ZHCSR87 December 2022 DRV8316C
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Output Stage
- 8.3.2 Control Modes
- 8.3.3 Device Interface Modes
- 8.3.4 Step-Down Mixed-Mode Buck Regulator
- 8.3.5 AVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
- 8.3.6 Charge Pump
- 8.3.7 Slew Rate Control
- 8.3.8 Cross Conduction (Dead Time)
- 8.3.9 Propagation Delay
- 8.3.10 Pin Diagrams
- 8.3.11 Current Sense Amplifiers
- 8.3.12 Active Demagnetization
- 8.3.13 Cycle-by-Cycle Current Limit
- 8.3.14
Protections
- 8.3.14.1 VM Supply Undervoltage Lockout (NPOR)
- 8.3.14.2 AVDD Undervoltage Lockout (AVDD_UV)
- 8.3.14.3 BUCK Undervoltage Lockout (BUCK_UV)
- 8.3.14.4 VCP Charge Pump Undervoltage Lockout (CPUV)
- 8.3.14.5 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.14.6 Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
- 8.3.14.7 Buck Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.14.8 Thermal Warning (OTW)
- 8.3.14.9 Thermal Shutdown (OTS)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 SPI Communication
- 8.6 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.11.1 Current Sense Amplifier Operation
The SOx pin on the DRV8316C outputs an analog voltage proportional to current flowing in the low side FETs multiplied by the gain setting (GCSA). The gain setting is adjustable between four different levels which can be set by the GAIN pin (in hardware device variant) or the GAIN bits (in SPI device variant).
Figure 8-28 shows the internal architecture of the current sense amplifiers. The current sense is implemented with the sense FET on each low-side FET of the DRV8316C device. This current information is fed to the internal I/V converter, which generates the CSA output voltage on the SOX pin based on the voltage on VREF pin and the Gain setting. The CSA output voltage can be calculated as :
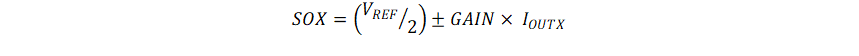
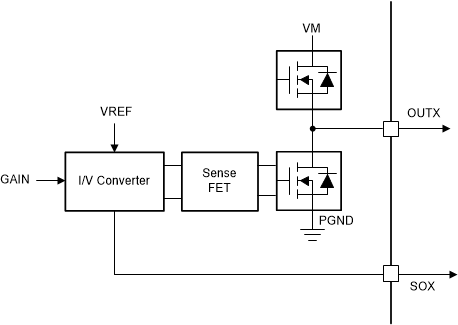 Figure 8-28 Integrated Current Sense Amplifier
Figure 8-28 Integrated Current Sense AmplifierFigure 8-29 and Figure 8-30 show the detail of the amplifier operational range. In bi-directional operation, the amplifier output for 0-V input is set at VREF / 2. Any change in the differential input results in a corresponding change in the output times the CSA_GAIN factor. The amplifier has a defined region in which it can maintain a linear operation.