ZHCSKE4C october 2016 – december 2020 DS280MB810
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
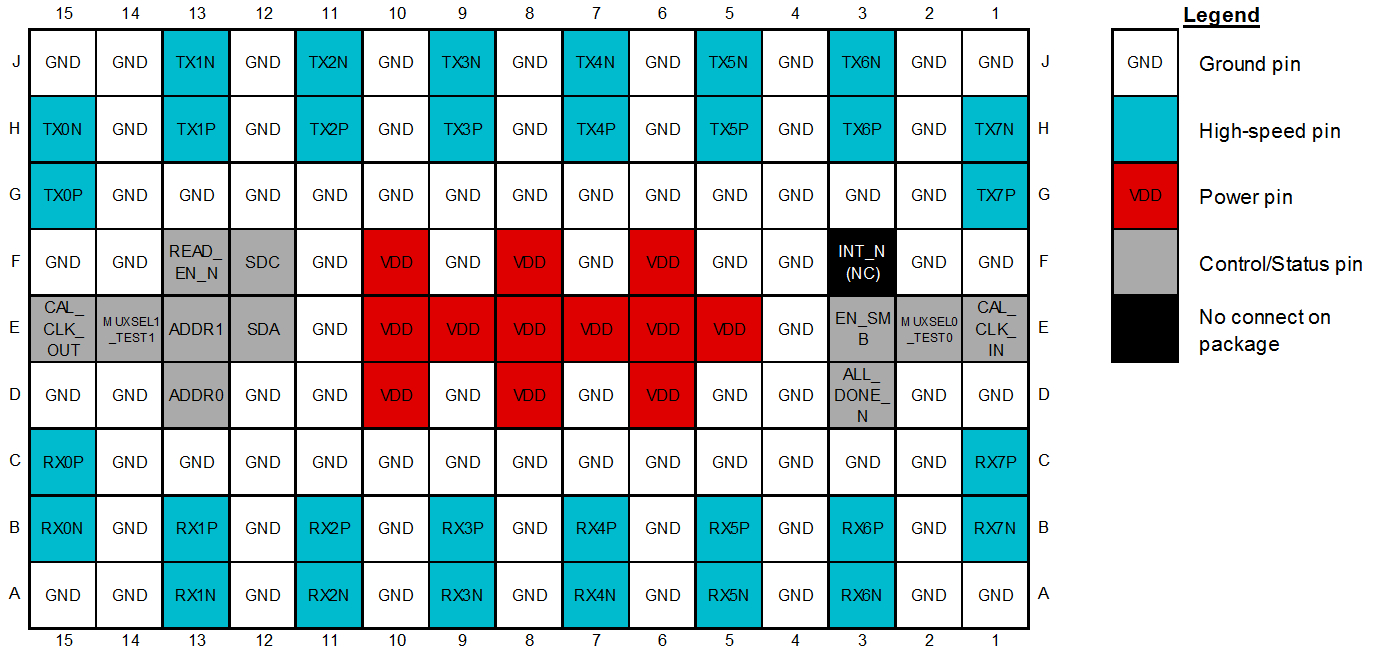 Figure 6-1 Top
View
Figure 6-1 Top
View| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| High Speed Differential I/O | |||
| RX0P | C15 | Input | Inverting and non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. An on-chip 100-Ω termination resistor connects RXP to RXN. These inputs are AC coupled with 220 nF capacitors assembled on the package substrate. |
| RX0N | B15 | Input | |
| RX1P | B13 | Input | Inverting and non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. An on-chip 100-Ω termination resistor connects RXP to RXN. These inputs are AC coupled with 220 nF capacitors assembled on the package substrate. |
| RX1N | A13 | Input | |
| RX2P | B11 | Input | Inverting and non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. An on-chip 100-Ω termination resistor connects RXP to RXN. These inputs are AC coupled with 220 nF capacitors assembled on the package substrate. |
| RX2N | A11 | Input | |
| RX3P | B9 | Input | Inverting and non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. An on-chip 100-Ω termination resistor connects RXP to RXN. These inputs are AC coupled with 220 nF capacitors assembled on the package substrate. |
| RX3N | A9 | Input | |
| RX4P | B7 | Input | Inverting and non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. An on-chip 100-Ω termination resistor connects RXP to RXN. These inputs are AC coupled with 220 nF capacitors assembled on the package substrate. |
| RX4N | A7 | Input | |
| RX5P | B5 | Input | Inverting and non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. An on-chip 100-Ω termination resistor connects RXP to RXN. These inputs are AC coupled with 220 nF capacitors assembled on the package substrate. |
| RX5N | A5 | Input | |
| RX6P | B3 | Input | Inverting and non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. An on-chip 100-Ω termination resistor connects RXP to RXN. These inputs are AC coupled with 220 nF capacitors assembled on the package substrate. |
| RX6N | A3 | Input | |
| RX7P | C1 | Input | Inverting and non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. An on-chip 100-Ω termination resistor connects RXP to RXN. These inputs are AC coupled with 220 nF capacitors assembled on the package substrate. |
| RX7N | B1 | Input | |
| TX0P | G15 | Output | Inverting and non-inverting 50-Ω driver outputs. Compatible with AC-coupled differential inputs. |
| TX0N | H15 | Output | |
| TX1P | H13 | Output | Inverting and non-inverting 50-Ω driver outputs. Compatible with AC-coupled differential inputs. |
| TX1N | J13 | Output | |
| TX2P | H11 | Output | Inverting and non-inverting 50-Ω driver outputs. Compatible with AC-coupled differential inputs. |
