ZHCSN40K February 2019 – April 2024 DRA829J , DRA829J-Q1 , DRA829V , DRA829V-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Device Comparison
-
5 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 5.1 Pin Diagram
- 5.2 Pin Attributes
- 5.3
Signal Descriptions
- 5.3.1 ADC
- 5.3.2 DDRSS
- 5.3.3 GPIO
- 5.3.4 I2C
- 5.3.5 I3C
- 5.3.6 MCAN
- 5.3.7 MCSPI
- 5.3.8 UART
- 5.3.9 MDIO
- 5.3.10 CPSW2G
- 5.3.11 CPSW9G
- 5.3.12 ECAP
- 5.3.13 EQEP
- 5.3.14 EHRPWM
- 5.3.15 USB
- 5.3.16 SERDES
- 5.3.17 OSPI
- 5.3.18 Hyperbus
- 5.3.19 GPMC
- 5.3.20 MMC
- 5.3.21 CPTS
- 5.3.22 UFS
- 5.3.23 PRU_ICSSG [Currently Not Supported]
- 5.3.24 MCASP
- 5.3.25 DSS
- 5.3.26 DP
- 5.3.27 Camera Streaming Interface Receiver (CSI_RX_IF) Subsystem
- 5.3.28 DSI_TX
- 5.3.29 VPFE
- 5.3.30 DMTIMER
- 5.3.31 Emulation and Debug
- 5.3.32 System and Miscellaneous
- 5.3.33 Power Supply
- 5.4 Pin Multiplexing
- 5.5 Pin Connectivity Requirements
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Power-On-Hour (POH) Limits
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Operating Performance Points
- 6.6
Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.1 I2C, Open-Drain, Fail-Safe (I2C OD FS) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.2 Fail-Safe Reset (FS Reset) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.3 HFOSC/LFOSC Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.4 eMMCPHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.5 SDIO Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.6 CSI-2/DSI D-PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.7 ADC12B Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.8 MLB LVCMOS Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.9 LVCMOS Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.10 USB2PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.11 SerDes 4-L-PHY/2-L-PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.12 UFS M-PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.13 eDP/DP AUX-PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.14 DDR0 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 6.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 6.9
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 6.9.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 6.9.2
Power Supply Sequencing
- 6.9.2.1 Power Supply Slew Rate Requirement
- 6.9.2.2 Combined MCU and Main Domains Power-Up Sequencing
- 6.9.2.3 Combined MCU and Main Domains Power- Down Sequencing
- 6.9.2.4 Isolated MCU and Main Domains Power- Up Sequencing
- 6.9.2.5 Isolated MCU and Main Domains, Primary Power- Down Sequencing
- 6.9.2.6 Entry and Exit of MCU Only State
- 6.9.2.7 Entry and Exit of DDR Retention State
- 6.9.3 System Timing
- 6.9.4
Clock Specifications
- 6.9.4.1
Input and Output Clocks / Oscillators
- 6.9.4.1.1 WKUP_OSC0 Internal Oscillator Clock Source
- 6.9.4.1.2 WKUP_OSC0 LVCMOS Digital Clock Source
- 6.9.4.1.3 Auxiliary OSC1 Internal Oscillator Clock Source
- 6.9.4.1.4 Auxiliary OSC1 LVCMOS Digital Clock Source
- 6.9.4.1.5 Auxiliary OSC1 Not Used
- 6.9.4.1.6 WKUP_LFOSC0 Internal Oscillator Clock Source
- 6.9.4.2 Output Clocks
- 6.9.4.3 PLLs
- 6.9.4.4 Module and Peripheral Clocks Frequencies
- 6.9.4.1
Input and Output Clocks / Oscillators
- 6.9.5
Peripherals
- 6.9.5.1 ATL
- 6.9.5.2 VPFE
- 6.9.5.3
CPSW2G
- 6.9.5.3.1 CPSW2G MDIO Interface Timings
- 6.9.5.3.2 CPSW2G RMII Timings
- 6.9.5.3.3
CPSW2G RGMII Timings
- 6.9.5.3.3.1 RGMII[x]_RXC Timing Requirements – RGMII Mode
- 6.9.5.3.3.2 CPSW2G Timing Requirements for RGMII[x]_RD[3:0], and RGMII[x]_RCTL – RGMII Mode
