ZHCSJH7 March 2019 DS90UB940N-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 AC Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Timing Requirements for the Serial ControlBus
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics
- 6.9 Timing Diagrams and Test Circuits
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 High-Speed Forward Channel Data Transfer
- 7.3.2 Low-Speed Back Channel Data Transfer
- 7.3.3 FPD-Link III Port Register Access
- 7.3.4 Clock and Output Status
- 7.3.5 LVCMOS VDDIO Option
- 7.3.6 Power Down (PDB)
- 7.3.7 Interrupt Pin — Functional Description and Usage (INTB_IN)
- 7.3.8 General-Purpose I/O (GPIO)
- 7.3.9 SPI Communication
- 7.3.10 Backward Compatibility
- 7.3.11 Adaptive Equalizer
- 7.3.12 I2S Audio Interface
- 7.3.13 Built-In Self Test (BIST)
- 7.3.14 Internal Pattern Generation
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1
Configuration Select
- 7.4.1.1 1-Lane FPD-Link III Input, 4 MIPI® Lanes Output
- 7.4.1.2 1-Lane FPD-Link III Input, 2 MIPI® Lanes Output
- 7.4.1.3 2-Lane FPD-Link III Input, 4 MIPI® Lanes Output
- 7.4.1.4 2-Lane FPD-Link III Input, 2 MIPI® Lanes Output
- 7.4.1.5 1- or 2-Lane FPD-Link III Input, 2 or 4 MIPI® Lanes Output in Replicate
- 7.4.2 MODE_SEL[1:0]
- 7.4.3 CSI-2 Interface
- 7.4.4 Input Display Timing
- 7.4.5 MIPI® CSI-2 Output Data Formats
- 7.4.6 Non-Continuous / Continuous Clock
- 7.4.7 Ultra-Low-Power State (ULPS)
- 7.4.8 CSI-2 Data Identifier
- 7.4.1
Configuration Select
- 7.5
Programming
- 7.5.1 Serial Control Bus
- 7.5.2 Multi-Master Arbitration Support
- 7.5.3 I2C Restrictions on Multi-Master Operation
- 7.5.4 Multi-Master Access to Device Registers for Newer FPD-Link III Devices
- 7.5.5 Multi-Master Access to Device Registers for Older FPD-Link III Devices
- 7.5.6 Restrictions on Control Channel Direction for Multi-Master Operation
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
DS90UB940N-Q1 Registers
- 7.6.1.1 I2C_Device_ID Register (Address = 0h) [reset = Strap]
- 7.6.1.2 Reset Register (Address = 1h) [reset = 4h]
- 7.6.1.3 General_Configuration_0 Register (Address = 2h) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.4 General_Configuration_1 Register (Address = 3h) [reset = F0h]
- 7.6.1.5 BCC_Watchdog_Control Register (Address = 4h) [reset = FEh]
- 7.6.1.6 I2C_Control_1 Register (Address = 5h) [reset = 1Eh]
- 7.6.1.7 I2C_Control_2 Register (Address = 6h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.8 REMOTE_ID Register (Address = 7h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.9 SlaveID_0 Register (Address = 8h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.10 SlaveID_1 Register (Address = 9h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.11 SlaveID_2 Register (Address = Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.12 SlaveID_3 Register (Address = Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.13 SlaveID_4 Register (Address = Ch) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.14 SlaveID_5 Register (Address = Dh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.15 SlaveID_6 Register (Address = Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.16 SlaveID_7 Register (Address = Fh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.17 SlaveAlias_0 Register (Address = 10h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.18 SlaveAlias_1 Register (Address = 11h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.19 SlaveAlias_2 Register (Address = 12h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.20 SlaveAlias_3 Register (Address = 13h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.21 SlaveAlias_4 Register (Address = 14h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.22 SlaveAlias_5 Register (Address = 15h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.23 SlaveAlias_6 Register (Address = 16h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.24 SlaveAlias_7 Register (Address = 17h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.25 MAILBOX_18 Register (Address = 18h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.26 MAILBOX_19 Register (Address = 19h) [reset = 1h]
- 7.6.1.27 GPIO_9_Global_GPIO_Config Register (Address = 1Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.28 Frequency_Counter Register (Address = 1Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.29 General_Status Register (Address = 1Ch) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.30 GPIO0_Config Register (Address = 1Dh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.31 GPIO1_2_Config Register (Address = 1Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.32 GPIO_3_Config Register (Address = 1Fh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.33 GPIO_5_6_Config Register (Address = 20h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.34 GPIO_7_8_Config Register (Address = 21h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.35 Datapath_Control Register (Address = 22h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.36 RX_Mode_Status Register (Address = 23h) [reset = Strap]
- 7.6.1.37 BIST_Control Register (Address = 24h) [reset = 8h]
- 7.6.1.38 BIST_ERROR_COUNT Register (Address = 25h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.39 SCL_High_Time Register (Address = 26h) [reset = 83h]
- 7.6.1.40 SCL_Low_Time Register (Address = 27h) [reset = 84h]
- 7.6.1.41 Datapath_Control_2 Register (Address = 28h) [reset = Loaded from SER]
- 7.6.1.42 I2S_Control Register (Address = 2Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.43 PCLK_Test_Mode Register (Address = 2Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.44 DUAL_RX_CTL Register (Address = 34h) [reset = 1h]
