ZHCSL81A May 2020 – June 2021 INA229-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.5.1.1 SPI Frame
SPI communication to the INA229-Q1 device is performed through register address access. Communication to every register starts with a 6-bit register address followed by a "0" and a R/W bit. Setting the R/W bit to "1" indicates that the current SPI frame will read from a device register while setting the R/W bit to "0" indicates the current SPI frame will write data to a device register.
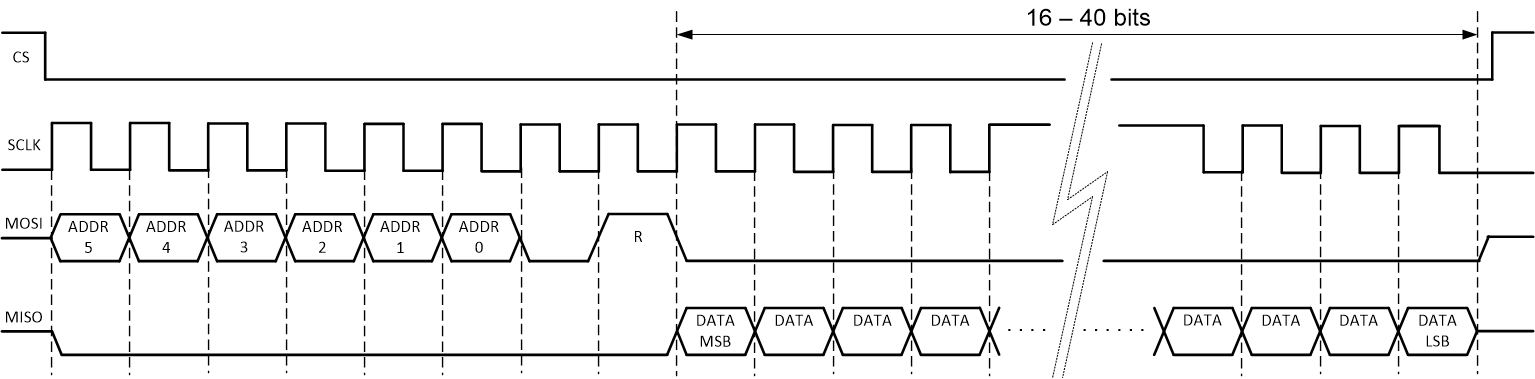 Figure 7-7 SPI Read Frame
Figure 7-7 SPI Read Frame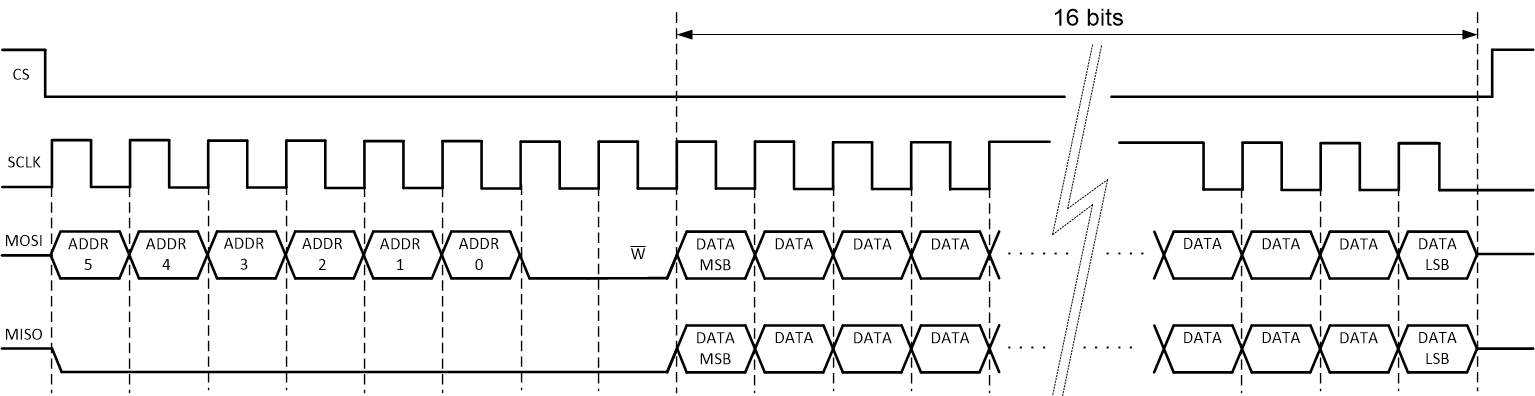 Figure 7-8 SPI Write Frame
Figure 7-8 SPI Write FrameNote that while the read frame can be variable in length due to the different length registers in the INA229-Q1 device, the write frame is fixed in length as all writable registers are 16 bits wide. During an SPI write frame, while new data is shifted into the INA229-Q1 register, the old data from the same register is shifted out on the MISO line.
The first 8-bits of each SPI frame are presented in Table 7-2, which shows access to a certain register address on the MOSI line as well as read/write functionality. On an SPI read operation, the INA229-Q1 returns the data read in the same SPI frame.
| COMMAND | b7 | b6 | b5 | b4 | b3 | b2 | b1 | b0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| READ | ADDR5 | ADDR4 | ADDR3 | ADDR2 | ADDR1 | ADDR0 | 0 | 1 |
| WRITE | 0 |