ZHCSEW6G may 2013 – november 2020 DS90UB913A-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1特性
- 2应用
- 3说明
- 4Revision History
- Device Comparison Table
- 5Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Recommended Serializer Timing For PCLK
- 6.7 AC Timing Specifications (SCL, SDA) - I2C-Compatible
- 6.8 Bidirectional Control Bus DC Timing Specifications (SCL, SDA) - I2C-Compatible
- 6.9 Timing Diagrams
- 6.10 Serializer Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics
- 7Detailed Description
- Application and Implementation
- Power Supply Recommendations
- 8Layout
- 9Device and Documentation Support
- Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.5.3 I2C Pass-Through
I2C pass-through provides a way to access remote devices at the other end of the FPD-Link III interface. This option is used to determine if an I2C instruction is transferred over to the remote I2C bus. For example, when the I2C master is connected to the deserializer and I2C pass-through is enabled on the deserializer, any I2C traffic targeted for the remote serializer or remote slave will be allowed to pass through the deserializer to reach those respective devices.
See Figure 7-13 for an example of this function and refer to application note I2C over DS90UB913/4 FPD-Link III with Bidirectional Control Channel (SNLA222).
If master controller transmits I2C transaction for address 0xA0, the DES A with I2C pass-through enabled will transfer I2C commands to remote Camera A. The DES B with I2C pass-through disabled, any I2C commands will NOT be passed on the I2C bus to Camera B.
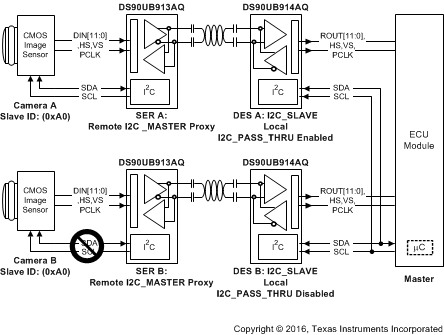 Figure 7-13 I2C Pass-Through
Figure 7-13 I2C Pass-Through