- 7.6.1.45 AEQ_CTL1 Register (Address = 35h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.46 MODE_SEL Register (Address = 37h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.47 I2S_DIVSEL Register (Address = 3Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.48 Adaptive_EQ_Status Register (Address = 3Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.49 LINK_ERROR_COUNT Register (Address = 41h) [reset = 3h]
- 7.6.1.50 HSCC_CONTROL Register (Address = 43h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.51 ADAPTIVE_EQ_BYPASS Register (Address = 44h) [reset = 60h]
- 7.6.1.52 ADAPTIVE_EQ_MIN_MAX Register (Address = 45h) [reset = 88h]
- 7.6.1.53 CML_OUTPUT_CTL1 Register (Address = 52h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.54 CML_OUTPUT_ENABLE Register (Address = 56h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.55 CML_OUTPUT_CTL2 Register (Address = 57h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.56 CML_OUTPUT_CTL3 Register (Address = 63h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.57 PGCTL Register (Address = 64h) [reset = 10h]
- 7.6.1.58 PGCFG Register (Address = 65h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.59 PGIA Register (Address = 66h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.60 PGID Register (Address = 67h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.61 PGDBG Register (Address = 68h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.62 PGTSTDAT Register (Address = 69h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.63 CSICFG0 Register (Address = 6Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.64 CSICFG1 Register (Address = 6Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.65 CSIIA Register (Address = 6Ch) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.66 CSIID Register (Address = 6Dh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.67 GPIO_Pin_Status_1 Register (Address = 6Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.68 GPIO_Pin_Status_2 Register (Address = 6Fh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.69 ID0 Register (Address = F0h) [reset = 5Fh]
- 7.6.1.70 ID1 Register (Address = F1h) [reset = 55h]
- 7.6.1.71 ID2 Register (Address = F2h) [reset = 48h]
- 7.6.1.72 ID3 Register (Address = F3h) [reset = 39h]
- 7.6.1.73 ID4 Register (Address = F4h) [reset = 34h]
- 7.6.1.74 ID5 Register (Address = F5h) [reset = 30h]
- 7.6.2
CSI-2 Indirect Registers
- 7.6.2.1 CSI_TCK_PREP Register (Address = 0h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.2 CSI_TCK_ZERO Register (Address = 1h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.3 CSI_TCK_TRAIL Register (Address = 2h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.4 CSI_TCK_POST Register (Address = 3h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.5 CSI_THS_PREP Register (Address = 4h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.6 CSI_THS_ZERO Register (Address = 5h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.7 CSI_THS_TRAIL Register (Address = 6h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.8 CSI_THS_EXIT Register (Address = 7h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.9 CSI_TLPX Register (Address = 8h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.10 RAW_ALIGN Register (Address = 9h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.11 CSI_EN_PORT0 Register (Address = 13h) [reset = 3Fh]
- 7.6.2.12 CSI_EN_PORT1 Register (Address = 14h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.13 CSIPASS Register (Address = 16h) [reset = 2h]
- 7.6.2.14 CSI_VC_ID Register (Address = 2Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1
DS90UB940N-Q1 Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
7.4.3 CSI-2 Interface
The DS90UB940N-Q1 (in default mode) takes RGB 24-bpp data bits defined in the serializer and directly maps the bits to the pixel color space in the data frame. The DS90UB940N-Q1 follows the general frame format as described per the CSI-2 standard (Figure 31). At the end of the vertical sync pulse (VS), the DS90UB940N-Q1 generates the frame end and frame start synchronization packets within the vertical blanking period. The timing of the frame start will not reflect the timing of the VS signal.
On the rising edge of the DE signal, each active line outputs as a long data packet with the defined data format (Figure 13). At the end of each packet, the data lanes Dn± return to the LP-11 state and the clock lane CLK± continues to output the high-speed clock.
The DS90UB940N-Q1 CSI-2 transmitter consists of a high-speed clock (CLK±) and data (Dn±) outputs based on a source synchronous interface. The half rate clock at CLK± is derived from the pixel clock sourced by the clock/data recovery circuit of the DS90UB940N-Q1. The CSI-2 clock frequency is 3.5 times (four MIPI lanes) or seven times (two MIPI lanes) more than the recovered pixel clock frequency. The MIPI DPHY outputs either two or four high-speed data lanes (Dn±) according to the CSI-2 protocol. The data rate of each lane is seven times (four MIPI lanes) or 14 times (two MIPI lanes) higher than the pixel clock. For example, in a 4-MPIP-line configuration at a pixel clock of 150 MHz, the CLK± runs at 525 MHz and each data lane runs at 1050 Mbps.
The half-rate clock maintains a quadrature phase relationship to the data signals and allows the receiver to sample data at the rising and falling edges of the clock (DDR). Figure 10 shows the timing relationship of the clock and data lines. The DS90UB940N-Q1 supports a continuous high-speed clock. High-speed data is sent out at data lanes Dn± in bursts. In between data bursts, the data lanes return to low power (LP) states according to the protocol defined in the D-PHY standard. The rising edge of the differential clock (CSI_CLK+ – CSI_CLK–) is sent during the first payload bit of a transmission burst in the data lanes.
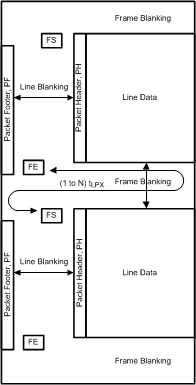 Figure 31. CSI-2 General Frame Format
Figure 31. CSI-2 General Frame Format