ZHCS343C May 2012 – January 2023 DRV2665
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Support for Haptic Piezo Actuators
- 7.3.2 Flexible Front End Interface
- 7.3.3 Ramp Down Behavior
- 7.3.4 Low Latency Startup
- 7.3.5 Low Power Standby Mode
- 7.3.6 Device Reset
- 7.3.7 Amplifier Gain
- 7.3.8 Adjustable Boost Voltage
- 7.3.9 Adjustable Current Limit
- 7.3.10 Internal Charge Pump
- 7.3.11 Device Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Map
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.5.3.1 General I2C Operation
The I2C bus employs two signals, SDA (data) and SCL (clock), to communicate between integrated circuits in a system. The bus transfers data serially, one bit at a time. The 8-bit address and data bytes are transferred with the most-significant bit (MSB) first. In addition, each byte transferred on the bus is acknowledged by the receiving device with an acknowledge bit. Each transfer operation begins with the master device driving a start condition on the bus and ends with the master device driving a stop condition on the bus. The bus uses transitions on the data pin (SDA) while the clock is at logic high to indicate start and stop conditions. A high-to-low transition on the SDA signal indicates a start, and a low-to-high transition indicates a stop. Normal data-bit transitions must occur within the low time of the clock period. Figure 7-4 shows a typical sequence. The master device generates the 7-bit slave address and the read-write (R/W) bit to start communication with a slave device. The master device then waits for an acknowledge condition. The slave device holds the SDA signal low during the acknowledge clock period to indicate acknowledgment. When this acknowledgment occurs, the master transmits the next byte of the sequence. Each device is addressed by a unique 7-bit slave address plus a R/W bit (1 byte). All compatible devices share the same signals through a bidirectional bus using a wired-AND connection.
The number of bytes that can be transmitted between start and stop conditions is not limited. When the last word transfers, the master generates a stop condition to release the bus. Figure 7-4 shows a generic data-transfer sequence.
Use external pullup resistors for the SDA and SCL signals to set the logic-high level for the bus. Pullup resistors with values between 660 Ω and 4.7 kΩ are recommended. Do not allow the SDA and SCL voltages to exceed the DRV2665 supply voltage, VDD.
The DRV2665 device operates as an I2C-slave with 1.8-V logic thresholds, but can operate up to the VDD voltage.
The slave address for the DRV2665 device is 0x59 (7-bit), or 1011001 in binary, which is equivalent to 0xB2 (8-bit) for writing and 0xB3 (8-bit) for reading.
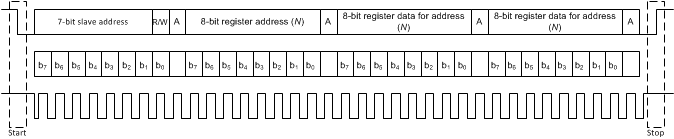 Figure 7-4 Typical I2C Sequence
Figure 7-4 Typical I2C Sequence