe Reset (FS Reset) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.3 HFOSC/LFOSC Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.4 eMMCPHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.5 SDIO Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.6 CSI-2/DSI D-PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.7 ADC12B Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.8 MLB LVCMOS Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.9 LVCMOS Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.10 USB2PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.11 SerDes 4-L-PHY/2-L-PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.12 UFS M-PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.13 eDP/DP AUX-PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.14 DDR0 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 6.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 6.9
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 6.9.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 6.9.2
Power Supply Sequencing
- 6.9.2.1 Power Supply Slew Rate Requirement
- 6.9.2.2 Combined MCU and Main Domains Power-Up Sequencing
- 6.9.2.3 Combined MCU and Main Domains Power- Down Sequencing
- 6.9.2.4 Isolated MCU and Main Domains Power- Up Sequencing
- 6.9.2.5 Isolated MCU and Main Domains, Primary Power- Down Sequencing
- 6.9.2.6 Entry and Exit of MCU Only State
- 6.9.2.7 Entry and Exit of DDR Retention State
- 6.9.3 System Timing
- 6.9.4
Clock Specifications
- 6.9.4.1
Input and Output Clocks / Oscillators
- 6.9.4.1.1 WKUP_OSC0 Internal Oscillator Clock Source
- 6.9.4.1.2 WKUP_OSC0 LVCMOS Digital Clock Source
- 6.9.4.1.3 Auxiliary OSC1 Internal Oscillator Clock Source
- 6.9.4.1.4 Auxiliary OSC1 LVCMOS Digital Clock Source
- 6.9.4.1.5 Auxiliary OSC1 Not Used
- 6.9.4.1.6 WKUP_LFOSC0 Internal Oscillator Clock Source
- 6.9.4.2 Output Clocks
- 6.9.4.3 PLLs
- 6.9.4.4 Module and Peripheral Clocks Frequencies
- 6.9.4.1
Input and Output Clocks / Oscillators
- 6.9.5
Peripherals
- 6.9.5.1 ATL
- 6.9.5.2 VPFE
- 6.9.5.3
CPSW2G
- 6.9.5.3.1 CPSW2G MDIO Interface Timings
- 6.9.5.3.2 CPSW2G RMII Timings
- 6.9.5.3.3
CPSW2G RGMII Timings
- 6.9.5.3.3.1 RGMII[x]_RXC Timing Requirements – RGMII Mode
- 6.9.5.3.3.2 CPSW2G Timing Requirements for RGMII[x]_RD[3:0], and RGMII[x]_RCTL – RGMII Mode
- 6.9.5.3.3.3 CPSW2G RGMII[x]_TXC Switching Characteristics – RGMII Mode
- 6.9.5.3.3.4 RGMII[x]_TD[3:0], and RGMII[x]_TX_CTL Switching Characteristics – RGMII Mode
- 6.9.5.4 CPSW9G
- 6.9.5.5 CSI-2
- 6.9.5.6 DDRSS
- 6.9.5.7 DSS
- 6.9.5.8 eCAP
- 6.9.5.9 EPWM
- 6.9.5.10 eQEP
- 6.9.5.11 GPIO
- 6.9.5.12 GPMC
- 6.9.5.13 HyperBus
- 6.9.5.14 I2C
- 6.9.5.15 I3C
- 6.9.5.16 MCAN
- 6.9.5.17 MCASP
- 6.9.5.18 MCSPI
- 6.9.5.19 MMCSD
- 6.9.5.20 CPTS
- 6.9.5.21 OSPI
- 6.9.5.22 PCIE
- 6.9.5.23 Timers
- 6.9.5.24 UART
- 6.9.5.25 USB
- 6.9.6 Emulation and Debug
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Processor Subsystems
- 7.3 Accelerators and Coprocessors
- 7.4
Other Subsystems
- 7.4.1 MSMC
- 7.4.2 NAVSS
- 7.4.3 PDMA Controller
- 7.4.4 Power Supply
- 7.4.5
Peripherals
- 7.4.5.1 ADC
- 7.4.5.2 ATL
- 7.4.5.3 CSI
- 7.4.5.4 CPSW2G
- 7.4.5.5 CPSW9G
- 7.4.5.6 DCC
- 7.4.5.7 DDRSS
- 7.4.5.8 DSS
- 7.4.5.9 VPFE
- 7.4.5.10 eCAP
- 7.4.5.11 EPWM
- 7.4.5.12 ELM
- 7.4.5.13 ESM
- 7.4.5.14 eQEP
- 7.4.5.15 GPIO
- 7.4.5.16 GPMC
- 7.4.5.17 Hyperbus
- 7.4.5.18 I2C
- 7.4.5.19 I3C
- 7.4.5.20 MCAN
- 7.4.5.21 MCASP
- 7.4.5.22 MCRC Controller
- 7.4.5.23 MCSPI
- 7.4.5.24 MMC/SD
- 7.4.5.25 OSPI
- 7.4.5.26 PCIE
- 7.4.5.27 SerDes
- 7.4.5.28 WWDT
- 7.4.5.29 Timers
- 7.4.5.30 UART
- 7.4.5.31 USB
- 7.4.5.32 UFS
-
8 Applications and
Implementation
- 8.1 Power Supply Mapping
- 8.2 Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 8.3
Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 8.3.1 LPDDR4 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.3.2 OSPI and QSPI Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.3.3 SERDES REFCLK Design Guidelines
- 8.3.4 USB VBUS Design Guidelines
- 8.3.5 System Power Supply Monitor Design Guidelines
- 8.3.6 High Speed Differential Signal Routing Guidance
- 8.3.7 Thermal Solution Guidance
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.5 System Power Supply Monitor Design Guidelines