| TX2N | J11 | Output | |
| TX3P | H9 | Output | Inverting and non-inverting 50-Ω driver outputs. Compatible with AC-coupled differential inputs. |
| TX3N | J9 | Output | |
| TX4P | H7 | Output | Inverting and non-inverting 50-Ω driver outputs. Compatible with AC-coupled differential inputs. |
| TX4N | J7 | Output | |
| TX5P | H5 | Output | Inverting and non-inverting 50-Ω driver outputs. Compatible with AC-coupled differential inputs. |
| TX5N | J5 | Output | |
| TX6P | H3 | Output | Inverting and non-inverting 50-Ω driver outputs. Compatible with AC-coupled differential inputs. |
| TX6N | J3 | Output | |
| TX7P | G1 | Output | Inverting and non-inverting 50-Ω driver outputs. Compatible with AC-coupled differential inputs. |
| TX7N | H1 | Output | |
| Calibration Clock Pins (For Supporting Upgrade Path to Pin-Compatible Retimer Device) | |||
| CAL_CLK_IN | E1 | Input | 25-MHz (±100 PPM) 2.5-V single-ended clock from external oscillator. No stringent phase noise or jitter requirements on this clock. A 25-MHz input clock is only required if there is a need to support a future upgrade to the pin-compatible Retimer device. If there is no need to support a future upgrade to a pin-compatible Retimer device, then a 25-MHz clock is not required. This input pin has a weak active pull down and can be left floating if the CAL_CLK feature is not required. |
| CAL_CLK_ OUT |
E15 | Output | 2.5-V buffered replica of calibration clock input (pin E1) for connecting multiple devices in a daisy-chained fashion. |
| System Management Bus (SMBus) Pins | |||
| ADDR0 | D13 | Input, 4-Level | 4-level strap pins used to set the SMBus address of the device. The
pin state is read on power-up. The multi-level nature of these pins
allows for 16 unique device addresses, see Table 8-1. The four strap options include: 0: 1 kΩ to GND R: 10 kΩ to GND F: Float 1: 1 kΩ to VDD |
| ADDR1 | E13 | Input, 4-Level | |
| EN_SMB | E3 | Input, 4-Level | 4-level 2.5-V
input used to select between SMBus master mode (float) and SMBus
slave mode (high). The four defined levels are: 0: 1 kΩ to GND - RESERVED R: 10 kΩ to GND - RESERVED, TI test mode F: Float - SMBus master mode 1: 1 kΩ to VDD - SMBus slave mode |
| SDA | E12 | I/O, 3.3 V LVCMOS, Open Drain | SMBus data input or open drain output. External 2-kΩ to 5-kΩ pull-up resistor is required. This pin is 3.3-V LVCMOS tolerant. |
| SDC | F12 | I/O, 3.3 V LVCMOS, Open Drain | SMBus clock input or open drain clock output. External 2-kΩ to 5-kΩ pull-up resistor is required. This pin is 3.3-V LVCMOS tolerant. |
| READ_EN_N | F13 | Input, 3.3 V LVCMOS |
