ZHCSGP4C August 2017 – May 2019 INA1650-Q1 , INA1651-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
8.2.1.3 Application Curves
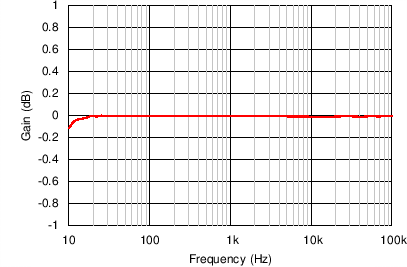
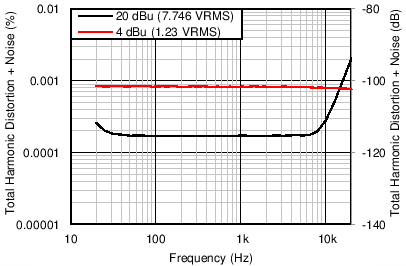
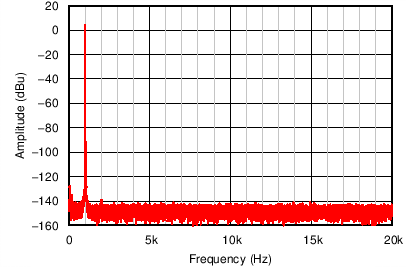
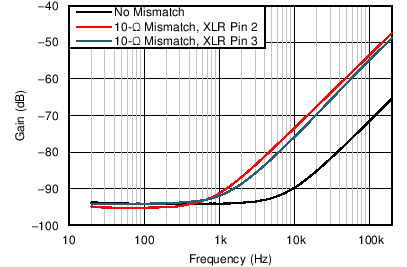
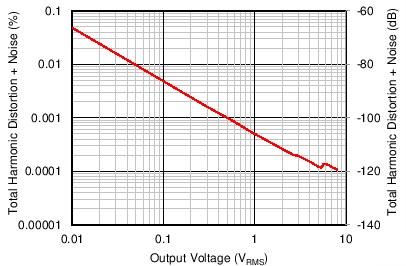
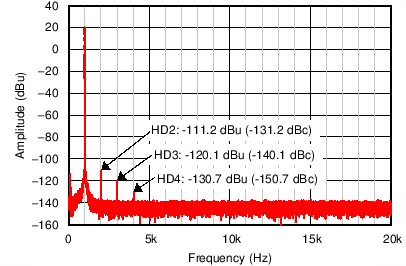
Figure 54 through Figure 59 illustrate the measured performance of the line receiver circuit. Figure 54 shows the measured frequency response. The gain of the circuit is 0 dB as expected with 0.1-dB magnitude variation at 10 Hz. The measured CMRR of the circuit (Figure 55) at 1 kHz equals 94 dB without any source impedance mismatch. Adding a 10-Ω source impedance mismatch degrades the CMRR at 1 kHz to 92 dB. The high-frequency degradation of CMRR shown in Figure 55 for the 10-Ω source impedance mismatch cases is due to the capacitance of the cables used for the measurement. The total harmonic distortion plus noise (THD+N) is plotted over frequency in Figure 56. For a 4-dBu (1.23 VRMS) input signal level, the THD+N remains flat at –101.6 dB (0.0008%) over the measured frequency range. Increasing the signal level to 20 dBu further decreases the THD+N to –113.2 dB (0.00022%) at 1 kHz, but the THD+N rises to greater than 7 kHz. Measuring the THD+N vs output amplitude (Figure 57) at 1 kHz shows a constant downward slope until the noise floor of the audio analyzer is reached at 5 VRMS. The constant downward slope indicates that noise from the device dominates THD+N at this frequency instead of distortion harmonics. Figure 58 and Figure 59 confirm this conclusion. For a 4–dBu signal level, the second harmonic is barely visible above the noise floor at –140 dBu. Increasing the signal level to 20 dBu produces distortion harmonics above the noise floor. The largest harmonic in this case is the second at
–111.2 dBu, or –131.2 dB relative to the fundamental.
| 90-kHz Measurement Bandwidth |
| 4–dBu Output Amplitude |
| 1-VRMS Common-Mode Signal |
| 22-kHz Measurement Bandwidth |
| 20–dBu Output Amplitude |