SNLS011D July 1999 – August 2016 DS90LV032A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | VCC | –0.3 | 4 | V |
| Input voltage | RIN+, RIN– | –0.3 | 3.9 | V |
| Enable input voltage | EN, EN* | –0.3 | VCC + 0.3 | V |
| Output voltage | ROUT | –0.3 | VCC + 0.3 | V |
| Lead temperature, soldering (4 s) | 260 | °C | ||
| Maximum junction temperature, TJ | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge(1) | Human-body model (HBM)(1) | ±4500 | V |
| Machine model (MM), EIAJ | ±250 | |||
(1) ESD Ratings: HBM (1.5 kΩ, 100 pF) ≥ 4.5 kV and EIAJ (0 Ω, 200 pF) ≥ 250 V
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| Receiver input voltage | GND | 3 | V | ||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 25 | 85 | °C |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | DS90LV032A | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW (TSSOP) | D (SOIC) | |||
| 16 PINS | 16 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 110 | 75 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 47 | 36 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 55 | 32 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 6 | 6 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 54 | 31.7 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
over supply voltage and operating temperature ranges (unless otherwise noted)(1)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VTH | Differential input high threshold | VCM = 1.2 V, RIN+, RIN– pin(2) | 20 | 100 | mV | ||
| VTL | Differential input low threshold | –100 | –20 | mV | |||
| VCMR | Common mode voltage range | VID = 200 mV peak to peak, RIN+, RIN– pin(3) | 0.1 | 2.3 | V | ||
| IIN | Input current | VCC = 3.6 V or 0 V, RIN+, RIN– pin |
VIN = 2.8 V | –10 | ±1 | 10 | µA |
| VIN = 0 V | –10 | ±1 | 10 | µA | |||
| VCC = 0 V, VIN = 3.6 V, RIN+, RIN– pin | –20 | 20 | µA | ||||
| VOH | Output high voltage | IOH = –0.4 mA, VID = 200 mV, ROUT pin | 2.7 | 3 | V | ||
| IOH = –0.4 mA, input terminated, ROUT pin | 2.7 | 3 | V | ||||
| IOH = –0.4 mA, input shorted, ROUT pin | 2.7 | 3 | V | ||||
| VOL | Output low voltage | IOL = 2 mA, VID = –200 mV, ROUT pin | 0.1 | 0.25 | V | ||
| IOS | Output short-circuit current | Enabled, VOUT = 0 V, ROUT pin(4) | –15 | –48 | –120 | mA | |
| IOZ | Output TRI-STATE current | Disabled, VOUT = 0 V or VCC | –10 | ±1 | 10 | µA | |
| VIH | Input high voltage | EN, EN* pins | 2 | VCC | V | ||
| VIL | Input low voltage | EN, EN* pins | GND | 0.8 | V | ||
| II | Input current | VIN = 0 V or VCC, other input = VCC or GND, EN, EN* pins | –10 | ±1 | 10 | µA | |
| VCL | Input clamp voltage | ICL = –18 mA, EN, EN* pins | –1.5 | –0.8 | V | ||
| ICC | No load supply current | EN, EN* = VCC or GND, inputs open, VCC pin | 10 | 15 | mA | ||
| Receivers enabled | EN, EN* = 2.4 V or 0.5 V, inputs open, VCC pin | 10 | 15 | mA | |||
| ICCZ | No load supply current | Receivers disabled, EN = GND, EN* = VCC, inputs open, VCC pin | 3 | 5 | mA | ||
(1) Current into device pins is defined as positive. Current out of device pins is defined as negative. All voltages are referenced to ground unless otherwise specified.
(2) VCC is always higher than RIN+ and RIN– voltage. RIN– and RIN+ are allowed to have a voltage range –0.2 V to VCC – VID / 2. However, to be compliant with AC specifications, the common voltage range is 0.1 V to 2.3 V
(3) The VCMR range is reduced for larger VID. Example: if VID = 400 mV, the VCMR is 0.2 V to 2.2 V. The fail-safe condition with inputs shorted is valid over a common mode range of 0 V to 2.3 V. A VID up to VCC – 0 V may be applied to the RIN+/ RIN– inputs with the common mode voltage set to VCC / 2. Propagation delay and differential pulse skew decrease when VID is increased from 200 mV to 400 mV. Skew specifications apply for 200 mV ≤ VID ≤ 800 mV over the common mode range.
(4) Output short-circuit current (IOS) is specified as magnitude only, minus sign indicates direction only. Only one output must be shorted at a time, do not exceed maximum junction temperature specification.
