ZHCSGP4C August 2017 – May 2019 INA1650-Q1 , INA1651-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
7.3.3 EMI Rejection
The INA165x-Q1 use integrated electromagnetic interference (EMI) filtering to reduce the effects of EMI from sources (such as wireless communications) and densely-populated boards with a mix of analog signal-chain and digital components. The INA165x-Q1 devices are specifically designed to minimize susceptibility to EMI by incorporating an internal low-pass filter. Depending on the end-system requirements, additional EMI filters may be required near the signal inputs of the system; as well as incorporating known good practices, such as using short traces, low-pass filters, and damping resistors combined with parallel and shielded signal routing. Texas Instruments developed a method to accurately measure the immunity of an amplifier over a broad frequency spectrum, extending from 10 MHz to 6 GHz. This method uses an EMI rejection ratio (EMIRR) to quantify the ability of the INA165x-Q1 to reject EMI. Figure 41 and Figure 42 show the INA165x-Q1 EMIRR graph for both differential and common-mode EMI rejection across this frequency range. Table 1 shows the EMIRR values for the INA165x-Q1 at frequencies commonly encountered in real-world applications. Applications listed in Table 1 can be centered on or operated near the particular frequency shown.
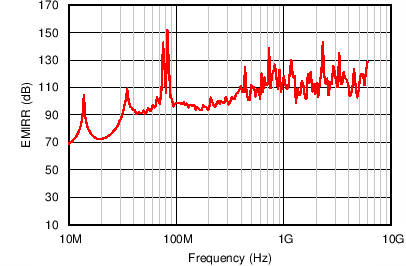
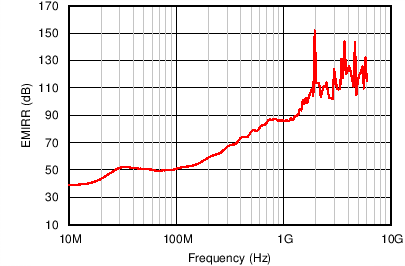
Table 1. EMIRR for Frequencies of Interest
| FREQUENCY | APPLICATION OR ALLOCATION | DIFFERENTIAL
EMIRR |
COMMON-MODE
EMIRR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 MHz | Mobile radio, mobile satellite, space operation, weather, radar, ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) applications | 73 dB | 111 dB |
| 900 MHz | Global system for mobile communications (GSM) applications, radio communication, navigation, GPS (up to 1.6 GHz), GSM, aeronautical mobile, UHF applications | 86 dB | 123 dB |
| 1.8 GHz | GSM applications, mobile personal communications, broadband, satellite,
L-band (1 GHz to 2 GHz) |
106 dB | 121 dB |
| 2.4 GHz | 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, Bluetooth®, mobile personal communications, industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) radio band, amateur radio and satellite, S-band (2 GHz to 4 GHz) | 112 dB | 119 dB |
| 3.6 GHz | Radiolocation, aero communication and navigation, satellite, mobile, S-band | 117 dB | 121 dB |
| 5.0 GHz | 802.11a, 802.11n, aero communication and navigation, mobile communication, space and satellite operation, C-band (4 GHz to 8 GHz) | 116 dB | 108 dB |