ZHCSFV5B December 2016 – November 2018 INA1650 , INA1651
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Line Receiver for Differential Audio Signals in a Split-Supply System
- 8.2.2 Differential Line Receiver for Single-Supply Applications
- 8.2.3 Floating Single-Ended Input Line Receiver for Ground Loop Noise Reduction
- 8.2.4 Floating Single-Ended Input Line Receiver With Differential Outputs
- 8.2.5 TRS Audio Interface in Single-Supply Applications
- 8.2.6 Differential Line Driver With Single-Ended Input
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.1.4 Input AC Coupling
The signal path in most audio systems is typically AC-coupled to avoid the propagation of DC voltages, which can potentially damage loudspeakers or saturate power amplifiers. The capacitor values must be selected to pass the desired bandwidth of audio signals. The high-pass corner frequency is calculated with Equation 5:
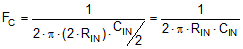
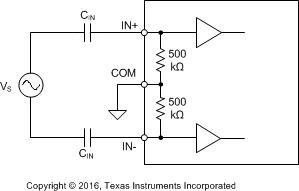 Figure 47. AC-Coupling Capacitors Form a High-Pass Filter With INA165x Input Resistors
Figure 47. AC-Coupling Capacitors Form a High-Pass Filter With INA165x Input Resistors Although the input resistors of the INA165x are matched typically within 0.01%, large capacitors are usually mismatched. The mismatch in the values of the AC-coupling capacitors causes the corner frequencies at the two signal inputs (IN+ and IN–) to be different, which can degrade CMRR at low frequency. For this reason, TI recommends placing the high-pass corner frequency well below the audio bandwidth and to use a resistor in series with the COM pin (RCOM), as shown in Figure 42 if possible. See the Common-Mode Input Impedance section for more information on placing a resistor in series with the COM pin. Figure 48 shows the effect of a 5% mismatch in the values of the input AC-coupling capacitors with and without an RCOM resistor. Comparing CMRR at 100 Hz: 1-µF AC-coupling capacitors with a 5% mismatch degrade the CMRR to 75 dB, while 10-µF capacitors and a 1-MΩ RCOM resistor shows 92 dB of CMRR.
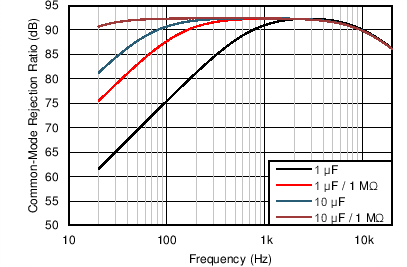 Figure 48. CMRR Degradation Due to a 5% Mismatch in AC-Coupling Capacitors
Figure 48. CMRR Degradation Due to a 5% Mismatch in AC-Coupling Capacitors