6.6 Switching Characteristics
over supply voltage and operating temperature ranges (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
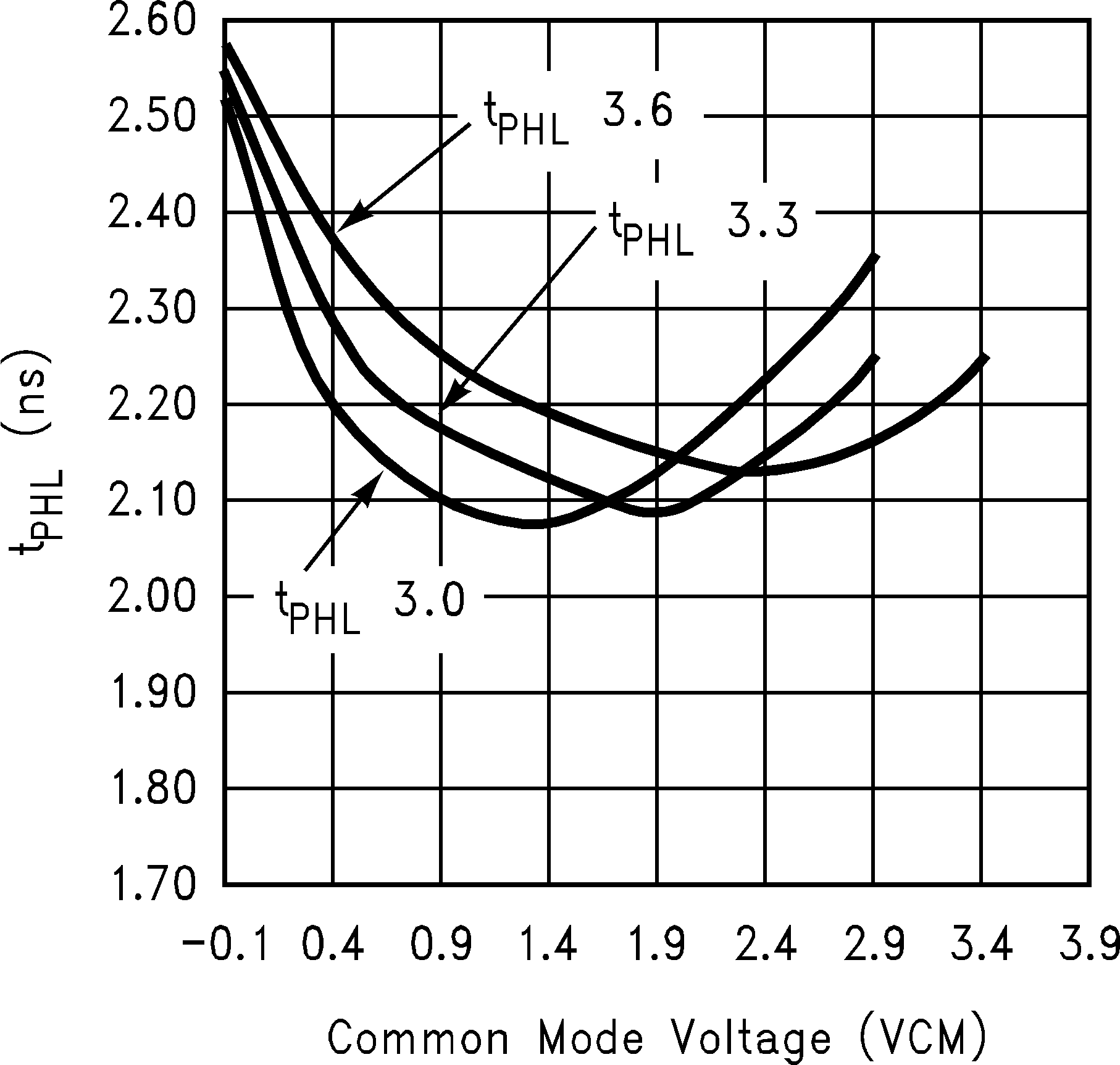
| tPHLD | Differential propagation delay, high to low |
CL = 10 pF | 1.8 | 3.3 | ns | |
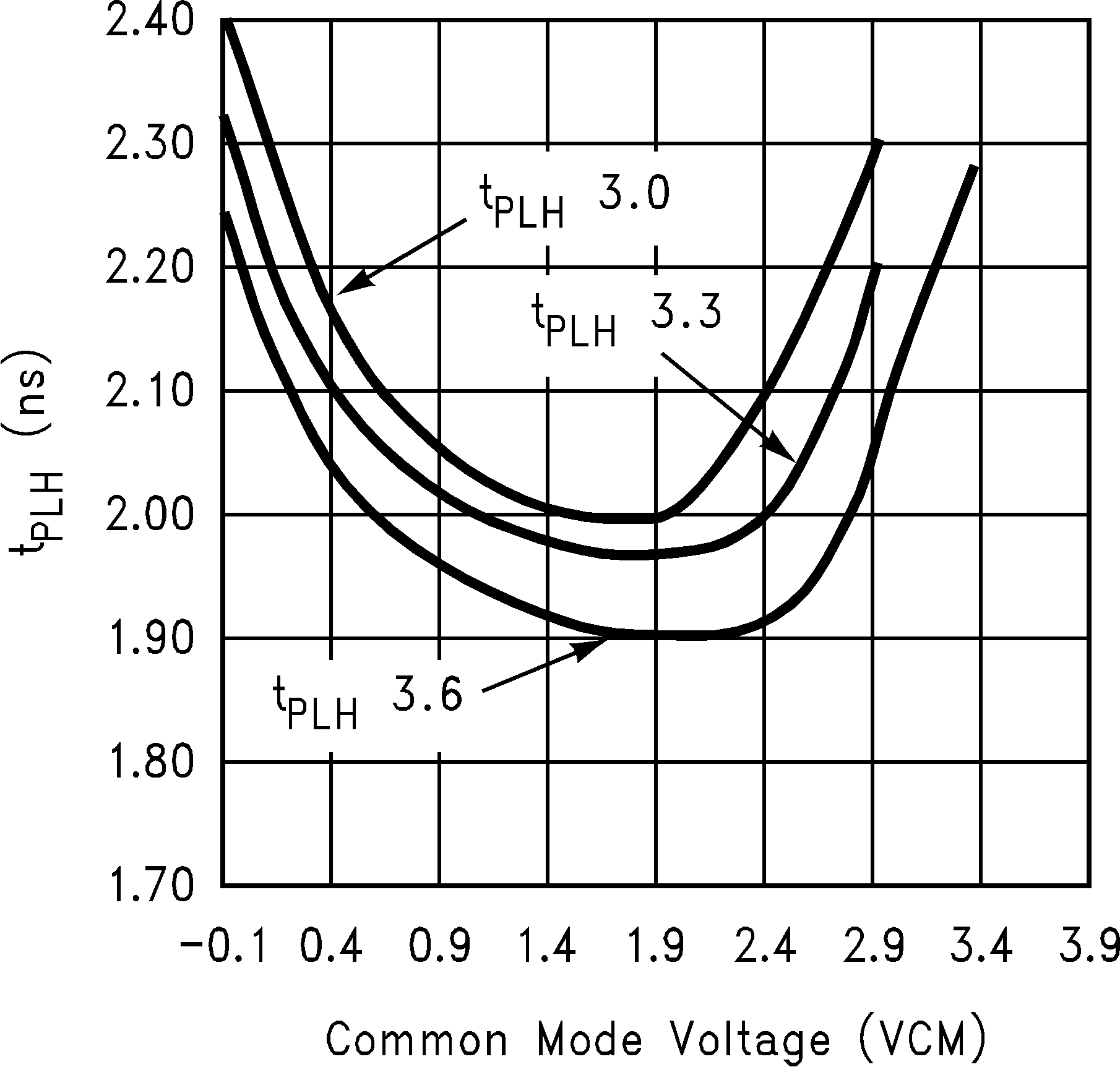
| tPLHD | Differential propagation delay, low to high |
VID = 200 mV | 1.8 | 3.3 | ns | |
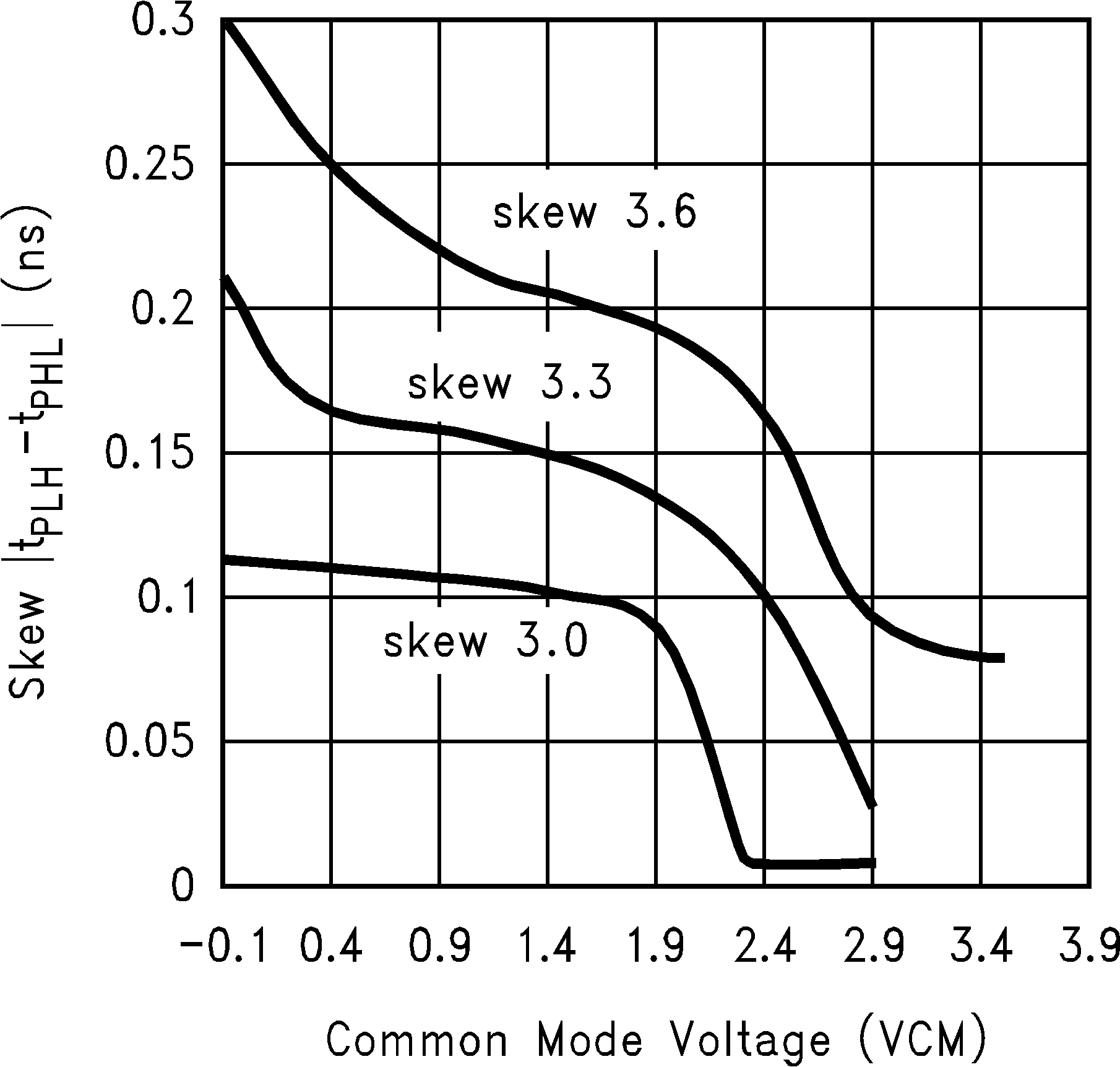
| tSKD1 | Differential pulse skew(3)
|tPHLD – tPLHD| |
See Figure 4 and Figure 5 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.35 | ns |
| tSKD2 | Differential channel-to-channel skew(4) | Same device | 0 | 0.1 | 0.5 | ns |
| tSKD3 | Differential part-to-part skew(5) | 1 | ns | |||
| tSKD4 | Differential part-to-part skew(6) | 1.5 | ns | |||
| tTLH | Rise time | 0.35 | 1.2 | ns | ||
| tTHL | Fall time | 0.35 | 1.2 | ns | ||
| tPHZ | Disable time high to Z | RL = 2 kΩ | 8 | 12 | ns | |
