ZHCSDR9D July 2012 – May 2015 DS125BR401
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用范围
- 3 说明
- 4 典型应用
- 5 修订历史记录
- 6 说明(续)
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
10 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
10.1 Application Information
The DS125BR401 is a high performance circuit capable of delivering excellent performance. Careful attention must be paid to the details associated with high-speed design as well as providing a clean power supply. Refer to the following information and Revision 4 of the LVDS Owner's Manual for more detailed information on high-speed design tips to address signal integrity design issues.
10.2 Typical Application
The DS125BR401 works to extend the reach possible by using active equalization on the channel, boosting attenuated signals so that they can be more easily recovered at the Rx endpoint. The capability of the repeater can be explored across a range of data rates and ASIC-to-link-partner signaling, as shown in the following test setup connections. The test setup connections diagrams shown represent typical generic application scenarios for the DS125BR401.
 Figure 9. Test Setup Connections Diagram
Figure 9. Test Setup Connections Diagram
 Figure 10. Test Setup Connections Diagram
Figure 10. Test Setup Connections Diagram
10.2.1 Design Requirements
As with any high speed design, there are many factors which influence the overall performance. Below are a list of critical areas for consideration and study during design.
- Use 100-Ω impedance traces. Generally these are very loosely coupled to ease routing length differences.
- Place AC-coupling capacitors near to the receiver end of each channel segment to minimize reflections.
- The maximum body size for AC-coupling capacitors is 0402.
- Back-drill connector vias and signal vias to minimize stub length.
- Use Reference plane vias to ensure a low inductance path for the return current.
10.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The DS125BR401 is designed to be placed at a location where the input CTLE can help to compensate for a portion of the overall channel attenuation. In order to optimize performance, the repeater requires tuning to extend the reach of the cable or trace