ZHCSJJ1A March 2019 – May 2021 INA302-Q1 , INA303-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.3.1.2 Voltage-Source-Controlled Current Limit
The second method for setting the out-of-range threshold is to directly drive the LIMITx pins with a programmable DAC or other external voltage source. The benefit of this method is the ability to adjust the current-limit threshold to account for different threshold voltages used for different system operating conditions. For example, this method can be used in a system with one current-limit threshold level that must be monitored during a power-up sequence, but different threshold levels must be monitored during other system operating modes.
The voltage applied at the LIMITx pins sets the threshold voltage for out-of-range detection. The value of the voltage for a given desired current trip point is calculated using Equation 4:
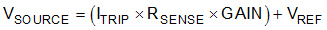
where
- ITRIP is the desired out-of-range current threshold.
- RSENSE is the current-sensing resistor.
- GAIN is the gain option of the device selected.
- VREF is the voltage applied to the REF pin.
The maximum voltage that can be applied to the LIMIT2 pin is VS – 0.6 V and the maximum voltage that can be applied to the LIMIT1 pin must not exceed VS.