ZHCSG01C February 2017 – August 2018 DRV8320 , DRV8320R , DRV8323 , DRV8323R
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Three Phase Smart Gate Drivers
- 8.3.2 DVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
- 8.3.3 Pin Diagrams
- 8.3.4 Low-Side Current Sense Amplifiers (DRV8323 and DRV8323R Only)
- 8.3.5 Step-Down Buck Regulator
- 8.3.6 Gate Driver Protective Circuits
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- Table 1. DRV832xS and DRV832xRS Register Map
- 8.6.1 Status Registers
- 8.6.2 Control Registers
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1
Primary Application
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.2 Alternative Application
- 9.2.1
Primary Application
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.1.4.2 TDRIVE: MOSFET Gate Drive Control
The TDRIVE component is an integrated gate drive state machine that provides automatic dead time insertion through handshaking between the high-side and low-side gate drivers, parasitic dV/dt gate turnon prevention, and MOSFET gate fault detection.
The first component of the TDRIVE state machine is automatic dead time insertion. Dead time is period of time between the switching of the external high-side and low-side MOSFETs to make sure that they do not cross conduct and cause shoot-through. The DRV832x family of devices uses VGS voltage monitors to measure the MOSFET gate-to-source voltage and determine the correct time to switch instead of relying on a fixed time value. This feature lets the dead time of the gate driver adjust for variation in the system such as temperature drift and variation in the MOSFET parameters. An additional digital dead time (tDEAD) can be inserted and is adjustable through the registers on SPI devices.
The second component of the TDRIVE state machine is parasitic dV/dt gate turnon prevention. To implement this component, the TDRIVE state machine enables a strong pulldown current (ISTRONG) on the opposite MOSFET gate whenever a MOSFET is switching. The strong pulldown occurs for the TDRIVE duration. This feature helps remove parasitic charge that couples into the MOSFET gate when the voltage half-bridge switch node slews rapidly.
The third component of the TDRIVE state machine implements a scheme for gate fault detection to detect pin-to-pin solder defects, a MOSFET gate failure, or stuck-high or stuck-low voltage condition on a MOSFET gate. This implementation occurs with a pair of VGS gate-to-source voltage monitors for each half-bridge gate driver. When the gate driver receives a command to change the state of the half-bridge, it starts to monitor the gate voltage of the external MOSFET. If the VGS voltage has not reached the correct threshold at the end of the tDRIVE period,, the gate driver reports a fault. To make sure that a false fault is not detected, a tDRIVE time should be selected that is longer than the time required to charge or discharge the MOSFET gate. The tDRIVE time does not increase the PWM time and will terminate if another PWM command is received while active. For additional details on the TDRIVE settings, see the Register Maps section for SPI devices. The hardware interface devices have a fixed tDRIVE of 4 µs.
Figure 27 shows an example of the TDRIVE state machine in operation.
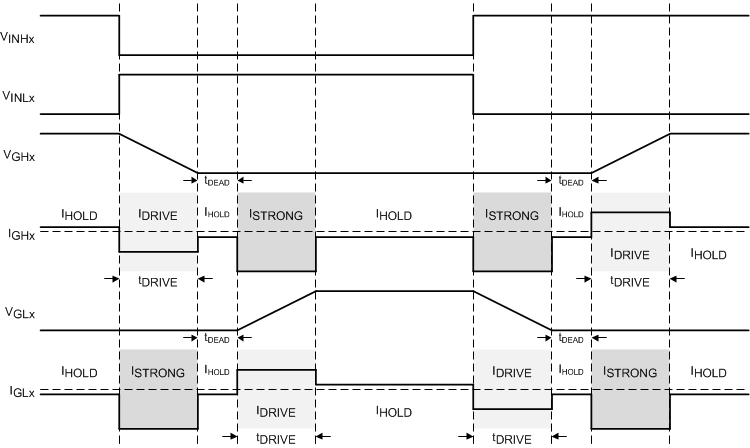 Figure 27. TDRIVE State Machine
Figure 27. TDRIVE State Machine