- 6.9.5.3.3.3 CPSW2G RGMII[x]_TXC Switching Characteristics – RGMII Mode
- 6.9.5.3.3.4 RGMII[x]_TD[3:0], and RGMII[x]_TX_CTL Switching Characteristics – RGMII Mode
- 6.9.5.4 CPSW9G
- 6.9.5.5 CSI-2
- 6.9.5.6 DDRSS
- 6.9.5.7 DSS
- 6.9.5.8 eCAP
- 6.9.5.9 EPWM
- 6.9.5.10 eQEP
- 6.9.5.11 GPIO
- 6.9.5.12 GPMC
- 6.9.5.13 HyperBus
- 6.9.5.14 I2C
- 6.9.5.15 I3C
- 6.9.5.16 MCAN
- 6.9.5.17 MCASP
- 6.9.5.18 MCSPI
- 6.9.5.19 MMCSD
- 6.9.5.20 CPTS
- 6.9.5.21 OSPI
- 6.9.5.22 PCIE
- 6.9.5.23 Timers
- 6.9.5.24 UART
- 6.9.5.25 USB
- 6.9.6 Emulation and Debug
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Processor Subsystems
- 7.3 Accelerators and Coprocessors
- 7.4
Other Subsystems
- 7.4.1 MSMC
- 7.4.2 NAVSS
- 7.4.3 PDMA Controller
- 7.4.4 Power Supply
- 7.4.5
Peripherals
- 7.4.5.1 ADC
- 7.4.5.2 ATL
- 7.4.5.3 CSI
- 7.4.5.4 CPSW2G
- 7.4.5.5 CPSW9G
- 7.4.5.6 DCC
- 7.4.5.7 DDRSS
- 7.4.5.8 DSS
- 7.4.5.9 VPFE
- 7.4.5.10 eCAP
- 7.4.5.11 EPWM
- 7.4.5.12 ELM
- 7.4.5.13 ESM
- 7.4.5.14 eQEP
- 7.4.5.15 GPIO
- 7.4.5.16 GPMC
- 7.4.5.17 Hyperbus
- 7.4.5.18 I2C
- 7.4.5.19 I3C
- 7.4.5.20 MCAN
- 7.4.5.21 MCASP
- 7.4.5.22 MCRC Controller
- 7.4.5.23 MCSPI
- 7.4.5.24 MMC/SD
- 7.4.5.25 OSPI
- 7.4.5.26 PCIE
- 7.4.5.27 SerDes
- 7.4.5.28 WWDT
- 7.4.5.29 Timers
- 7.4.5.30 UART
- 7.4.5.31 USB
- 7.4.5.32 UFS
-
8 Applications and
Implementation
- 8.1 Power Supply Mapping
- 8.2 Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 8.3
Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 8.3.1 LPDDR4 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.3.2 OSPI and QSPI Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.3.3 SERDES REFCLK Design Guidelines
- 8.3.4 USB VBUS Design Guidelines
- 8.3.5 System Power Supply Monitor Design Guidelines
- 8.3.6 High Speed Differential Signal Routing Guidance
- 8.3.7 Thermal Solution Guidance
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.9.4.1.1.1 Load Capacitance
The crystal circuit must be designed such that it applies the appropriate capacitive load to the crystal, as defined by the crystal manufacturer. The capacitive load, CL, of this circuit is a combination of discrete capacitors CL1, CL2, and several parasitic contributions. PCB signal traces which connect crystal circuit components to WKUP_OSC0_XI and WKUP_OSC0_XO have parasitic capacitance to ground, CPCBXI and CPCBXO, where the PCB designer should be able to extract parasitic capacitance for each signal trace. The WKUP_OSC0 circuits and device package have combined parasitic capacitance to ground, CPCBXI and CPCBXO, where these parasitic capacitance values are defined in Table 6-22.
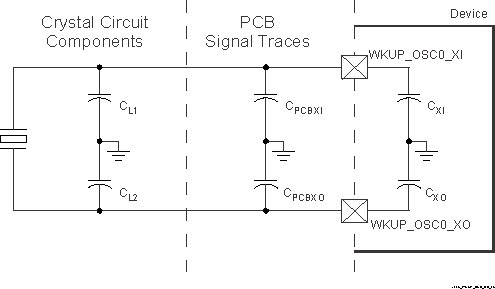 Figure 6-25 Load Capacitance
Figure 6-25 Load CapacitanceLoad capacitors, CL1 and CL2 in Figure 6-23, should be chosen such that the below equation is satisfied. CL in the equation is the load specified by the crystal manufacturer.
CL = [(CL1 + CPCBXI + CXI) × (CL2 + CPCBXO + CXO)] / [(CL1 + CPCBXI + CXI) + (CL2 + CPCBXO + CXO)]
To determine the value of CL1 and CL2, multiply the capacitive load value CL by 2. Using this result, subtract the combined values of CPCBXI + CXI to determine the value of CL1 and the combined values of CPCBXO + CXO to determine the value of CL2. For example, if CL = 10 pF, CPCBXI = 2.9 pF, CXI = 0.5 pF, CPCBXO = 3.7 pF, CXO = 0.5 pF, the value of CL1 = [(2CL) - (CPCBXI + CXI)] = [(2 × 10 pF) - 2.9 pF - 0.5 pF)] = 16.6 pF and CL2 = [(2CL) - (CPCBXO + CXO)] = [(2 × 10 pF) - 3.7 pF - 0.5 pF)] = 15.8 pF