The VMON_ER_VSYS pin provides a way to monitor a system power supply. This system power supply is typically a single pre-regulated power source for the entire system. This supply is monitored by comparing the output of an external voltage divider circuit sourced by this supply with an internal voltage reference, with a power fail event being triggered when the voltage applied to VMON_ER_VSYS drops below the internal reference voltage. The actual system power supply voltage trip point is determined by the system designer when selecting component values used to implement the external resistor voltage divider circuit. When designing the resistor divider circuit it is important to understand various factors which contribute to variability in the system power supply monitor trip point. The first thing to consider is the initial accuracy of the VMON_ER_VSYS input threshold which has a nominal value of 0.45 V, with a variation of ±3%. Precision 1% resistors with similar thermal coefficient are recommended for implementing the resistor voltage divider. This minimizes variability contributed by resistor value tolerances. Input leakage current associated with VMON_ER_VSYS must also be considered since any current flowing into the pin creates a loading error on the voltage divider output. The VMON_ER_VSYS input leakage current may be in the range of 10 nA to 2.5 μA when applying 0.45 V.
The resistor voltage divider shall be designed such that its output voltage never exceeds themaximum value defined in Section 6.4 , Recommended Operating Conditions during normal operating conditions.
Figure 8-5 presents an example, where the system power supply is nominally 5 V and the maximum trigger threshold is 5 V - 10%, or 4.5 V.
For this example, it is important to understand which variables effect the maximum trigger threshold when selecting resistor values. It is obvious a device which has a VMON_ER_VSYS input threshold of 0.45 V + 3% needs to be considered when trying to design a voltage divider that doesn’t trip until the system supply drops 10%. The effect of resistor tolerance and input leakage also needs to be considered, but how these contributions effect the maximum trigger point may not be obvious. When selecting component values which produce a maximum trigger voltage, the system designer must consider a condition where the value of R1 is 1% low and the value of R2 is 1% high combined with a condition where input leakage current for the VMON_ER_VSYS pin is 2.5 μA. When implementing a resistor divider where R1 = 4.81 KΩ and R2 = 40.2 KΩ, the result is a maximum trigger threshold of 4.523 V.
Once component values have been selected to satisfy the maximum trigger voltage as described above, the system designer can determine the minimum trigger voltage by calculating the applied voltage that produces an output voltage of 0.45 V - 3% when the value of R1 is 1% high and the value of R2 is 1% low, and the input leakage current is 10 nA, or zero. Using an input leakage of zero with the resistor values given above, the result is a minimum trigger threshold of 4.008 V.
This example demonstrates a system power supply voltage trip point that ranges from 4.008 V to 4.523 V. Approximately 250 mV of this range is introduced by VMON_ER_VSYS input threshold accuracy of ±3%, approximately 150 mV of this range is introduced by resistor tolerance of ±1%, and approximately 100 mV of this range is introduced by loading error when VMON_ER_VSYS input leakage current is 2.5 μA.
The resistor values selected in this example produces approximately 100 μA of bias current through the resistor divider when the system supply is 4.5 V. The 100 mV of loading error mentioned above could be reduced to about 10 mV by increasing the bias current through the resistor divider to approximately 1 mA. So resistor divider bias current vs loading error is something the system designer needs to consider when selecting component values.
The system designer should also consider implementing a noise filter on the voltage divider output since VMON_ER_VSYS has minimum hysteresis and a high-bandwidth response to transients. This could be done by installing a capacitor across R1 as shown in Figure 8-5. However, the system designer must determine the response time of this filter based on system supply noise and expected response to transient events.
Figure 8-5 presents an example, when the system power supply voltage is nominally 5 V and the desired trigger threshold is -10% or 4.5 V.
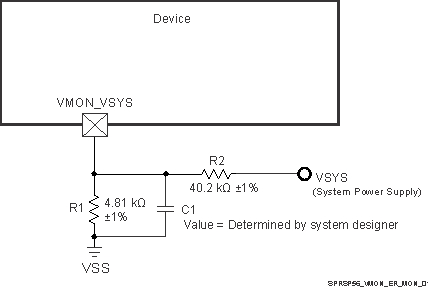 Figure 8-5 System Supply Monitor Voltage Divider
Circuit
Figure 8-5 System Supply Monitor Voltage Divider
Circuit