ZHCSM99 October 2020 INA280
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.1 Amplifier Input Common-Mode Range
The INA280 supports large input common-mode voltages from 2.7 V to 120 V and features a high DC CMRR of 140 dB (typical) and a 85-dB AC CMRR at 50 kHz. The minimum common-mode voltage is restricted by the supply voltage as shown in Figure 7-1. The topology of the internal amplifiers INA280 restricts operation to high-side, current-sensing applications.
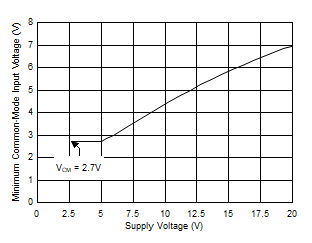
Figure 7-1 Minimum Common-Mode Voltage vs Supply