ZHCSLF9A June 2020 – June 2021 INA237-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.8 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25 °C, VVS = 3.3 V, VCM = 48 V, VSENSE = 0, and VVBUS = 48 V (unless otherwise noted)
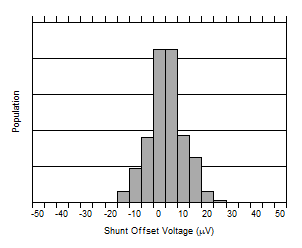
| VCM = 48 V |
Figure 6-4 Shunt Input Offset Voltage vs. Temperature
Figure 6-6 Shunt Input Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs. Temperature
| VCM = 24 V |
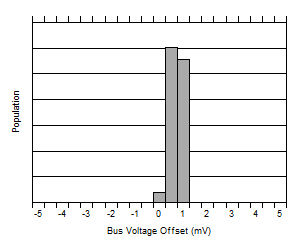
| VVBUS = 20 mV |
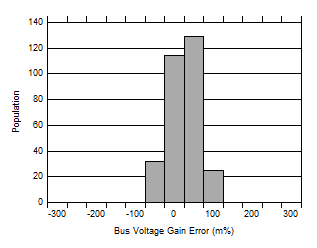 Figure 6-12 Bus Input Gain Error Production Distribution
Figure 6-12 Bus Input Gain Error Production DistributionFigure 6-14 Input Bias Current vs. Differential Input Voltage
Figure 6-16 Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
Figure 6-18 Active IQ vs. Temperature
Figure 6-20 Shutdown IQ vs. Supply Voltage
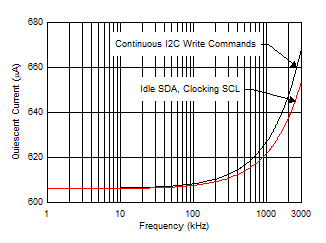 Figure 6-22 Active IQ vs. Clock Frequency
Figure 6-22 Active IQ vs. Clock FrequencyFigure 6-24 Internal Clock Frequency vs. Power Supply
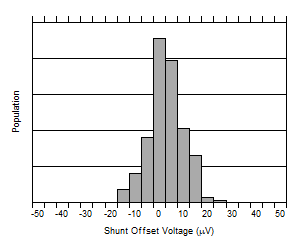
| VCM = 0 V |
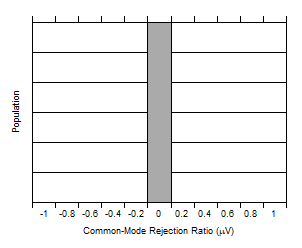 Figure 6-5 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio Production Distribution
Figure 6-5 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio Production Distribution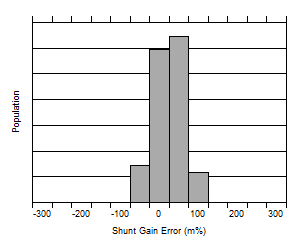
| VCM = 24 V |
Figure 6-9 Shunt Input Gain Error vs. Common-Mode Voltage
| VVBUS = 20 mV |
Figure 6-13 Bus Input Gain Error vs. Temperature
Figure 6-15 Input Bias Current (IB+ or IB–) vs. Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 6-17 Input Bias Current vs. Temperature, Shutdown
Figure 6-19 Active IQ vs. Supply Voltage
Figure 6-21 Shutdown IQ vs. Temperature
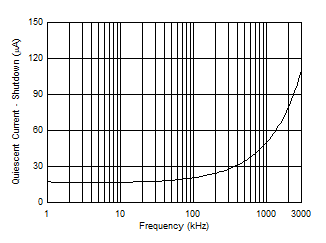 Figure 6-23 Shutdown IQ vs. Clock Frequency
Figure 6-23 Shutdown IQ vs. Clock FrequencyFigure 6-25 Internal Clock Frequency vs. Temperature