| tPLZ | Disable time low to Z | CL = 10 pF | 6 | 12 | ns | |
| tPZH | Enable time Z to high | See Figure 6 and Figure 7 | 11 | 17 | ns | |
| tPZL | Enable time Z to low | 11 | 17 | ns | ||
| fMAX | Maximum operating frequency(7) | All channels switching | 200 | 250 | MHz | |
(1) All typicals are given for: VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C.
(2) Generator waveform for all tests unless otherwise specified: f = 1 MHz, ZO = 50 Ω, tr and tf (0% to 100%) ≤ 3 ns for RIN.
(3) tSKD1 is the magnitude difference in differential propagation delay time between the positive going edge and the negative going edge of the same channel
(4) tSKD2, channel-to-channel skew, is defined as the difference between the propagation delay of one channel and that of the others on the same chip with any event on the inputs.
(5) tSKD3, part-to-part skew, is the differential channel-to-channel skew of any event between devices. This specification applies to devices at the same VCC, and within 5°C of each other within the operating temperature range.
(6) tSKD4, part-to-part skew, is the differential channel-to-channel skew of any event between devices. This specification applies to devices over recommended operating temperature and voltage ranges, and across process distribution. tSKD4 is defined as |Maximum – Minimum| differential propagation delay.
(7) fMAX generator input conditions: tr = tf < 1 ns (0% to 100%), 50% duty cycle, differential (1.05-V to 1.35-V peak-to-peak). Output criteria: 60% / 40% duty cycle, VOL (maximum: 0.4 V), VOH (minimum: 2.7 V), load = 10 pF (stray plus probes).
6.7 Dissipation Ratings
| MAXIMUM PACKAGE POWER DISSIPATION AT 25°C | |
|---|---|
| D package | 1025 mW |
| PW package | 866 mW |
| Derate D package | 8.2 mW/°C above 25°C |
| Derate PW package | 6.9 mW/°C above 25°C |