SLVSA73F April 2010 – July 2014 DRV8825
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Schematic
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9 Application and Implementation
9.1 Application Information
The DRV8825 is used in bipolar stepper control. The microstepping motor driver provides additional precision and a smooth rotation from the stepper motor. The following design is a common application of the DRV8825.
9.2 Typical Application
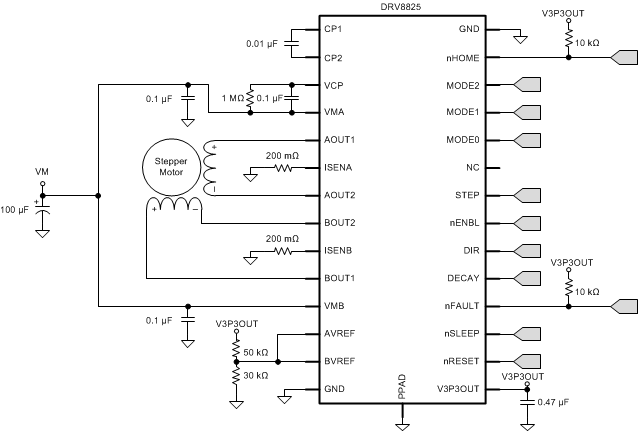
9.2.1 Design Requirements
| Design Parameter | Reference | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | VM | 24 V |
| Motor Winding Resistance | RL | 3.9 Ω |
| Motor Winding Inductance | IL | 2.9 mH |
| Motor Full Step Angle | θstep | 1.8°/step |
| Target Microstepping Level | nm | 8 µsteps per step |
| Target Motor Speed | v | 120 rpm |
| Target Full-Scale Current | IFS | 1.25 A |
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
9.2.2.1 Stepper Motor Speed
The first step in configuring the DRV8825 requires the desired motor speed and microstepping level. If the target application requires a constant speed, then a square wave with frequency ƒstep must be applied to the STEP pin.
If the target motor startup speed is too high, the motor will not spin. Make sure that the motor can support the target speed or implement an acceleration profile to bring the motor up to speed.
For a desired motor speed (v), microstepping level (nm), and motor full step angle (θstep),
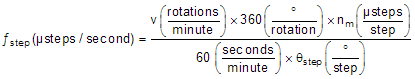
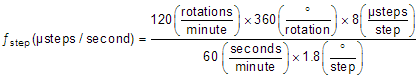
θstep can be found in the stepper motor data sheet or written on the motor itself.
For the DRV8825, the microstepping level is set by the MODE pins and can be any of the settings in Table 1. Higher microstepping will mean a smoother motor motion and less audible noise, but will increase switching losses and require a higher ƒstep to achieve the same motor speed.
9.2.2.2 Current Regulation
In a stepper motor, the set full-scale current (IFS) is the maximum current driven through either winding. This quantity depends on the xVREF analog voltage and the sense resistor value (RSENSE). During stepping, IFS defines the current chopping threshold (ITRIP) for the maximum current step. The gain of DRV8825 is set for 5 V/V.

To achieve IFS = 1.25 A with RSENSE of 0.2 Ω, xVREF should be 1.25 V.
9.2.2.3 Decay Modes
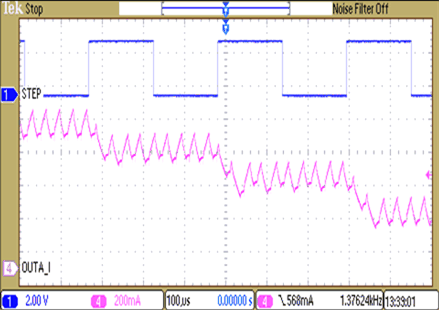
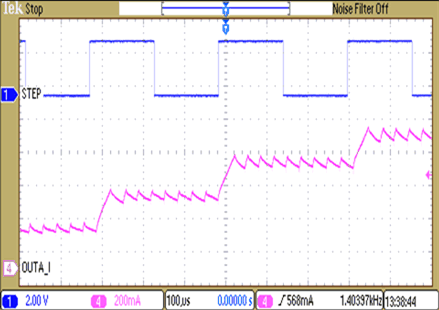
The DRV8825 supports three different decay modes: slow decay, fast decay, and mixed decay. The current through the motor windings is regulated using a fixed-frequency PWM scheme. This means that after any drive phase, when a motor winding current has hit the current chopping threshold (ITRIP), the DRV8825 will place the winding in one of the three decay modes until the PWM cycle has expired. Afterward, a new drive phase starts.
The blanking time, tBLANK, defines the minimum drive time for the current chopping. ITRIP is ignored during tBLANK, so the winding current may overshoot the trip level.
9.2.3 Application Curves