length while also recovering a solid eye opening. To tune the repeater, TI recommends the settings mentioned in Table 2 and Table 3 (for Pin Mode) as a default starting point for most applications. Once these settings are configured, additional tuning of the EQ and, to a lesser extent, VOD may be required to optimize the repeater performance for each specific application environment. Examples of the repeater performance as a generic high-speed datapath repeater are illustrated in the performance curves in the next section.
10.2.3 Application Curves
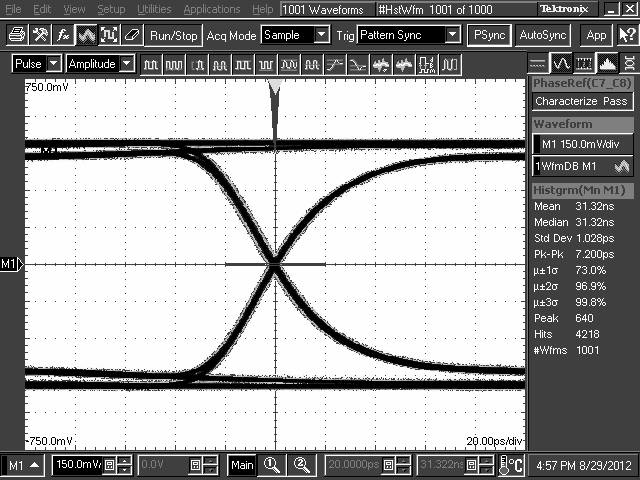
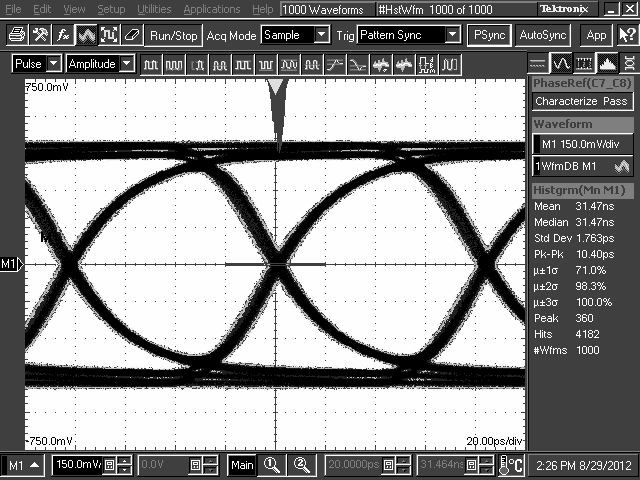
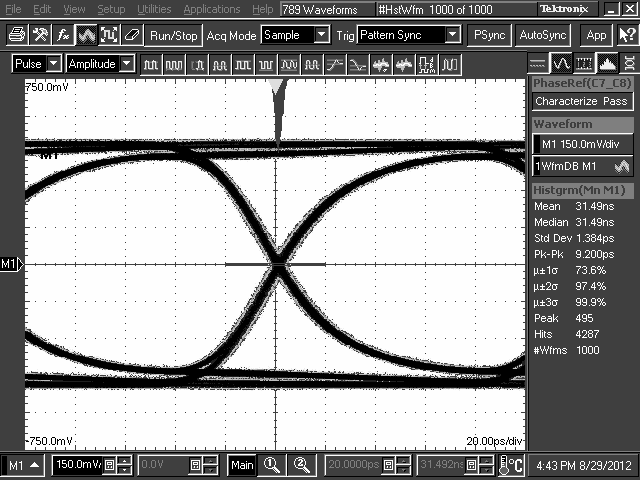
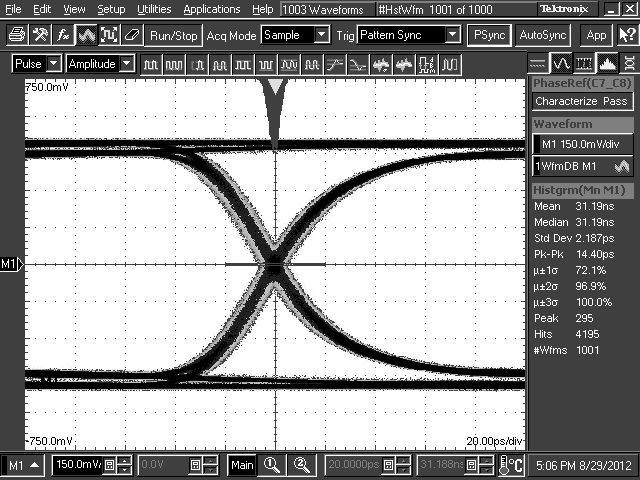
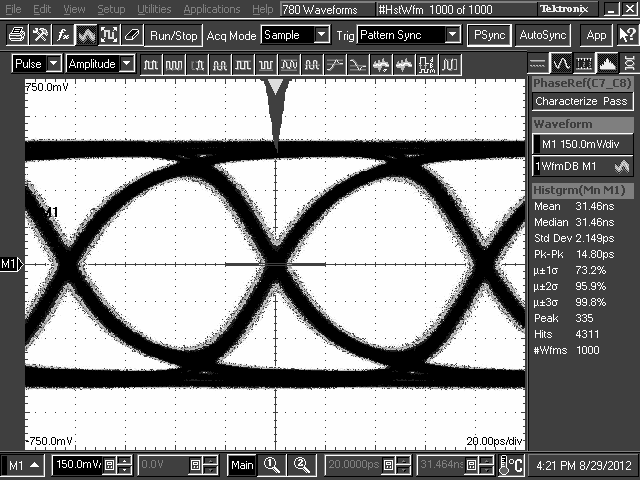
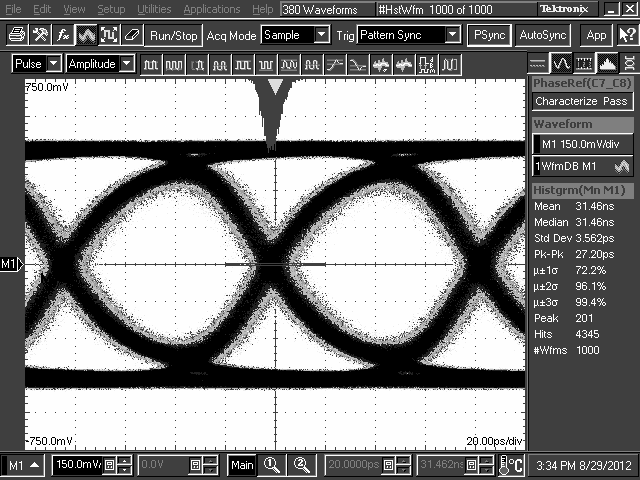
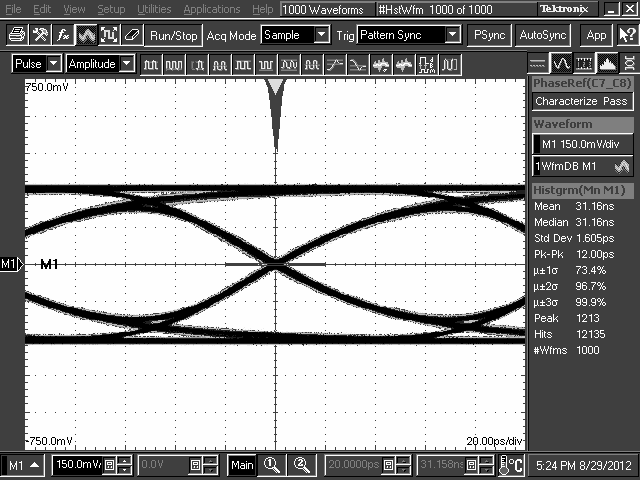
TL2 = 10-Inch 5-Mil FR4 Trace, 8 Gbps
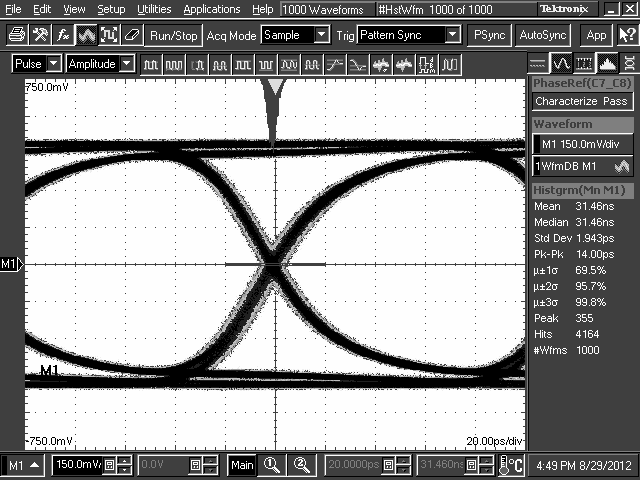
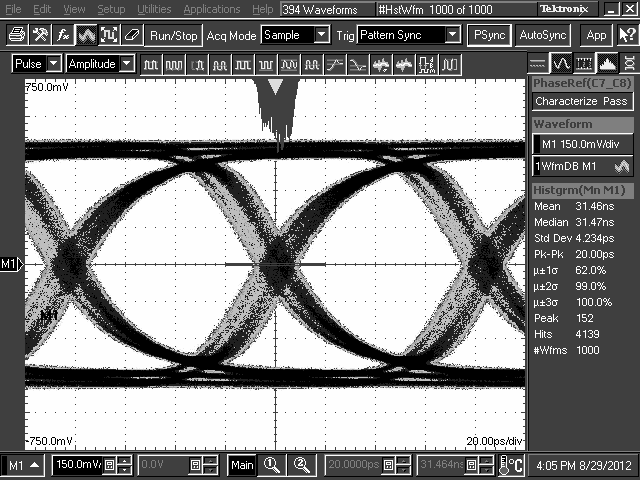
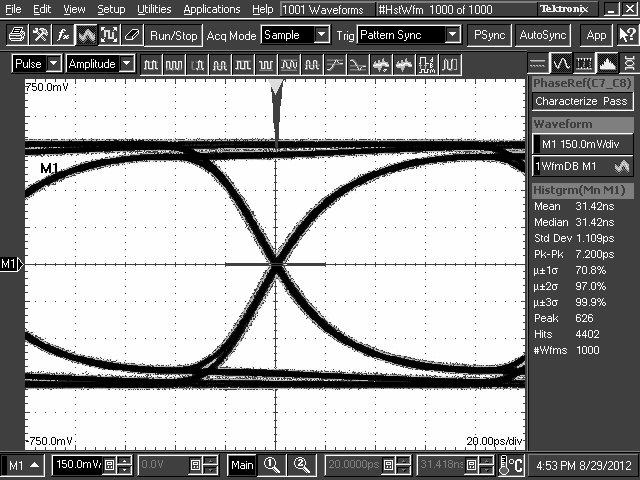
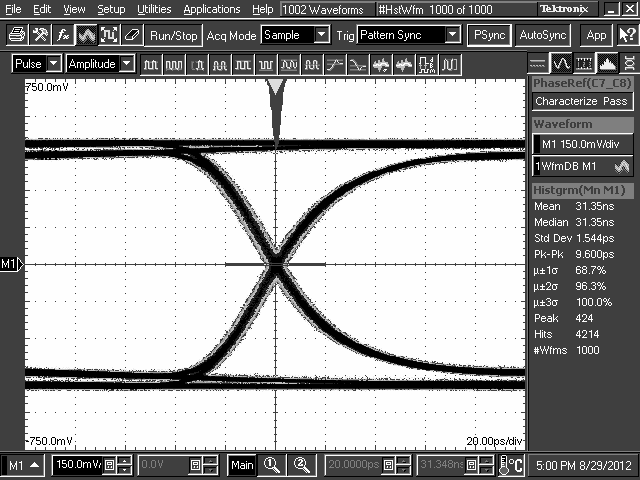
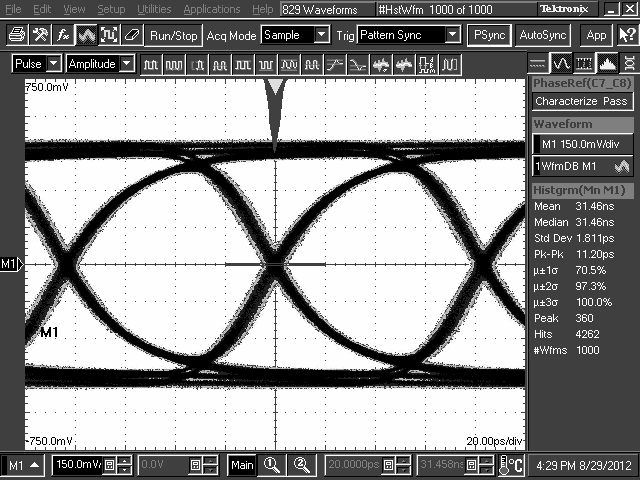



TL2 = 10-Inch 5-Mil FR4 Trace, 5 Gbps
