ZHCSJE3C february 2019 – august 2021 INA191 , INA2191
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.4.3 Bidirectional Mode (INA2191 Only)
The INA2191 is a dual channel bidirectional current-sense amplifier capable of measuring currents through a resistive shunt in two directions. This bidirectional monitoring is common in applications that include charging and discharging operations where the current flowing through the resistor can change directions.
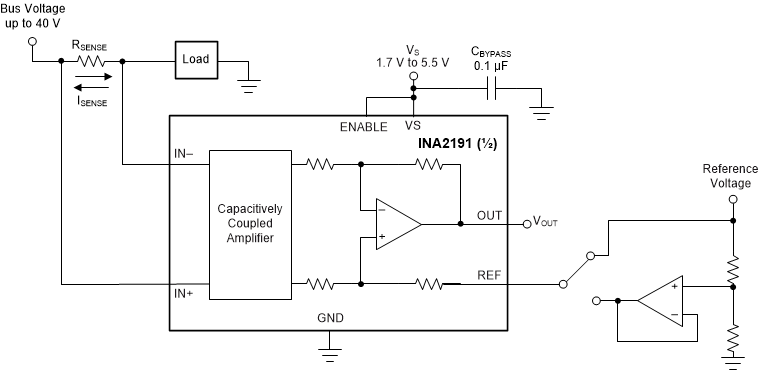 Figure 7-6 Bidirectional
Application
Figure 7-6 Bidirectional
ApplicationThe ability to measure this current flowing in both directions is achieved by applying a voltage to the REF pin, as shown in Figure 7-6. The voltage applied to REF (VREF) sets the output state that corresponds to the zero-input level state. The output then responds by increasing above VREF for positive differential signals (relative to the IN– pin) and responds by decreasing below VREF for negative differential signals. This reference voltage applied to the REF pin can be set anywhere between 0 V to VS. For bidirectional applications, VREF is typically set at VS/2 for equal signal range in both current directions. In some cases, VREF is set at a voltage other than VS/2, like when the bidirectional current and corresponding output signal do not need to be symmetrical.