SMBus master mode (EN_SMB = Float): When asserted low, initiates the SMBus master mode EEPROM read function. Once EEPROM read is complete (indicated by assertion of ALL_DONE_N low), this pin can be held low for normal device operation. SMBus slave mode (EN_SMB = 1 kΩ to VDD): When asserted low, this causes the device to be held in reset (SMBus state machine reset and register reset). This pin should be pulled high or left floating for normal operation in SMBus slave mode. This pin has an internal weak pull-up and is 3.3-V LVCMOS tolerant. |
| ALL_DONE_N | D3 | Output, LVCMOS |
Indicates the completion of a valid EEPROM register load operation when in SMBus master mode (EN_SMB = Float): High = External EEPROM load failed or incomplete. Low = External EEPROM load successful and complete. When in SMBus slave mode (EN_SMB = 1 kΩ to VDD), this output will be high-Z until READ_EN_N is driven low, at which point ALL_DONE_N will be driven low. This behavior allows the reset signal connected to READ_EN_N of one device to propagate to the subsequent devices when ALL_DONE_N is connected to READ_EN_N in an SMBus slave mode application. |
| Miscellaneous Pins | |||
| INT_N | F3 | No connect in package | No connect on package. For applications using DS280MB810 and pin-compatible TI Retimers, this pin can be connected to other devices’ INT_N pins. This is a recommendation for cases where there is a need to support a potential future upgrade to the pin-compatible Retimer device, which uses this pin as an interrupt signal to a system controller. |
| MUXSEL0_ TEST0 |
E2 | Input, LVCMOS | When operating the cross-point in pin-control mode (Shared
Reg_0x05[1]=1), MUXSEL0 controls the cross-point for channels 0–1
and 4–5, and MUXSEL1 controls the cross-point for channels 2–3 and
6–7. If these pins are not used for cross-point control, they may be left floating or tied to GND. These pins also serve as TI test pins when in test mode (EN_SMB = 10 kΩ to GND). These pins have an internal weak pull-up. |
| MUXSEL1_ TEST1 |
E14 | Input, LVCMOS | |
| Power | |||
| VDD | D6, D8, D10, E5, E6, E7, E8, E9, E10, F6, F8, F10 | Power | Power supply, VDD = 2.5 V +/- 5%. Use at least six de-coupling capacitors between the Repeater’s VDD plane and GND as close to the Repeater as possible. For example, four 0.1-μF capacitors and two 1-μF capacitors directly beneath the device or as close to the VDD pins as possible. The VDD pins on this device should be connected through a low-resistance path to the board VDD plane. For more information, see Section 10. |
| GND | A1, A2, A4, A6, A8, A10, A12, A14, A15, B2, B4, B6, B8, B10, B12, B14, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, C14, D1, D2, D4, D5, D7, D9, D11, D12, D14, D15, E4, E11, F1, F2, F4, F5, F7, F9, F11, F14, F15, G2, G3, G4, G5, G6, G7, G8, G9, G10, G11, G12, G13, G14, H2, H4, H6, H8, H10, H12, H14, J1, J2, J4, J6, J8, J10, J12, J14, J15 | Power | Ground reference. The GND pins on this device should be connected through a low-impedance path to the board GND plane. |