ZHCSDE7A February 2015 – March 2021 INA225-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.1.3 Application Curve
Figure 8-2 illustrates how the microcontroller can monitor the ADC measurements to determine if the device gain setting should be adjusted to ensure the output of the device remains within the linear output range as well as the linear input range of the ADC. When the output of the device rises to a level near the desired maximum voltage level, the microcontroller can change the GPIO settings connected to the G0 and G1 gain-select terminals to adjust the device gain setting, thus resulting in the output voltage dropping to a lower output range. When the input current increases, the output voltage increases again to the desired maximum voltage level. The microcontroller can again change the device gain setting to drop the output voltage back to a lower range.
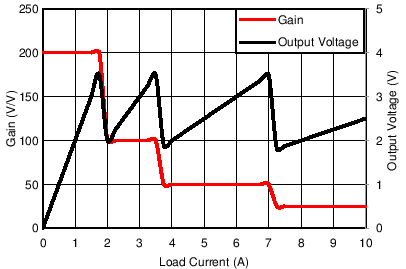 Figure 8-2 Microcontroller-Configured Gain Selection Response
Figure 8-2 Microcontroller-Configured Gain Selection Response