ZHCSQD1 August 2022 DS320PR810
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
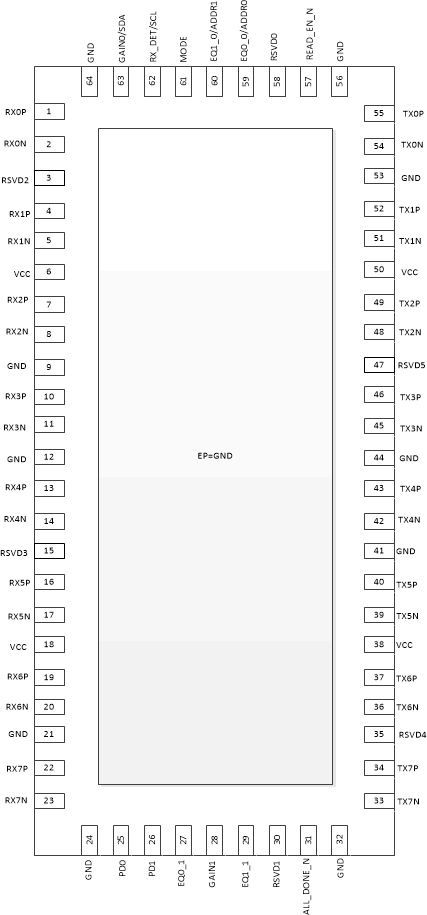 Figure 5-1 NJX
Package,64-Pin WQFN(Top View)
Figure 5-1 NJX
Package,64-Pin WQFN(Top View)Table 5-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| ALL_DONE_N | 31 | O, 3.3 V open drain | In SMBus/I2C Primary mode: Indicates the completion of a valid EEPROM register load operation. External pullup resistor such as 4.7 kΩ required for operation. High: External EEPROM load failed or incomplete Low: External EEPROM load successful and complete In SMBus/I2C Secondary/Pin mode: This output is High-Z. The pin can be left floating. |
| MODE | 61 | I, 5-level | Sets device control configuration modes. 5-level IO pin as
provided in Table 7-4. The pin can be exercised at device power up or in normal operation mode. L0: Pin mode – device control configuration is done solely by strap pins. L1: SMBus/I2C Primary mode – device control configuration is read from external EEPROM. When the DS320PR810 has finished reading from the EEPROM successfully, it will drive the ALL_DONE_N pin LOW. SMBus/I2C secondary operation is available in this mode before, during or after EEPROM reading. Note: during EEPROM reading if the external SMBus/I2C primary wants to access DS320PR810 registers it must support arbitration. L2: SMBus/I2C Secondary mode – device control configuration is done by an external controller with SMBus/I2C primary. L3 and L4 (Float): RESERVED – TI internal test modes. |
| EQ0 / ADDR0 | 59 | I, 5-level | In Pin mode:
Sets receiver linear equalization (CTLE) boost for channels 0-3 (Bank 0) as provided in Table 7-1. These pins are sampled at device power-up only. In SMBus/I2C mode: Sets SMBus / I2C secondary address as provided in Table 7-5. These pins are sampled at device power-up only. |
| EQ1 / ADDR1 | 60 | I, 5-level | |
| EQ0_1 | 27 | I, 5-level | Sets receiver linear equalization (CTLE) boost for channels 4-7 (Bank 1) as provided in Table 7-1 in Pin mode. The pin is sampled at device power-up only. |
| EQ1_1 | 29 | I, 5-level | |
| GAIN0 / SDA | 63 | I, 5-level / I/O, 3.3 V LVCMOS, open drain | In Pin mode:
Flat gain (DC and AC) from the input to the output of the device for channels 0-3 (Bank 0). The pin is sampled at device power-up only. In SMBus/I2C mode: 3.3 V SMBus/I2C data. External 1 kΩ to 5 kΩ pullup resistor is required as per SMBus / I2C interface standard. |
| GAIN1 | 28 | I, 5-level | Flat gain (DC and AC) from the input to the output of the device for channels 4-7 (Bank 1) in Pin mode. The pin is sampled at device power-up only. |
| GND | EP, 9, 12, 21, 24, 32, 41, 44, 53, 56, 64 | P | Ground reference for the device. EP: the Exposed Pad at the bottom of the QFN package. It is used as the GND return for the device. The EP should be connected to one or more ground planes through the low resistance path. A via array provides a low impedance path to GND. The EP also improves thermal dissipation. |
| PD0 | 25 | I, 3.3 V LVCMOS | 2-level logic controlling the operating state of the redriver.
Active in all device control modes. The pin has internal 1-MΩ weak pull-down
resistor. The pin triggers PCIe Rx detect state machine when toggled. High: power down for channels 0-3 Low: power up, normal operation for channels 0-3 |
| PD1 | 26 | I, 3.3 V LVCMOS | 2-level logic controlling the operating state of the redriver.
Active in all device control modes. The pin has internal 1-MΩ weak pull-down
resistor. The pin triggers PCIe Rx detect state machine when toggled. High: power down for channels 4-7 Low: power up, normal operation for channels 4-7 |
| READ_EN_N | 57 | I, 3.3 V LVCMOS | In SMBus/I2C Primary mode: After device power up, when the pin is low, it initiates the SMBus / I2C Primary mode EEPROM read function. When EEPROM read is complete (indicated by assertion of ALL_DONE_N low), this pin can be held low for normal device operation. During the EEPROM load process the device’s signal path is disabled. In SMBus/I2C Secondary and Pin modes: In these modes the pin is not used. The pin can be left floating. The pin has internal 1-MΩ weak pull-down resistor. |
| RSVD0 | 58 | — | Reserved use for TI. The pin must be left floating (NC). |
| RSVD1 | 30 | — | Reserved use for TI. The pin must be left floating (NC). |
| RX_DET / SCL | 62 | I, 5-level / I/O, 3.3 V LVCMOS, open drain | In Pin mode:
Sets receiver detect state machine options as provided in Table 7-3. The pin is sampled at device power-up only. In SMBus/I2C mode: 3.3V SMBus/I2C clock. External 1 kΩ to 5 kΩ pullup resistor is required as per SMBus / I2C interface standard. |
| RX0N | 2 | I | Inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 0. |
| RX0P | 1 | I | Non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 0. |
| RX1N | 5 | I | Inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 1. |
| RX1P | 4 | I | Non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 1. |
| RX2N | 8 | I | Inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 2. |
| RX2P | 7 | I | Non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 2. |
| RX3N | 11 | I | Inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 3. |
| RX3P | 10 | I | Non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 3. |
| RX4N | 14 | I | Inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 4. |
| RX4P | 13 | I | Non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 4. |
| RX5N | 17 | I | Inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 5. |
| RX5P | 16 | I | Non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. An on-chip, 100 Ω termination resistor connects RXP to RXN. Channel 5. |
| RX6N | 20 | I | Inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 6. |
| RX6P | 19 | I | Non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 6. |
| RX7N | 23 | I | Inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 7. |
| RX7P | 22 | I | Non-inverting differential inputs to the equalizer. Integrated 50 Ω termination resistor from the pin to internal CM bias voltage. Channel 7. |
| TX0N | 54 | O | Inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 0. |
| TX0P | 55 | O | Non-inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 0. |
| TX1N | 51 | O | Inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 1. |
| TX1P | 52 | O | Non-inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 1. |
| TX2N | 48 | O | Inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 2. |
| TX2P | 49 | O | Non-inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 2. |
| TX3N | 45 | O | Inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 3. |
| TX3P | 46 | O | Non-inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 3. |
| TX4N | 42 | O | Inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 4. |
| TX4P | 43 | O | Non-inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 4. |
| TX5N | 39 | O | Inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 5. |
| TX5P | 40 | O | Non-inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 5. |
| TX6N | 36 | O | Inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 6. |
| TX6P | 37 | O | Non-inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 6. |
| TX7N | 33 | O | Inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 7. |
| TX7P | 34 | O | Non-inverting pin for 100 Ω differential driver output. Channel 7. |
| VCC | 6, 18, 38, 50 | P | Power supply pins. VCC = 3.3 V ±10%. The VCC pins on this device should be connected through a low-resistance path to the board VCC plane. Install a decoupling capacitor to GND near each VCC pin. |
| RSVD2, 3, 4, 5 | 3, 15, 35, 47 | — | Reserved pins – for best signal integrity performance connect the pins to GND. Alternate option would be 0 Ω resistors from pins to GND. |
(1) I = input, O = output, P = power